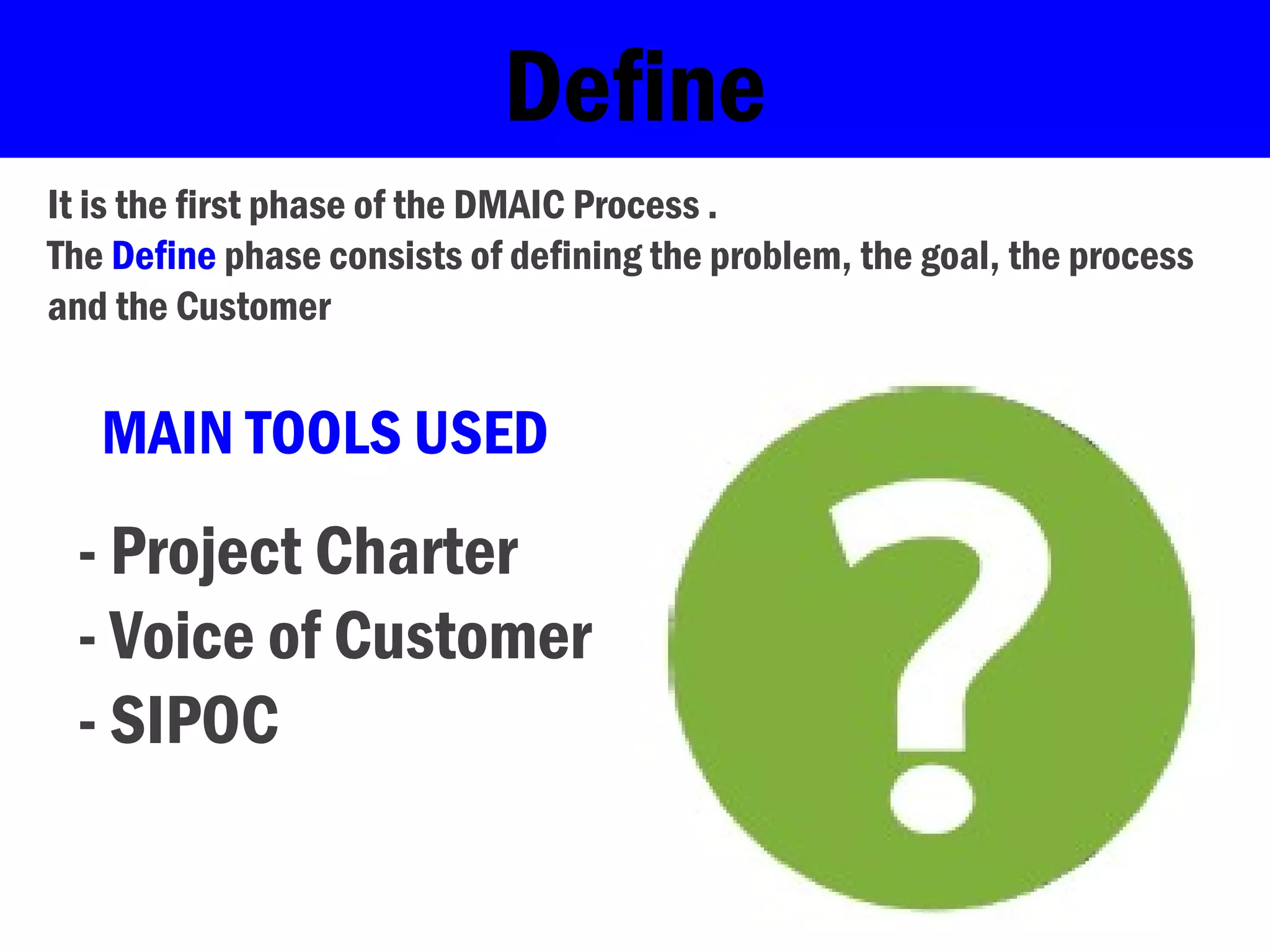
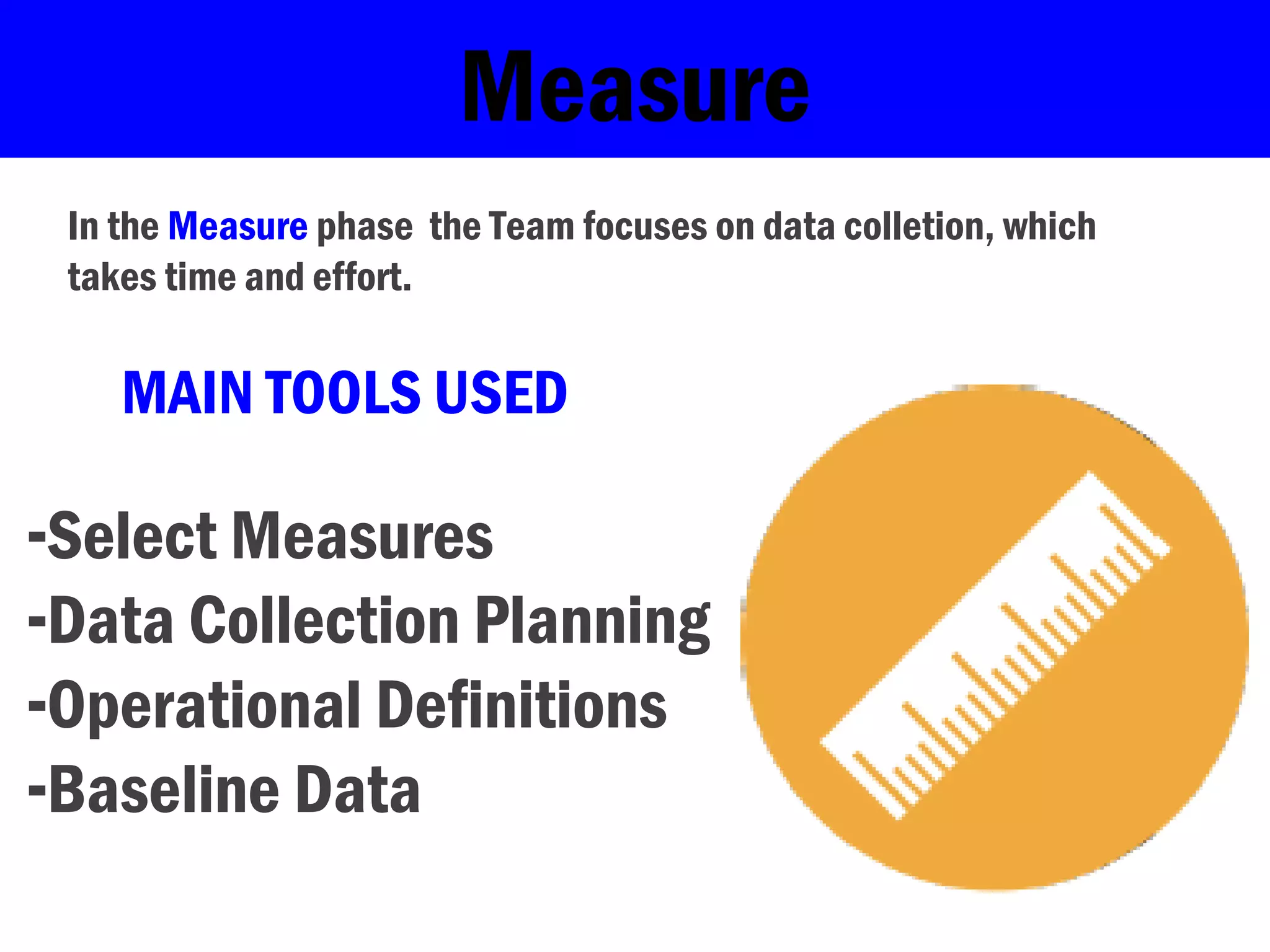
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that uses the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) process to systematically identify and eliminate waste and defects. It involves selecting projects with known problems and potential for improvement. The DMAIC process first defines the problem and goals, then measures key aspects, analyzes data to find root causes, improves the process by addressing causes, and controls the new process to hold gains.