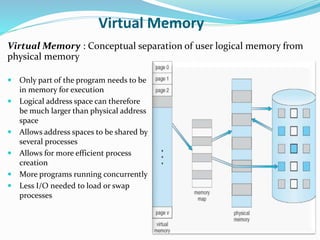
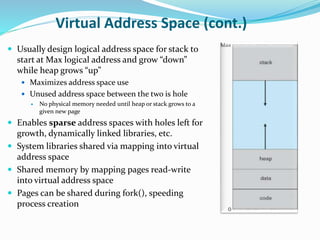
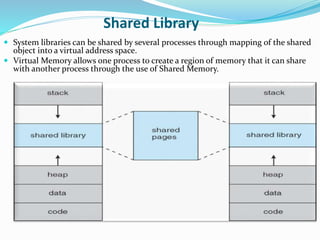
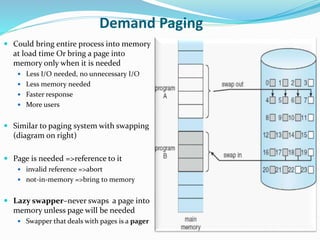
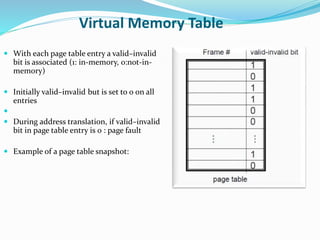
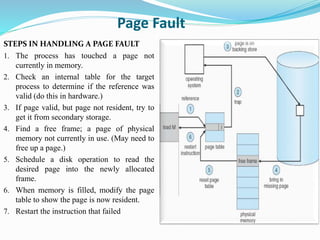
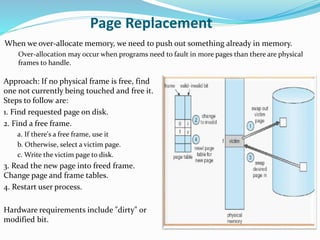
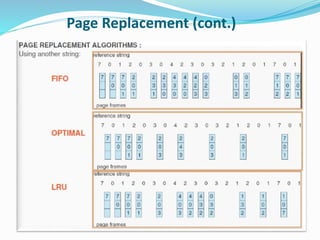
The document discusses virtual memory management. It describes key concepts like virtual memory, virtual address spaces, demand paging, and page replacement. Virtual memory allows processes to have a logical address space that is larger than physical memory by mapping portions of virtual memory to physical memory frames as needed. When a process accesses a page not in memory, a page fault occurs which is resolved through demand paging by loading the missing page from secondary storage. If no physical frame is available during a page fault, an existing page must be replaced using an algorithm like least recently used.