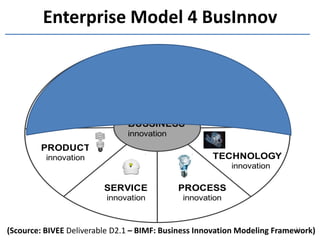
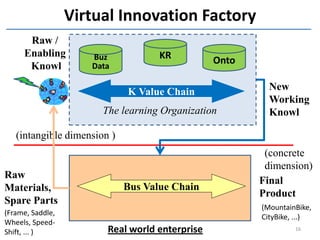
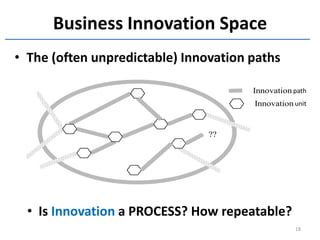
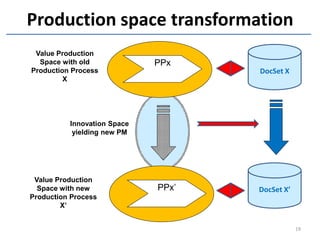
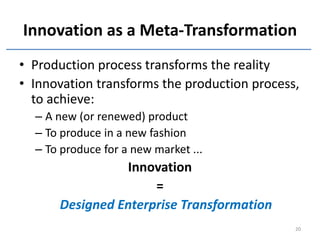
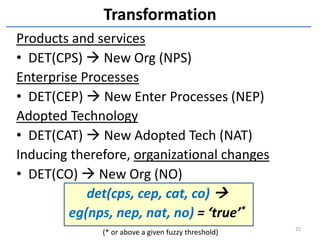
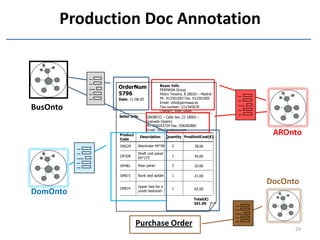
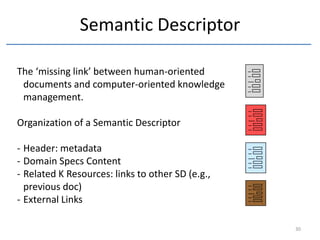
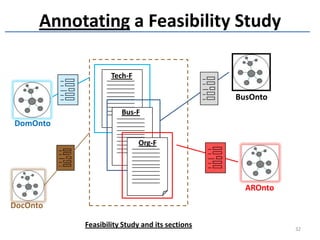
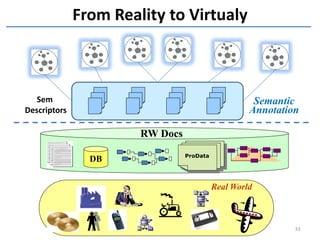
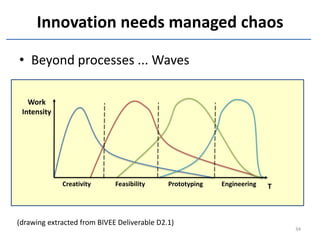
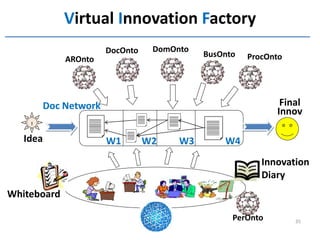
The document discusses methods and tools for enterprise innovation in a networked economy using a knowledge-centric approach. It proposes a virtual innovation factory (VIF) that operates in an innovation space, transforming raw and enabling knowledge into new working knowledge and final products through a value production chain. The VIF is intended to facilitate open innovation using a social semantic knowledge management platform to manage enterprise documents in a semantically enriched way using ontologies. The goal is to support continuous business innovation through knowledge management and transformation of enterprise processes, products, and technologies.