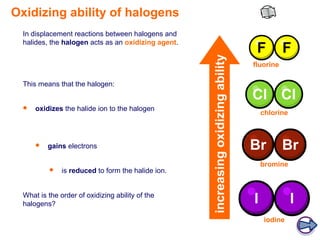
The document discusses the chemical properties of halogens, specifically their oxidizing abilities in displacement reactions. It states that in displacement reactions between halogens and halides, the halogen acts as an oxidizing agent by oxidizing the halide ion and being reduced to form the halide ion itself. The order of increasing oxidizing ability among the halogens is F > Cl > Br > I. An example reaction of chlorine displacing bromine is provided, and it is explained that in the reaction, chlorine is reduced while bromide is oxidized.