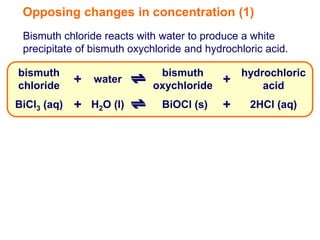
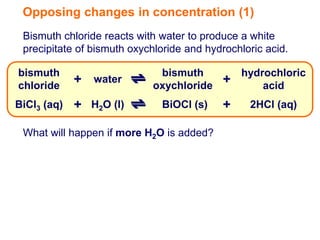
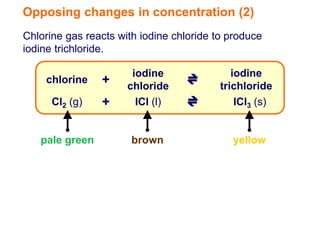
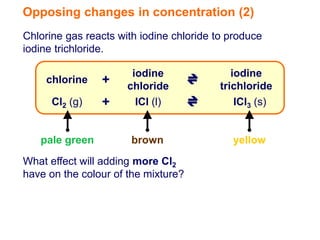
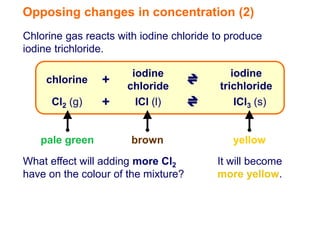
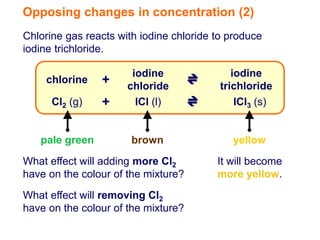
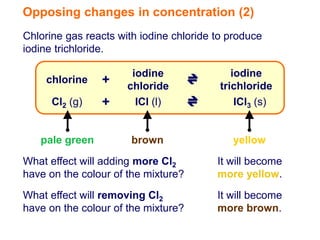
Increasing the concentration of a substance in a reversible reaction shifts the equilibrium to decrease the concentration of that substance. For example, adding more water to a reaction producing bismuth oxychloride and hydrochloric acid from bismuth chloride and water would shift the equilibrium right, producing more products. Similarly, adding more chlorine gas to a reaction producing iodine trichloride from chlorine and iodine chloride would make the mixture appear more yellow by shifting the equilibrium to the right.