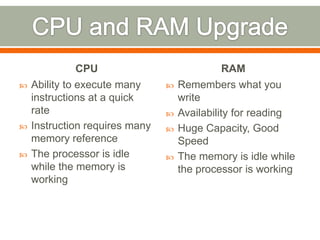
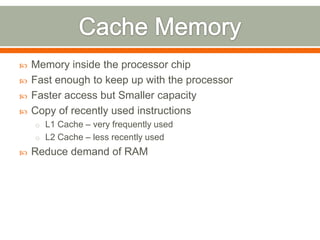
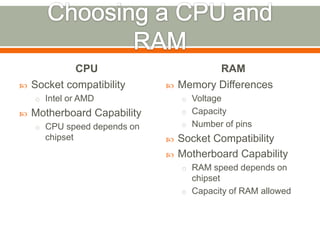
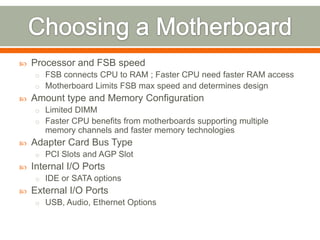
This document discusses considerations for upgrading computer hardware and software components. It covers whether an upgrade is needed or worth it based on compatibility, risks of issues, and whether current versions are still supported. Key factors to evaluate include new features, performance improvements, bug fixes in updates, and avoiding early upgrades to allow time for major problems to be addressed.