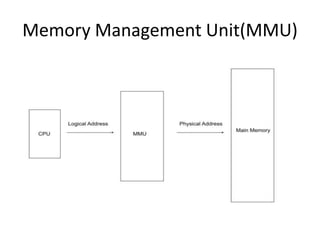
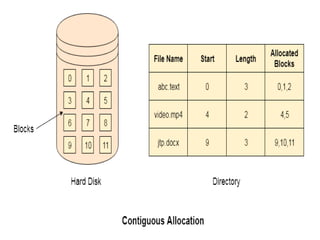
Memory management is the process of allocating memory to different processes during execution, aiming for efficient memory utilization. It involves translating logical addresses generated by the CPU into physical addresses using a memory management unit (MMU) and methods like contiguous and non-contiguous memory allocation. Allocation strategies include fixed and dynamic partitioning, as well as algorithms such as first-fit, best-fit, and worst-fit for managing memory partitions.