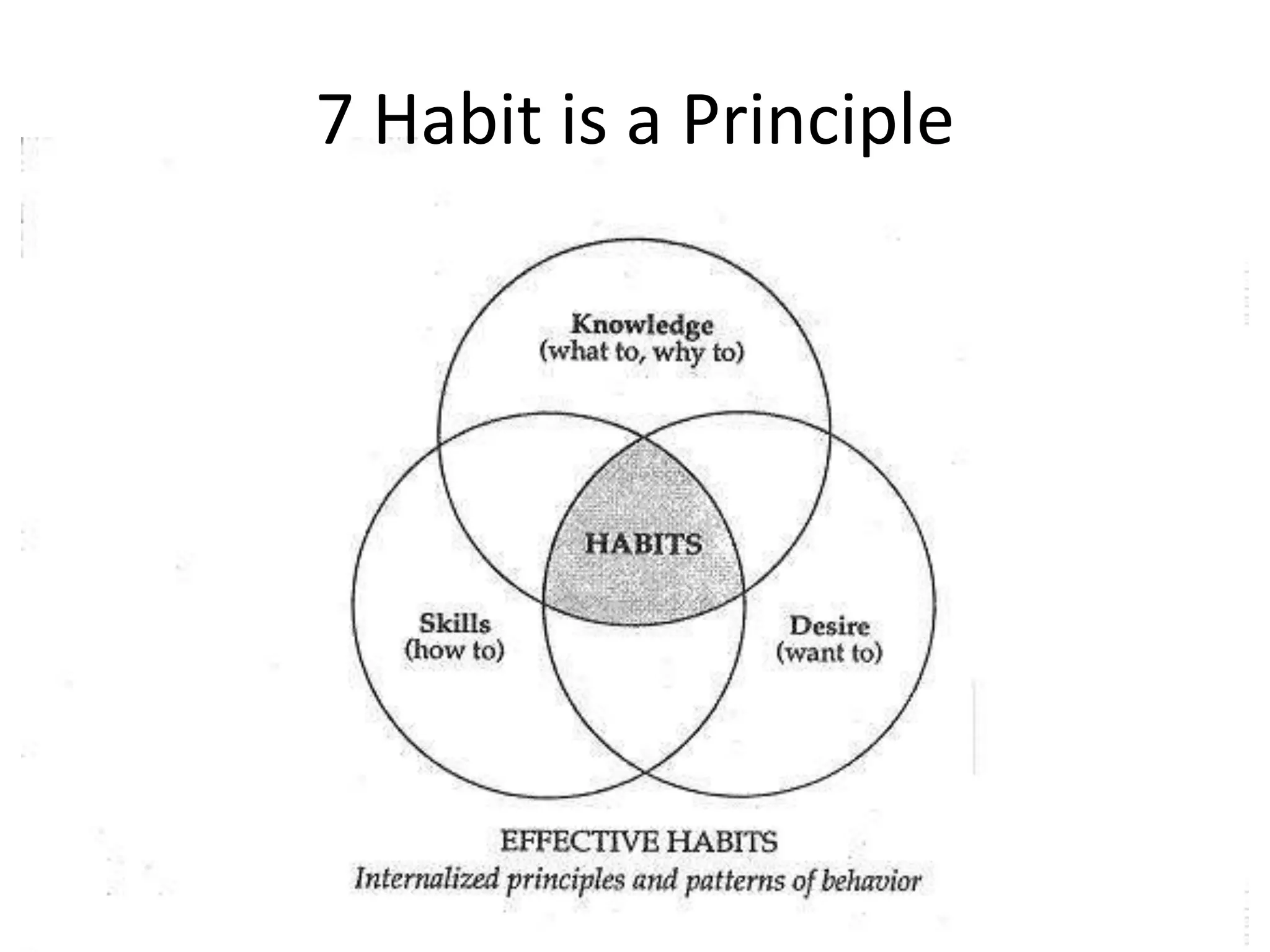
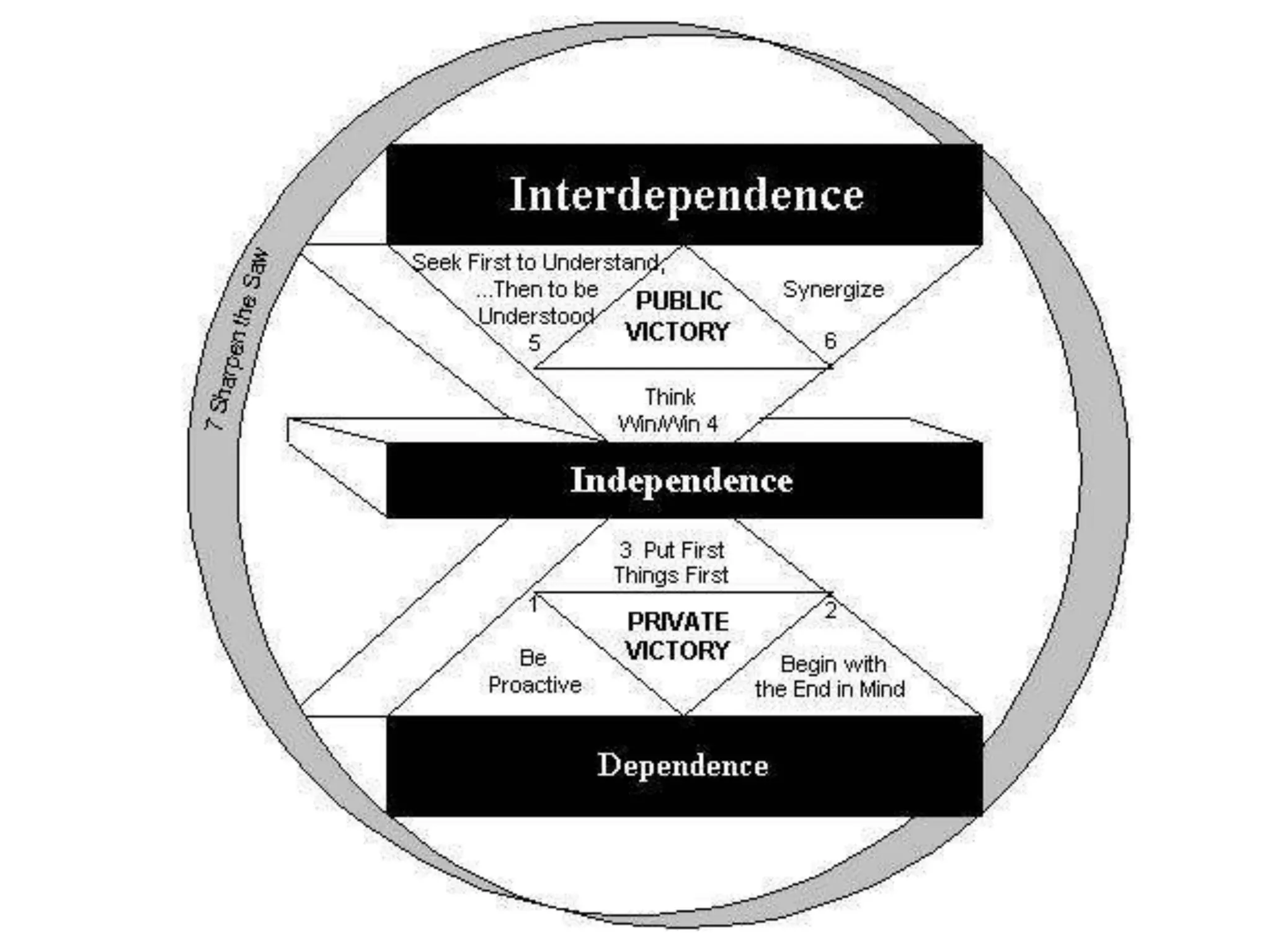
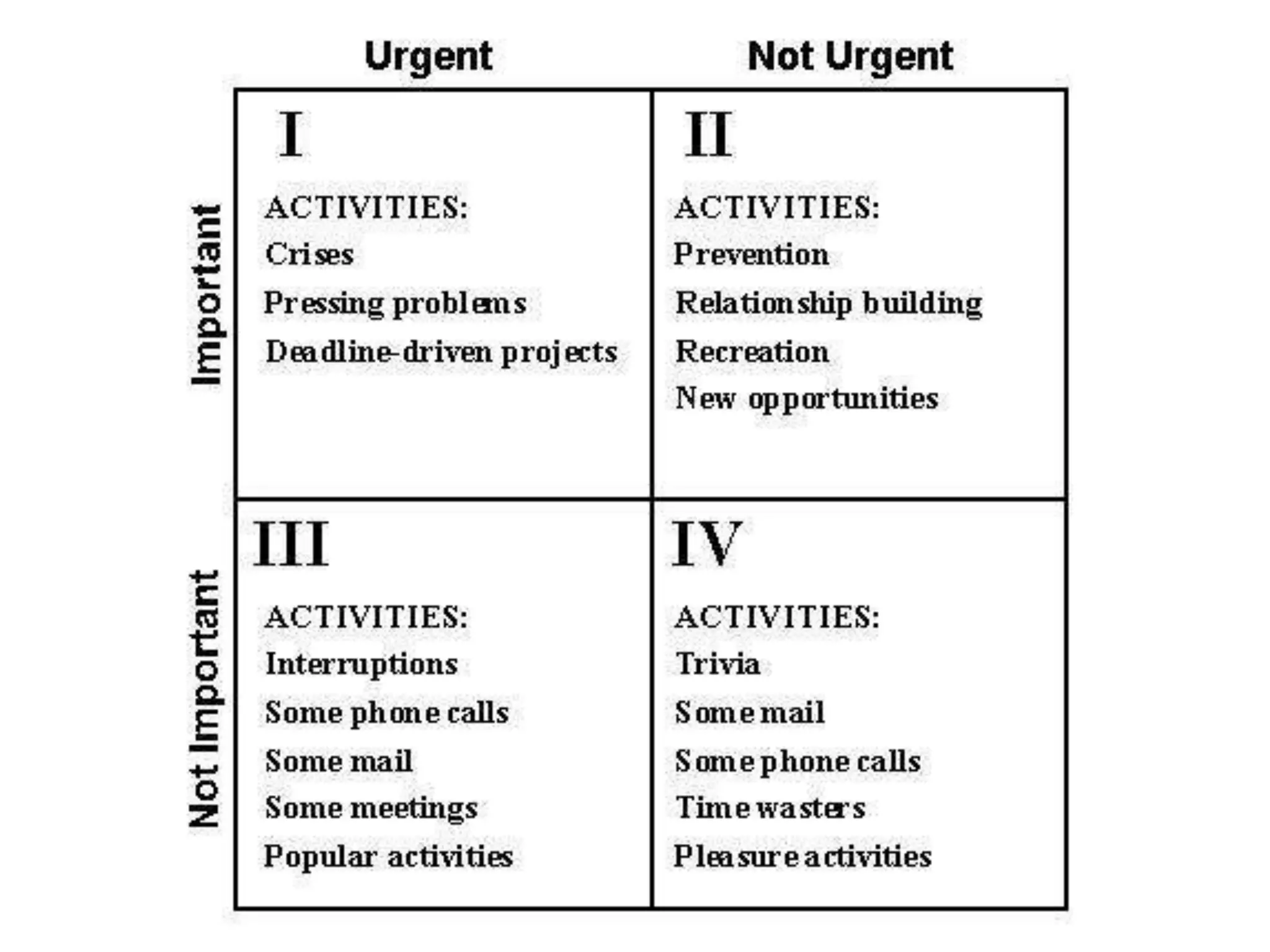
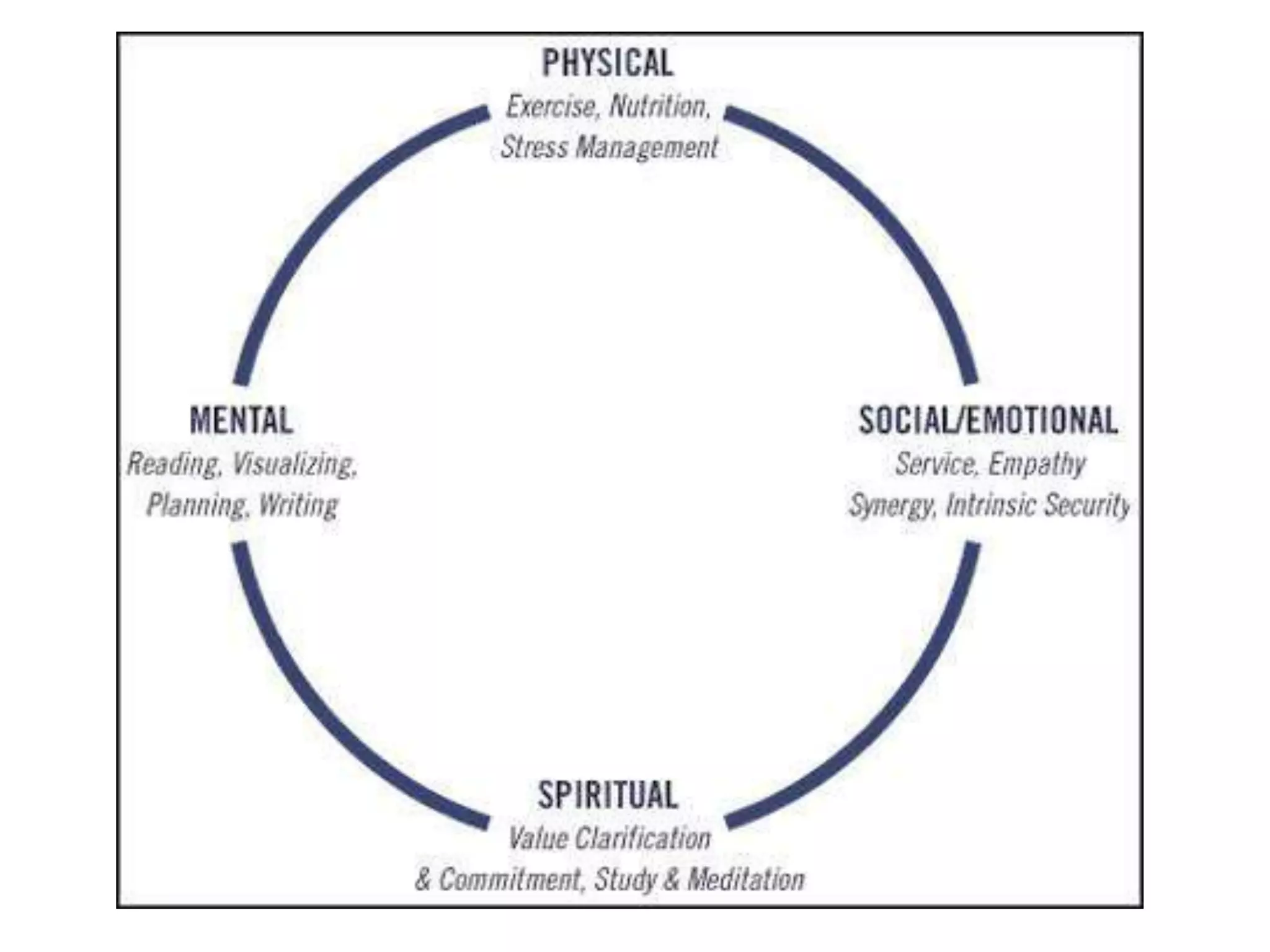
The document outlines the principles and habits for effective human relations as described in 'The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People.' It emphasizes the importance of proactive behavior, vision in goal setting, and seeking mutual benefit through interdependence rather than competition. Additionally, it highlights the significance of understanding and valuing differences among individuals to enhance collaboration and effectiveness.