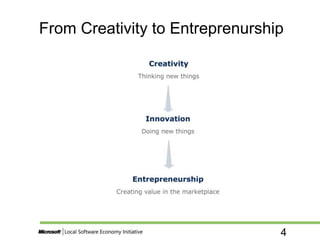
The document discusses the essential relationship between creativity, innovation, and entrepreneurship, highlighting the steps in the creative process and the characteristics of successful entrepreneurs. It identifies four types of innovation—invention, extension, duplication, and synthesis—and explores common myths associated with innovation while emphasizing action-oriented principles for entrepreneurs. Ultimately, it portrays entrepreneurship as a dynamic process that transforms creative ideas into marketable innovations, necessitating both vision and systematic evaluation.