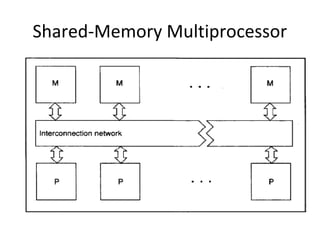
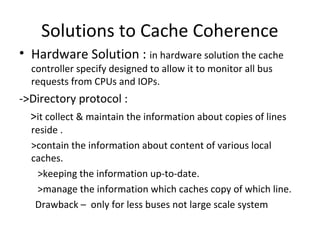
The document discusses cache coherence in multiprocessor systems. It describes the cache coherence problem that can arise when multiple processors have caches and can access shared memory. It then summarizes two primary hardware solutions: directory protocols which maintain information about which caches hold which memory lines; and snoopy cache protocols where cache controllers monitor bus traffic to maintain coherence without a directory. Finally it mentions a software-based solution relying on compiler analysis and operating system support.