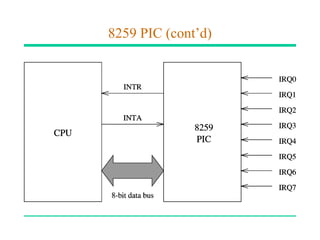
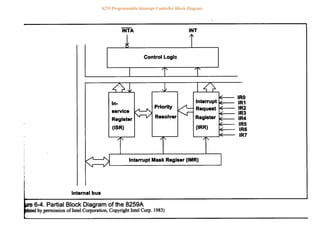
Interrupts alter a program's flow of control by causing a transfer to an interrupt service routine (ISR). ISRs handle anticipated and unanticipated internal and external events. Interrupts can be initiated by both software and hardware, whereas procedures can only be initiated by software. When an interrupt occurs, registers are automatically saved before the ISR runs; the original program resumes after the ISR completes.