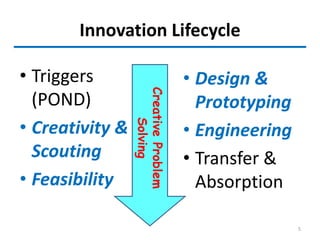
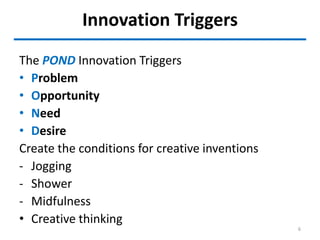
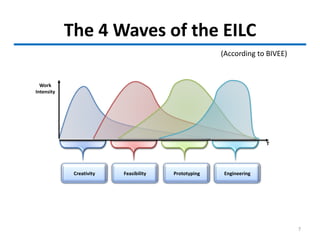
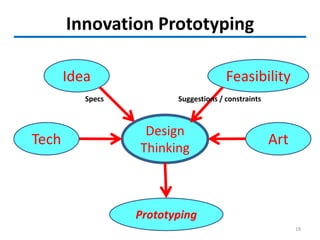
This document outlines the innovation lifecycle process, which includes 4 main waves: creativity, feasibility, prototyping, and engineering.
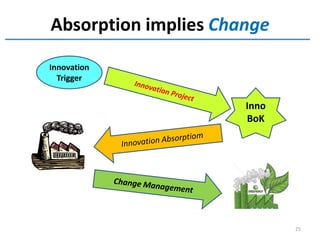
The creativity wave involves generating ideas through triggers, divergent thinking, walking to stimulate alpha waves, and considering different perspectives. Feasibility assesses the technical, financial, market, and competency feasibility of ideas. Prototyping transforms ideas into working prototypes to test and refine. Engineering transforms successful prototypes into real products by addressing costs, usability, and production plans. The final stage is transferring knowledge to production and ensuring organizations are ready to absorb innovation and change.