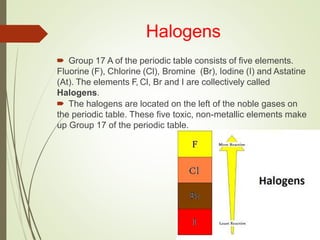
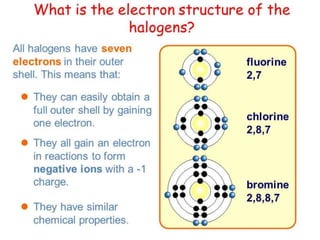
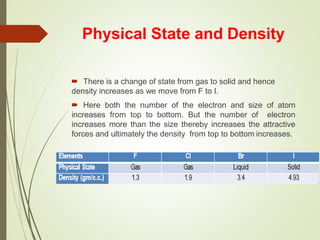
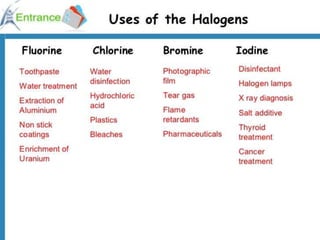
The document discusses halogens and their medicinal uses. It covers the five halogens found in group 17 of the periodic table (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine) and their physical properties like density and electronegativity decreasing from fluorine to iodine. Halogens and halogenides have medical importance, with chlorinated lime, iodine solutions, and salts like sodium chloride being used. Hypochlorites are also discussed as unstable compounds containing hypochlorite ion, used for bleaching, disinfection and water treatment when in aqueous solution.