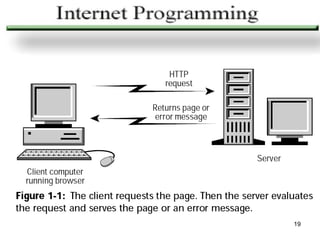
This document provides an overview of HTML and the World Wide Web. It discusses that the Web is a network of computers that can exchange text, graphics, and multimedia over the Internet. It also defines key terms like websites, web servers, URLs, browsers, hyperlinks, and HTML. HTML uses tags to mark up text and enable it to function as hypertext that can link between web pages.