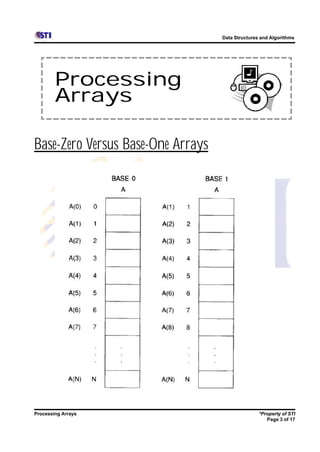
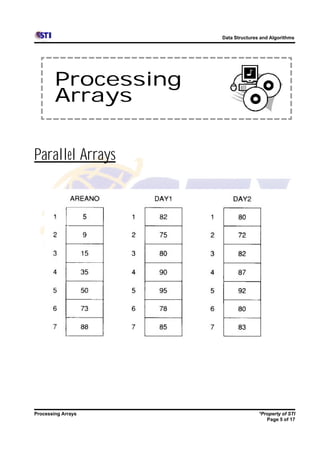
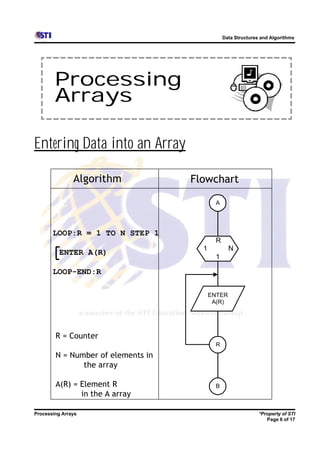
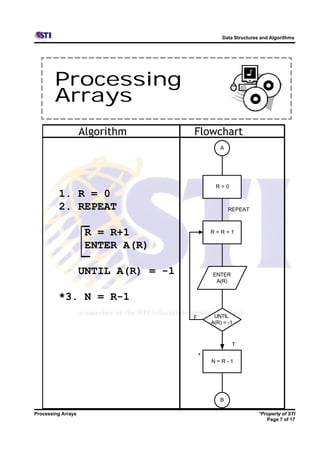
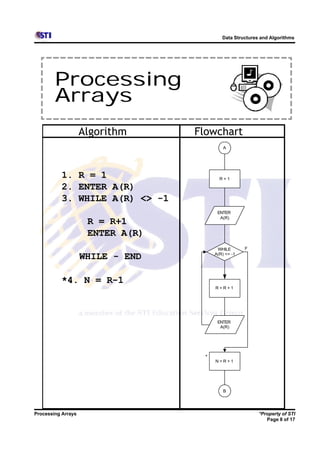
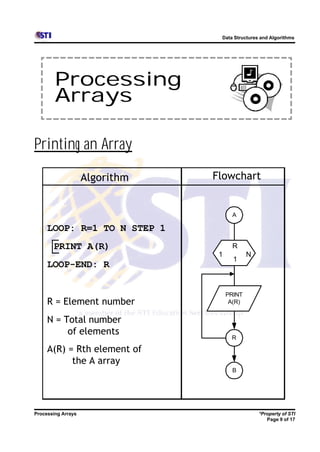
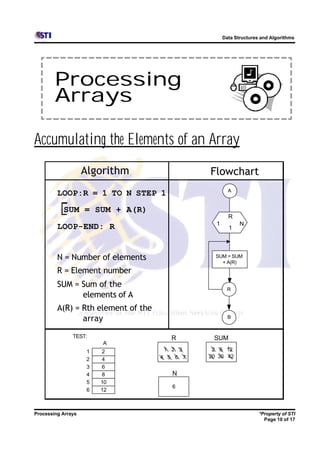
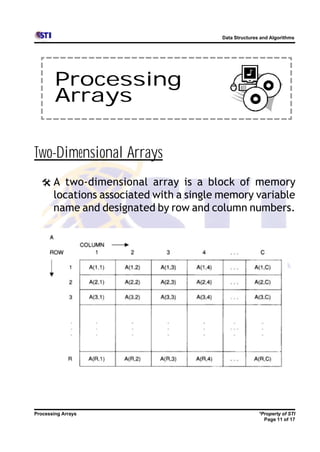
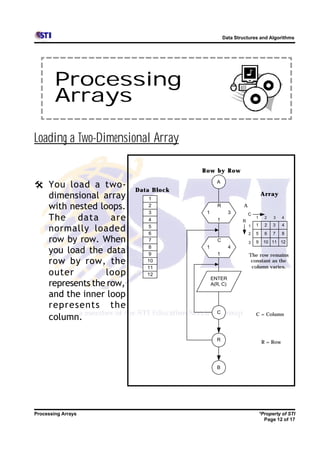
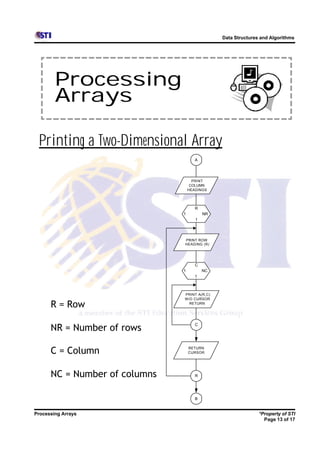
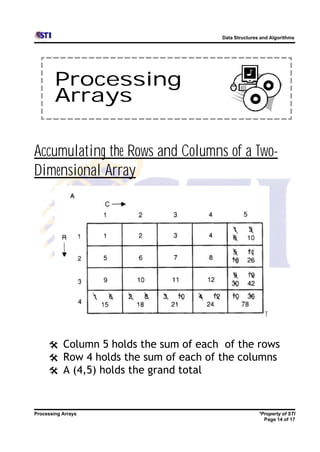
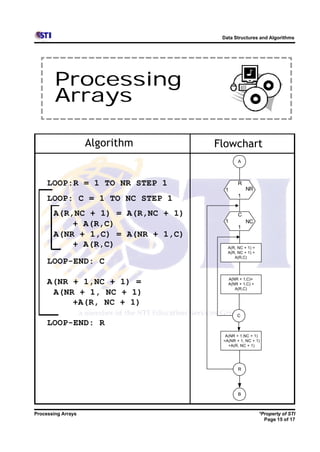
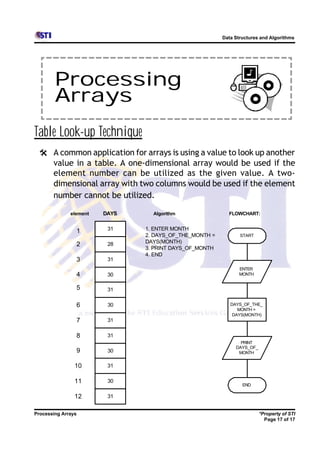
Arrays allow storing multiple values for the same variable in computer memory. Static arrays have a fixed size set at initialization, while dynamic arrays can expand and contract during runtime. Most programming languages use zero-based indexing for arrays, where the first element is index 0 rather than 1. One-dimensional arrays store elements in a single list, while two-dimensional arrays use two indices like rows and columns to access elements. Data is typically loaded into two-dimensional arrays using nested loops to iterate through rows and columns.