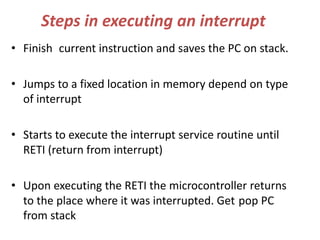
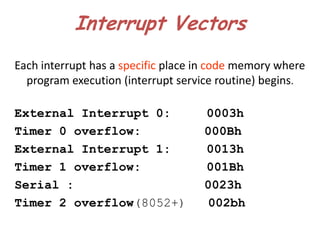
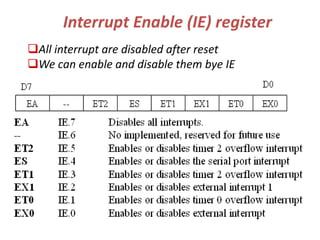
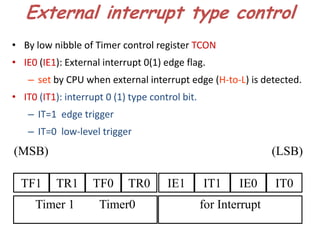
The document discusses interrupts in the 8051 microcontroller. It describes interrupts as events that interrupt normal program flow to service external devices. Interrupts provide faster response than polling. The interrupt service routine starts at a specific memory location. When an interrupt occurs, the program counter is saved and the ISR begins. Upon returning from the ISR, normal code execution resumes. The 8051 has several interrupt sources with different priority levels that determine service order. Interrupt enable bits and edge/level triggering are controlled through registers.