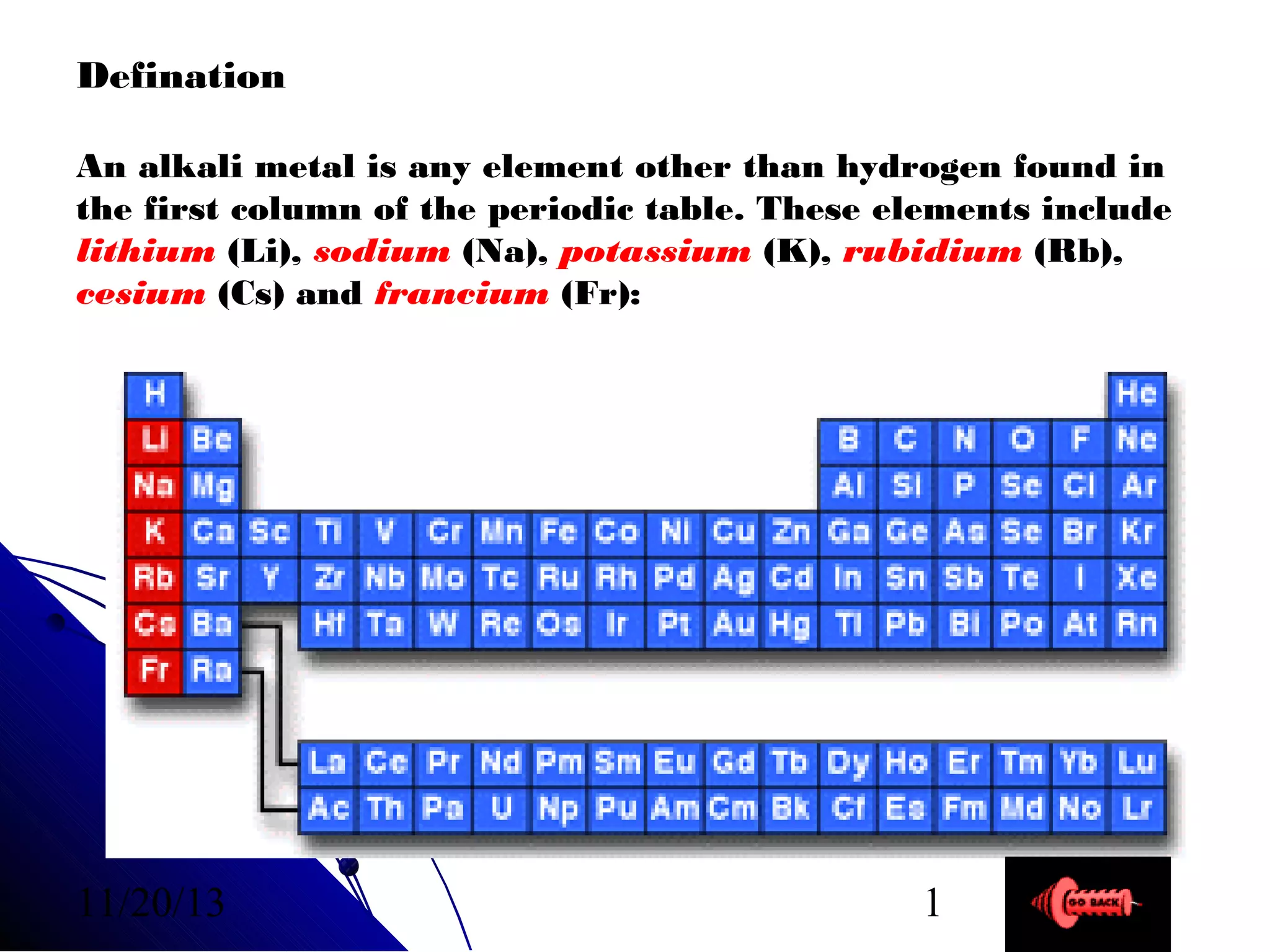
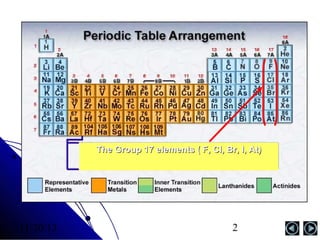
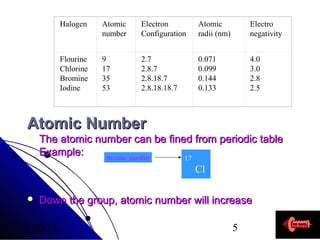
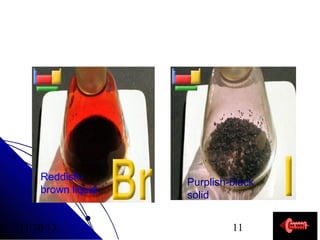
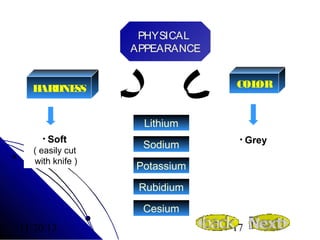
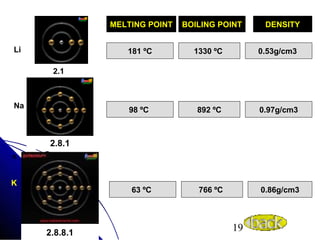
Alkali metals are elements found in Group 1 of the periodic table, including lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium. They have low melting and boiling points, are soft, and become liquid or gas at room temperature as you move down the group. Their density increases as atomic mass increases more than atomic radius.