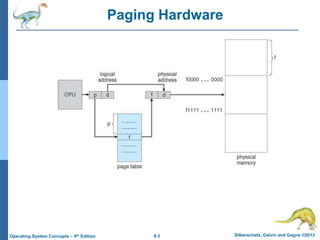
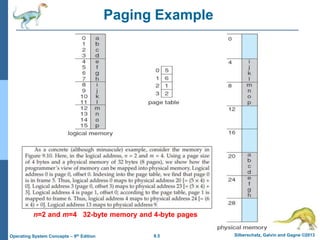
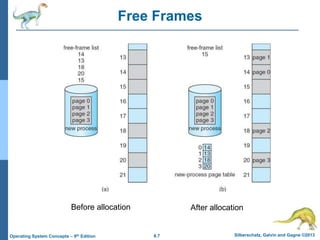
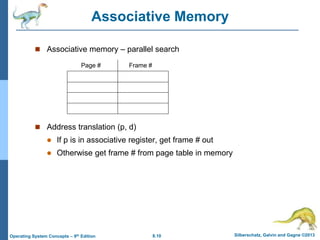
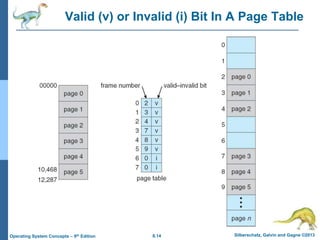
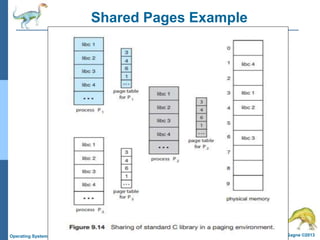
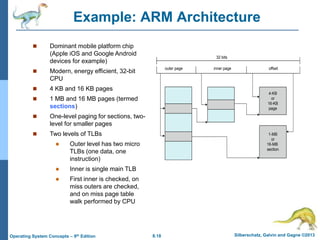
Paging is a memory management technique that allows a process to be allocated physical memory wherever it is available. It divides both physical memory and logical memory into fixed-sized blocks called frames and pages respectively. When a process runs, its pages are loaded into available free frames. A page table maps the logical addresses to physical frames and is used to translate logical addresses to physical addresses during execution. Address translation uses the page number as an index into the page table to find the physical frame number.