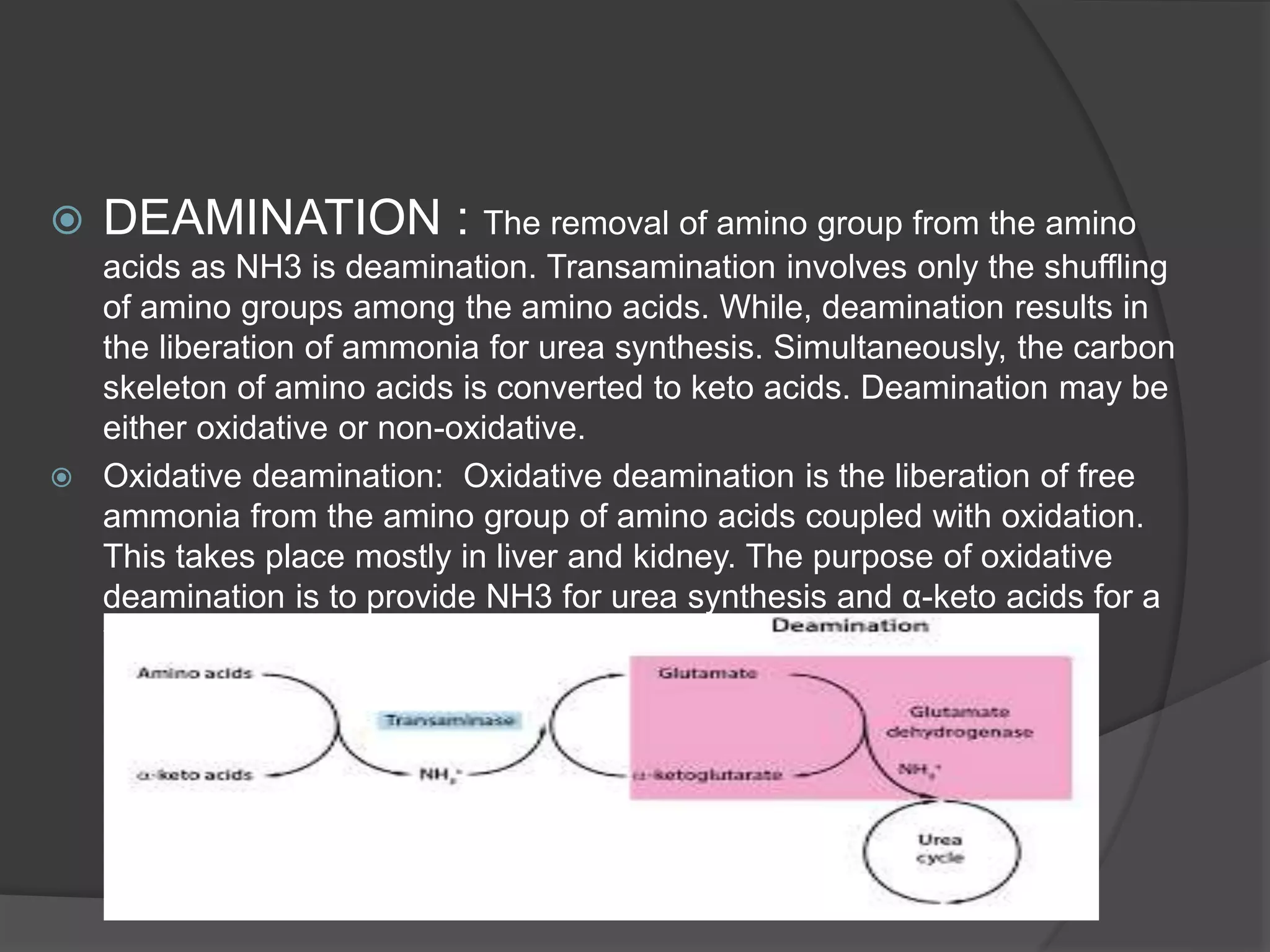
The document summarizes key aspects of amino acid metabolism, including transamination and deamination. Transamination involves the transfer of amino groups between amino acids and keto acids, catalyzed by transaminases. Deamination results in the liberation of ammonia from amino acids for urea synthesis. Ammonia produced from amino acid breakdown is toxic, so mammals excrete it as urea via the urea cycle in the liver and kidneys. The urea cycle involves several enzymes that incorporate ammonia into urea to allow its excretion and prevent toxicity.