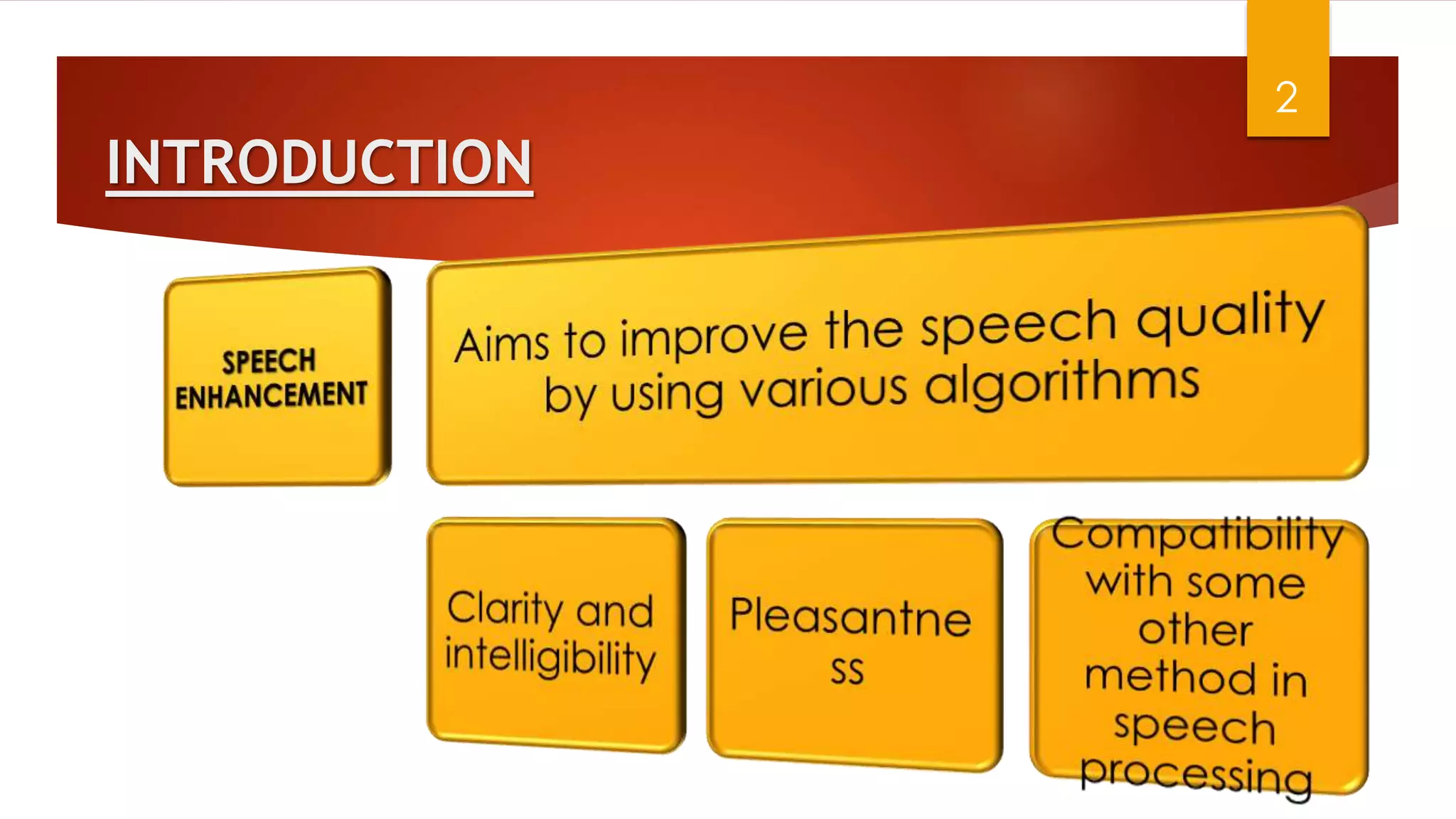
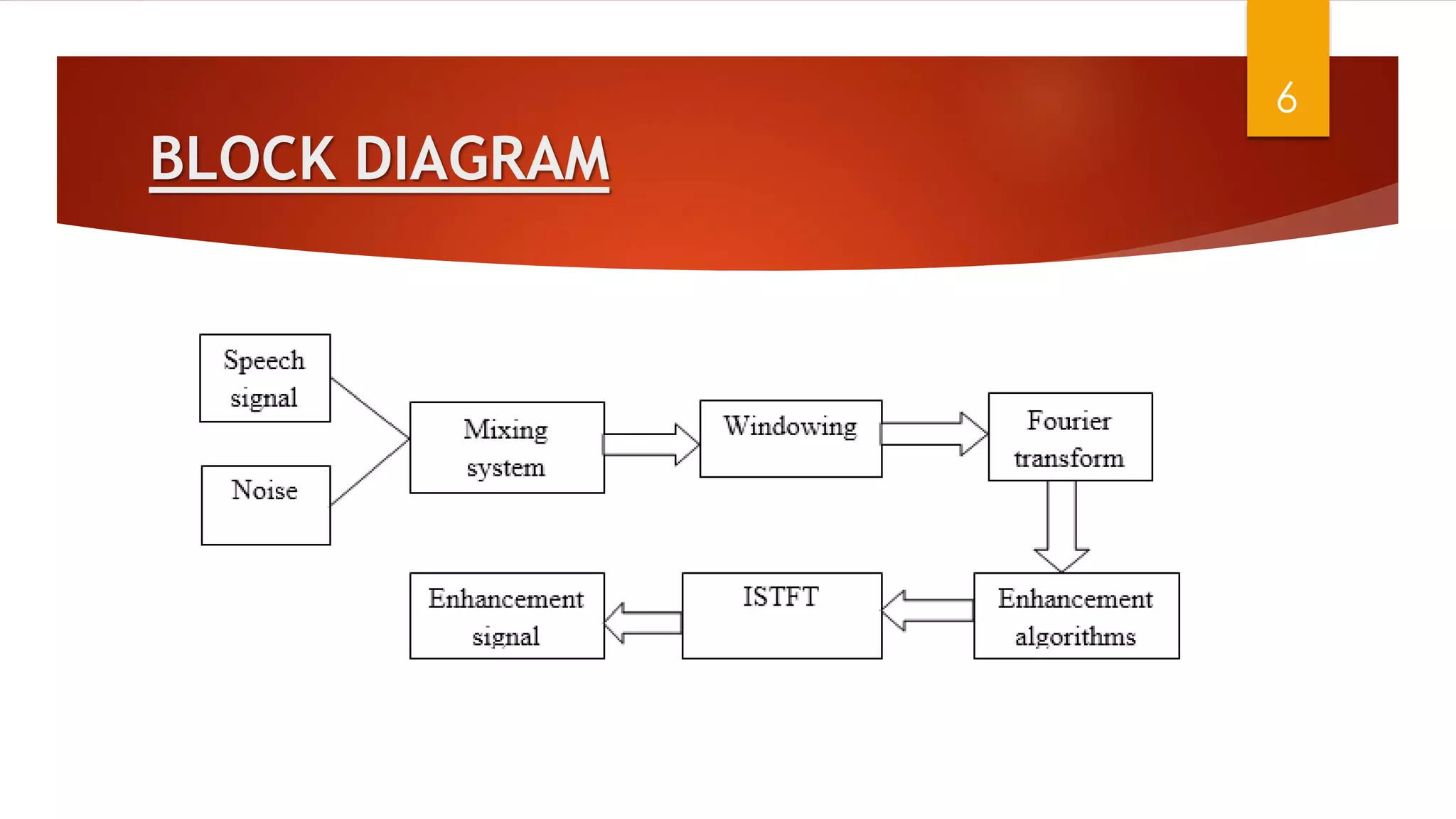
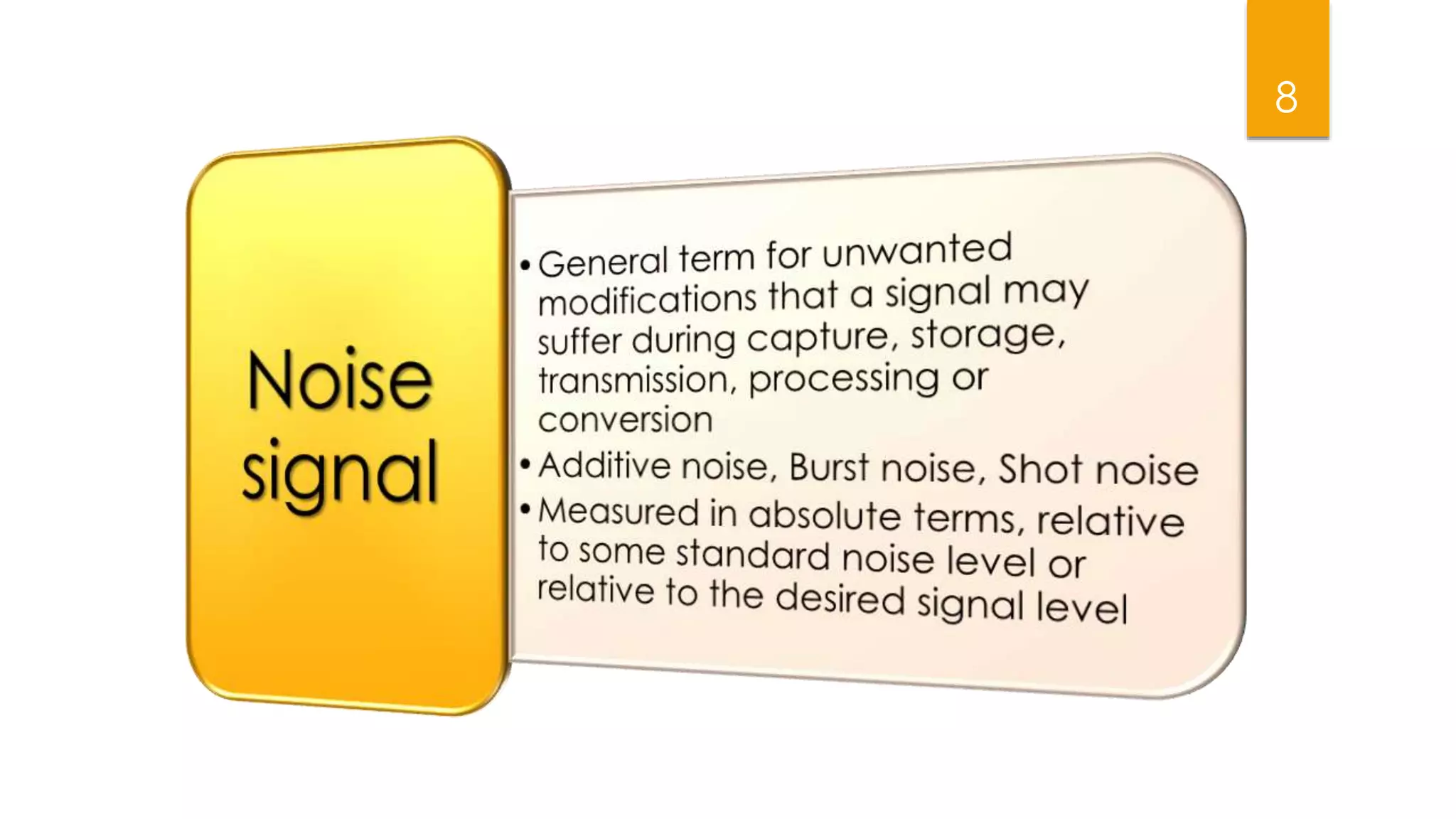
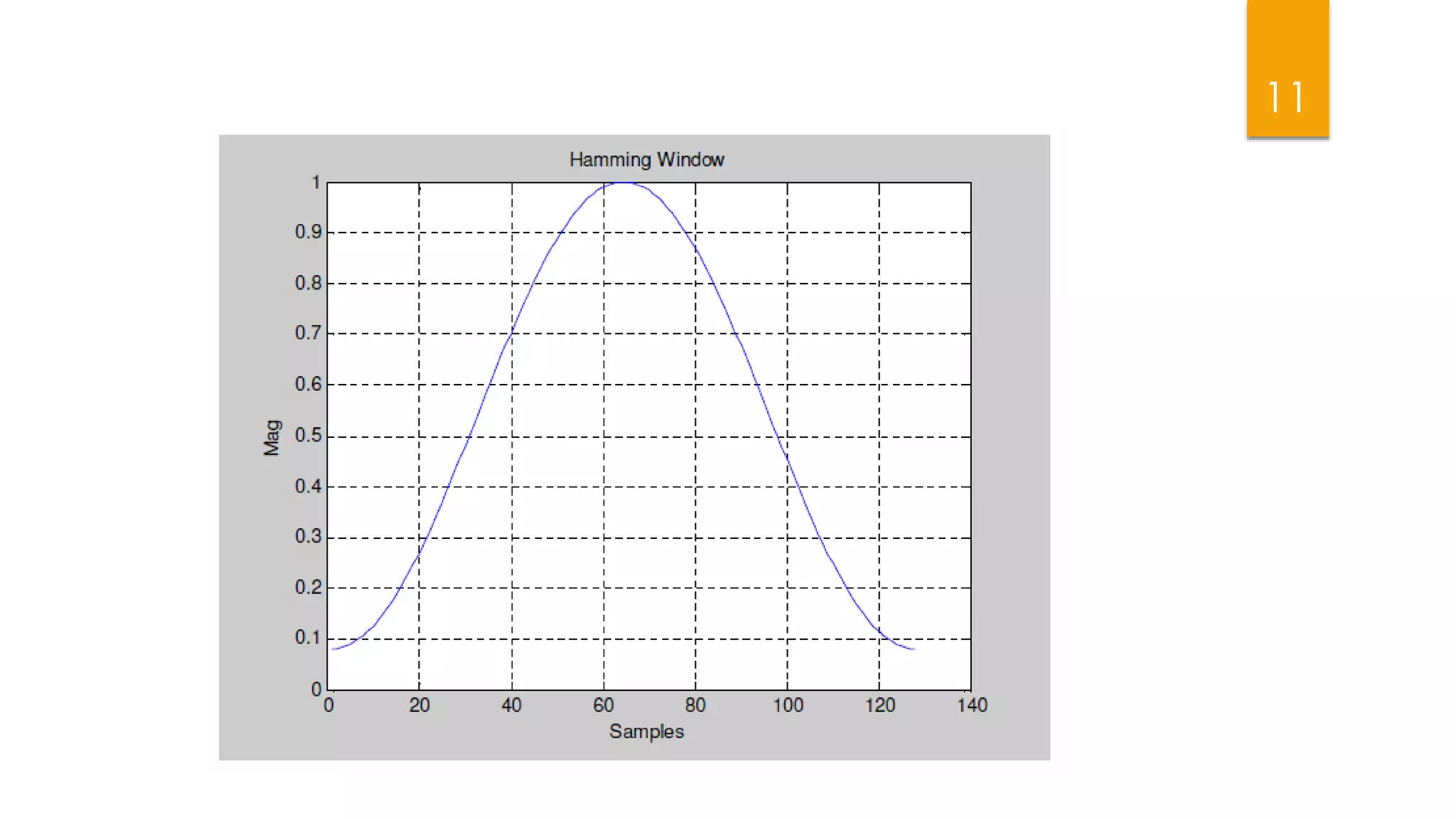
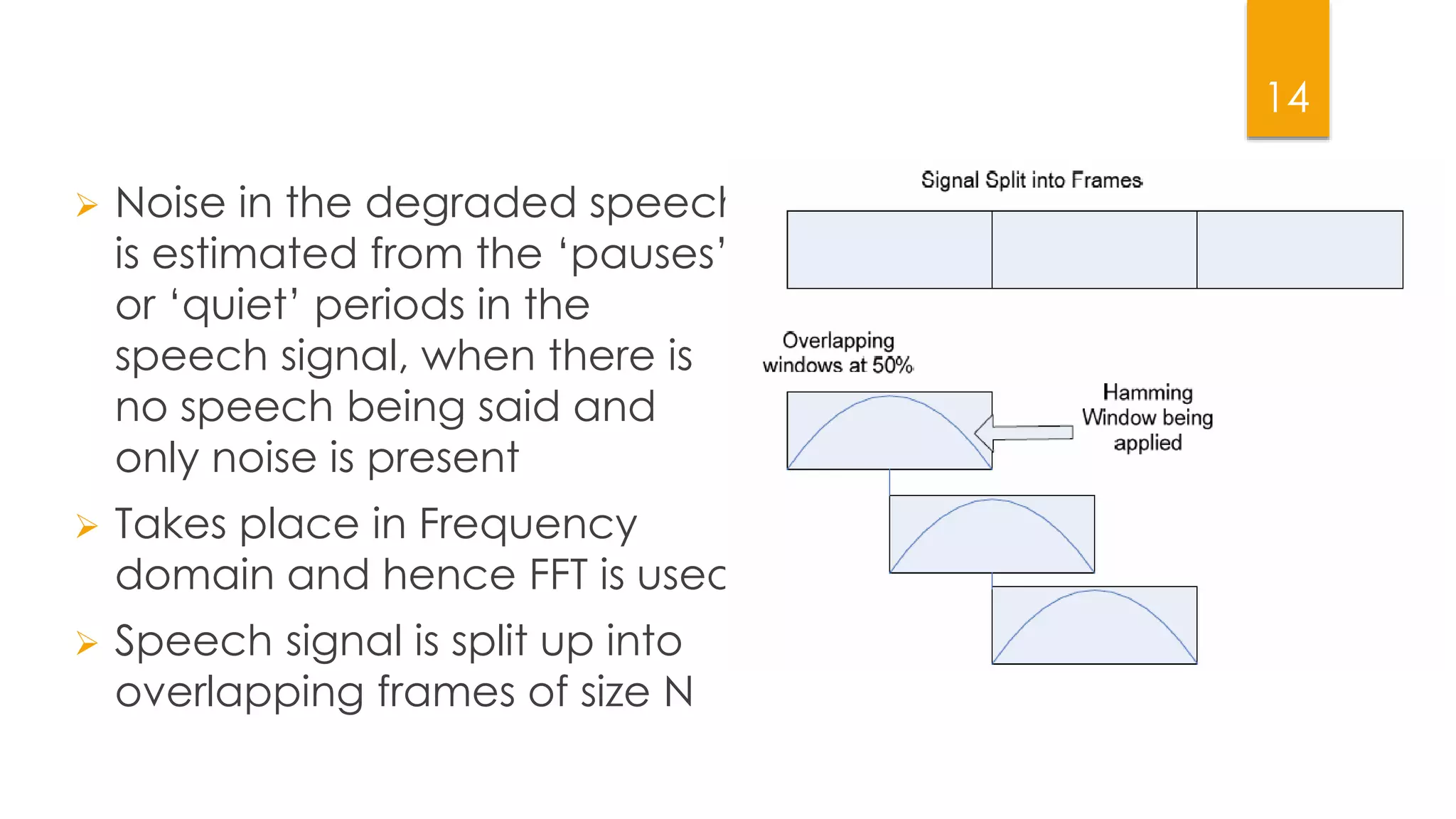
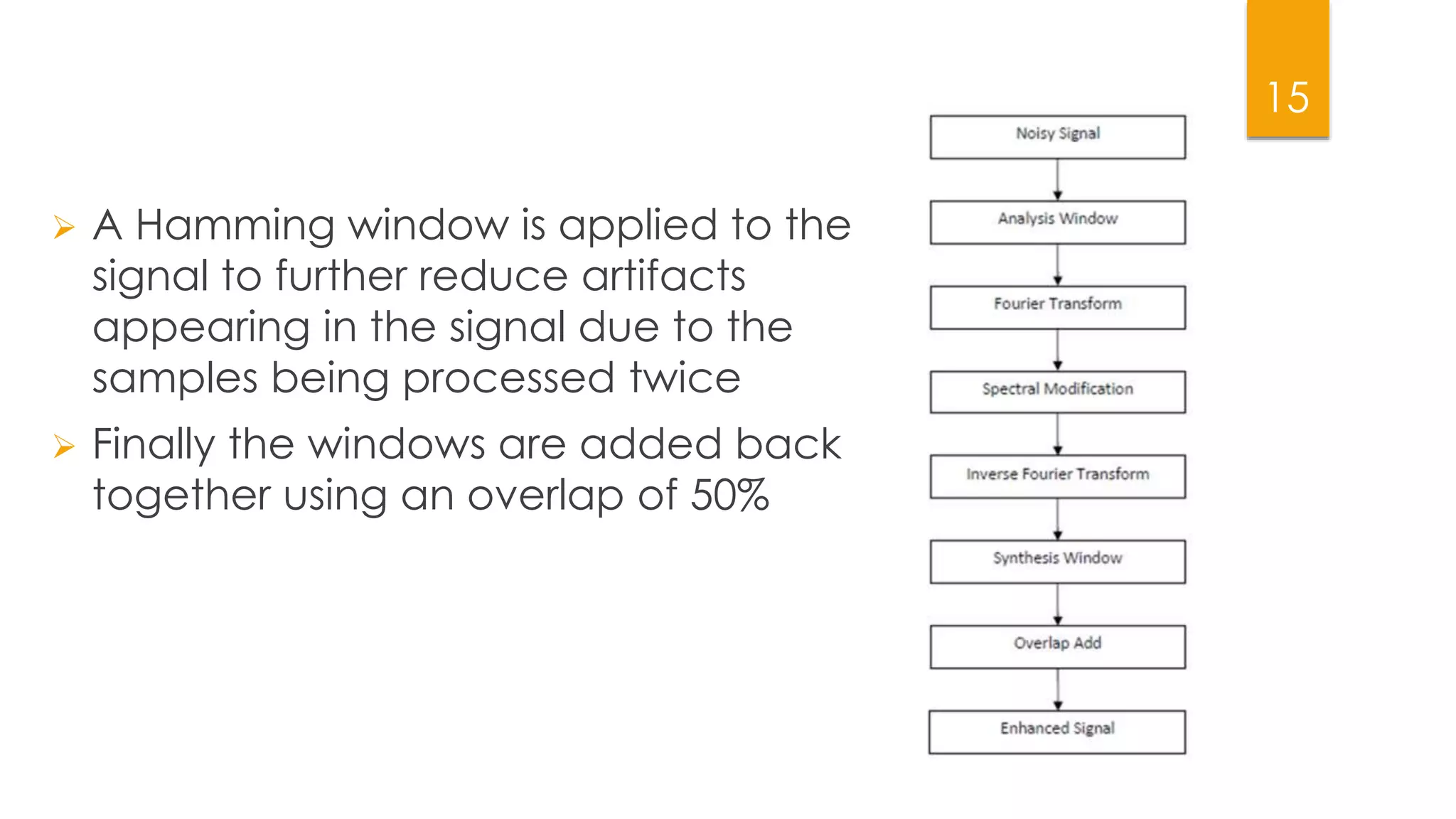
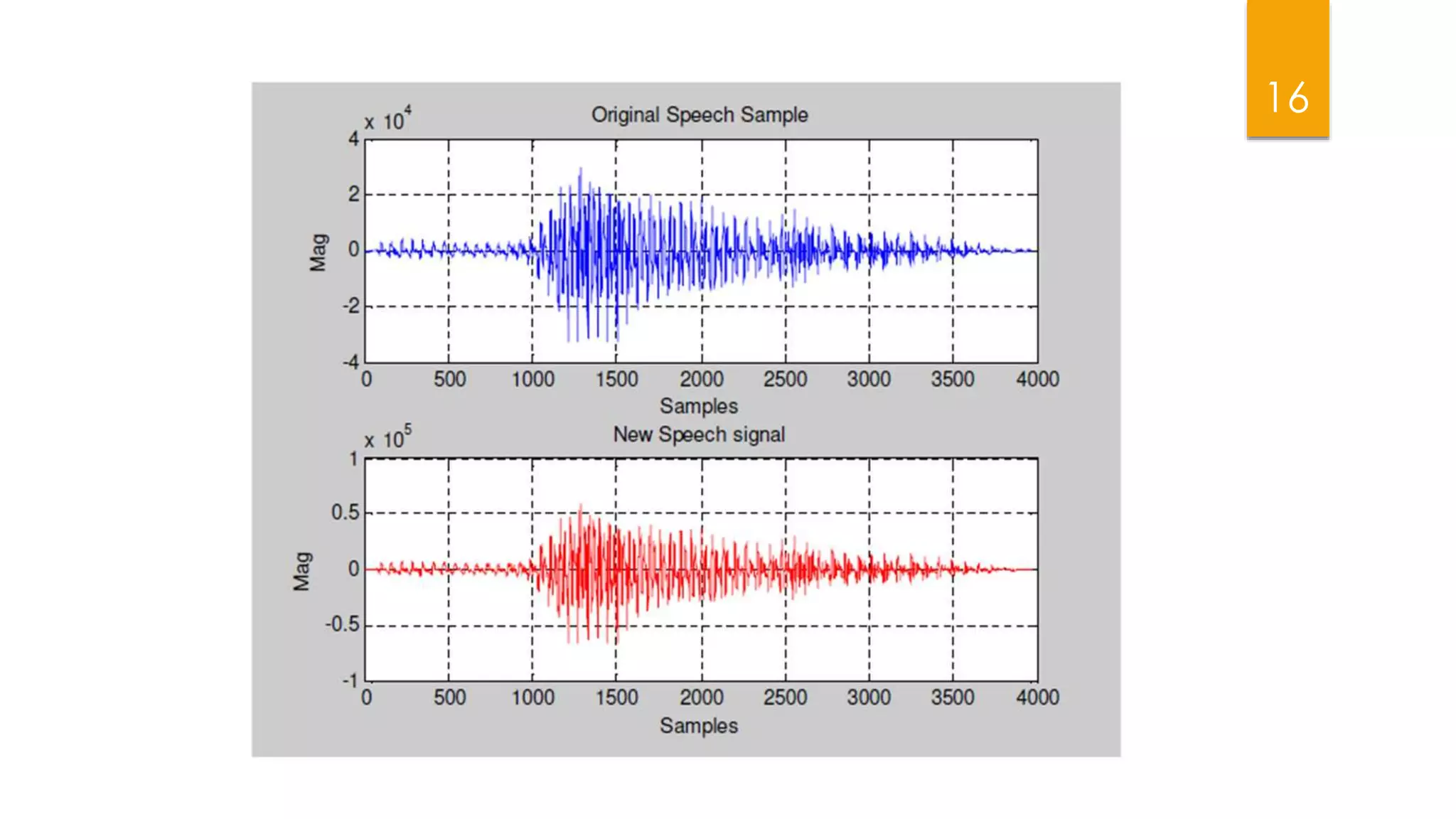
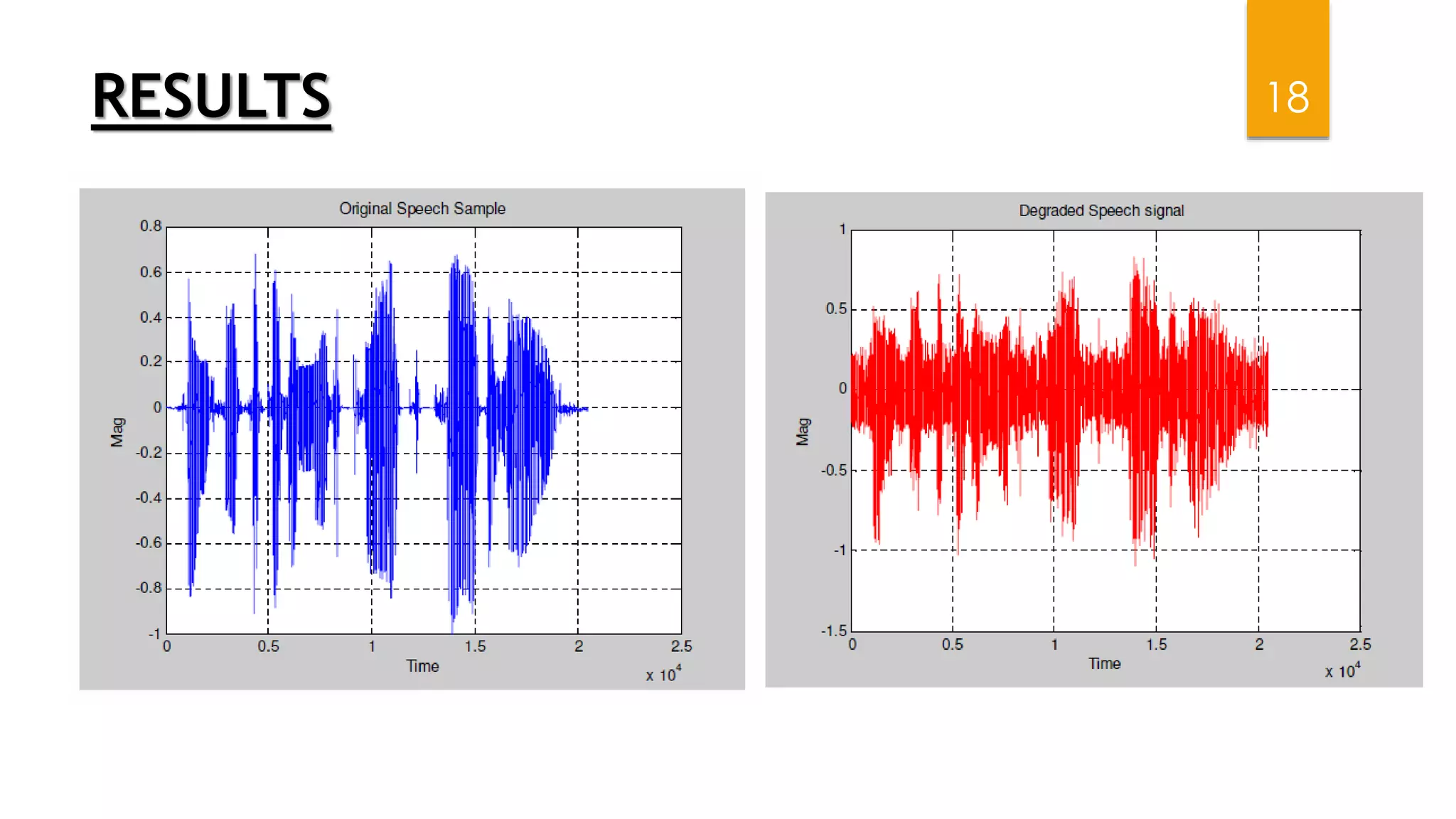
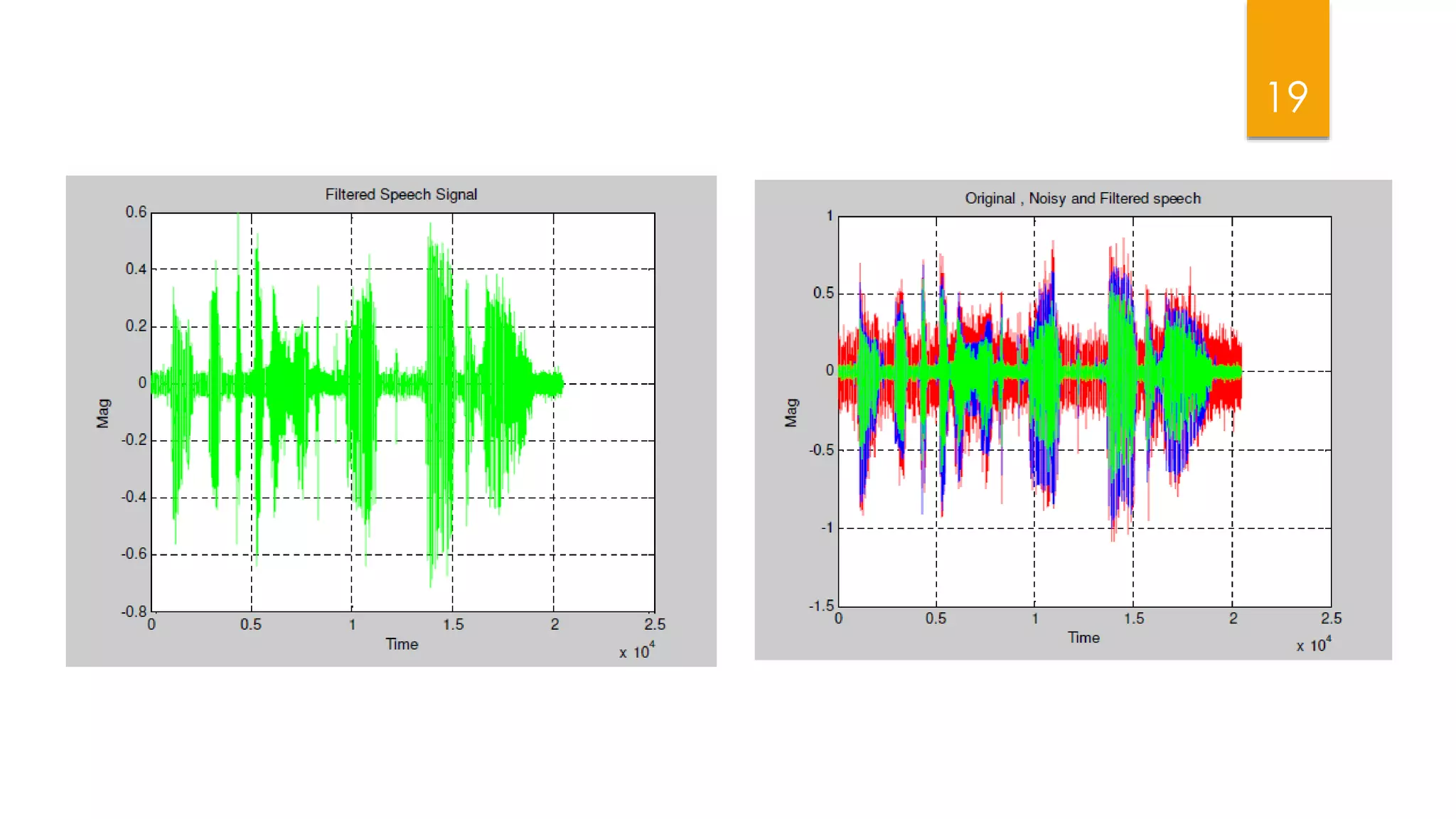
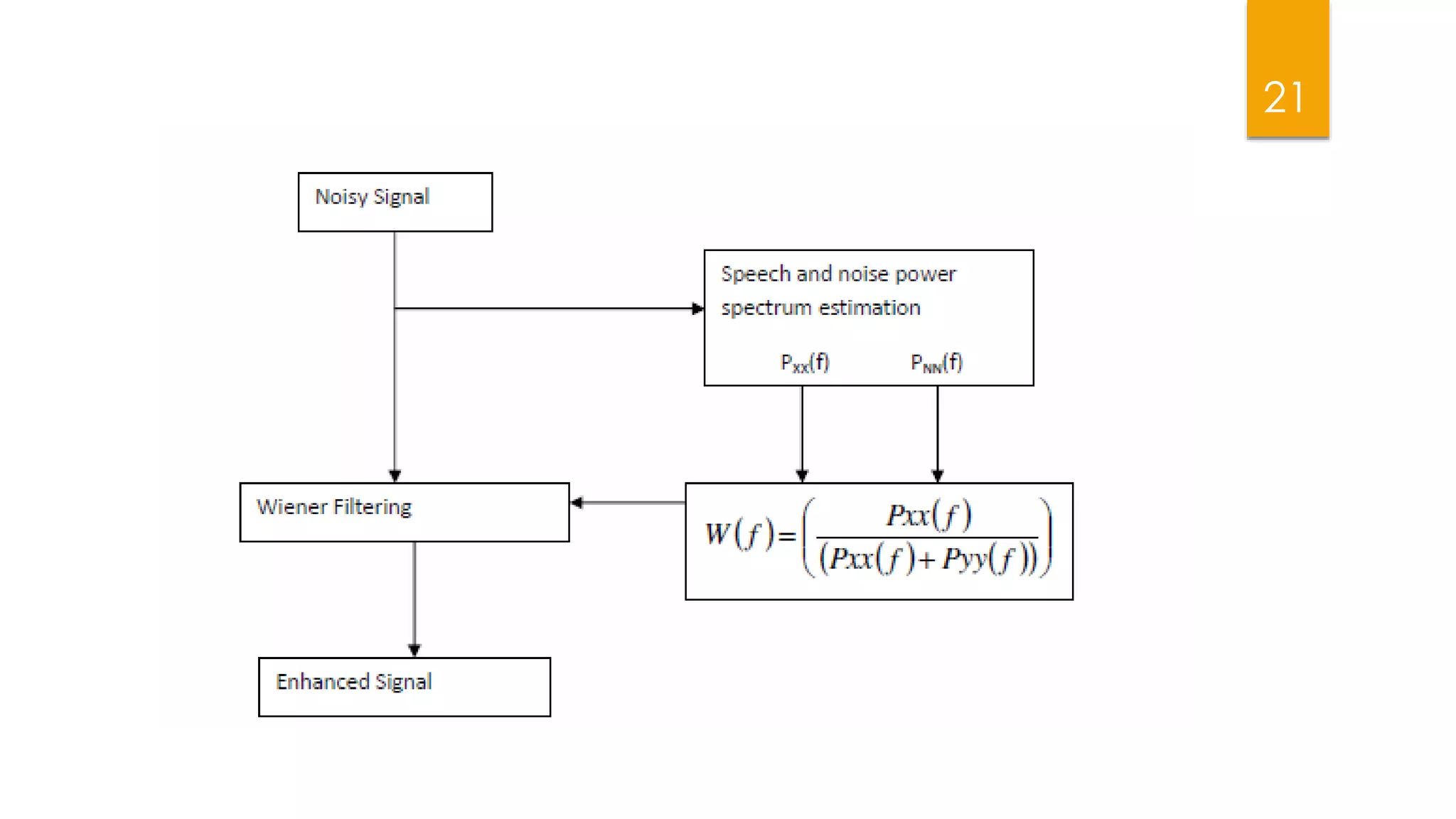
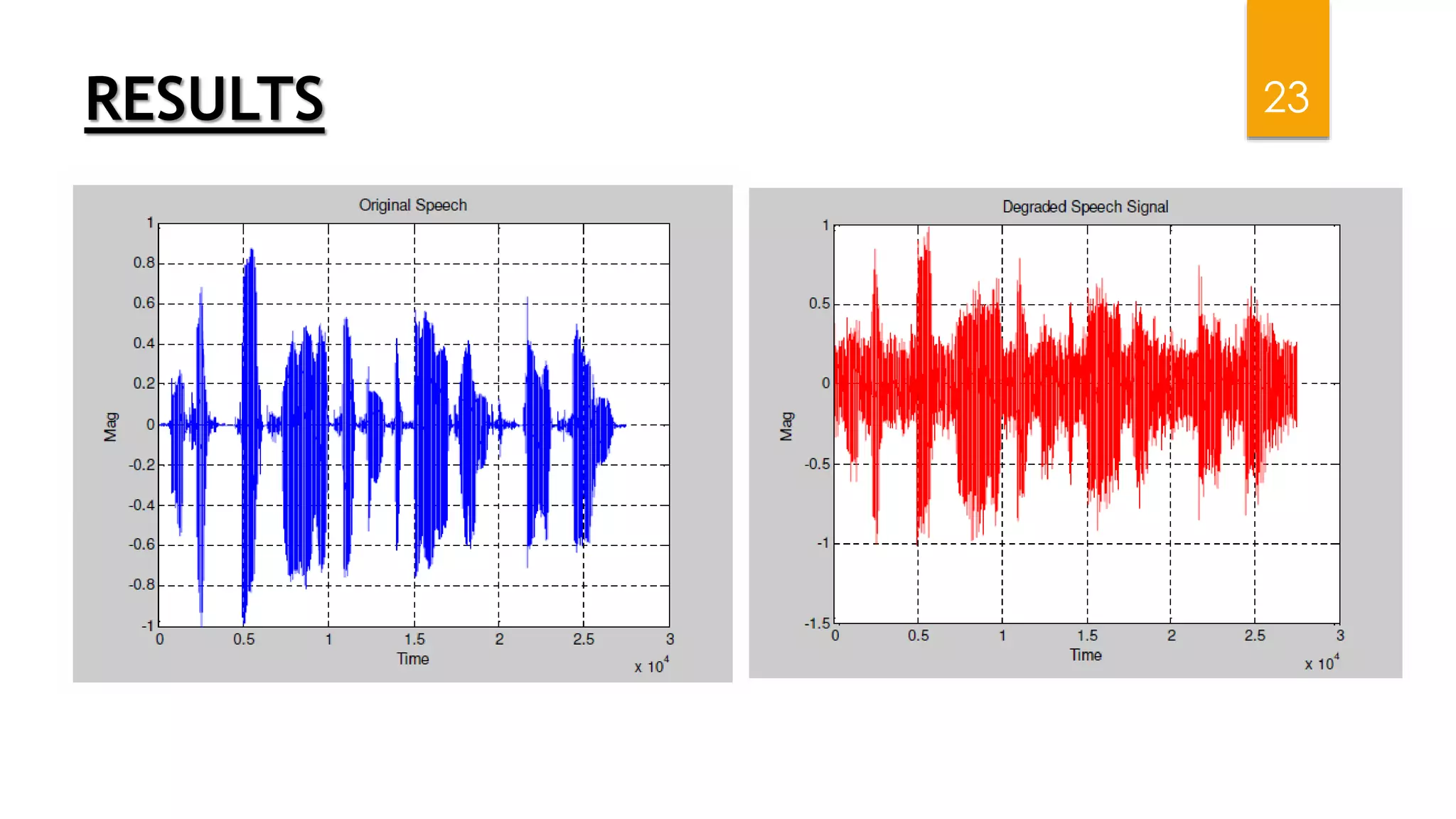
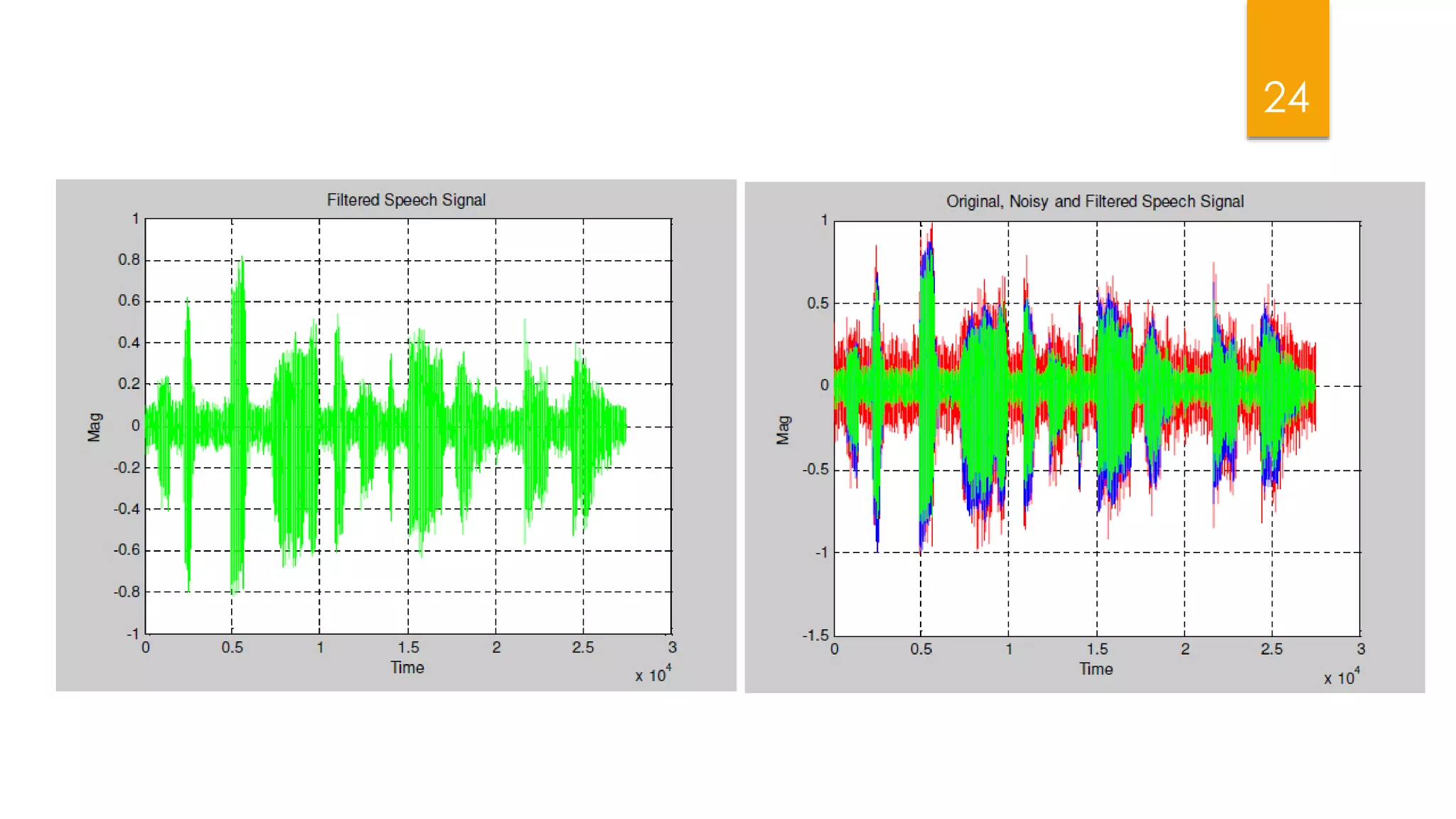
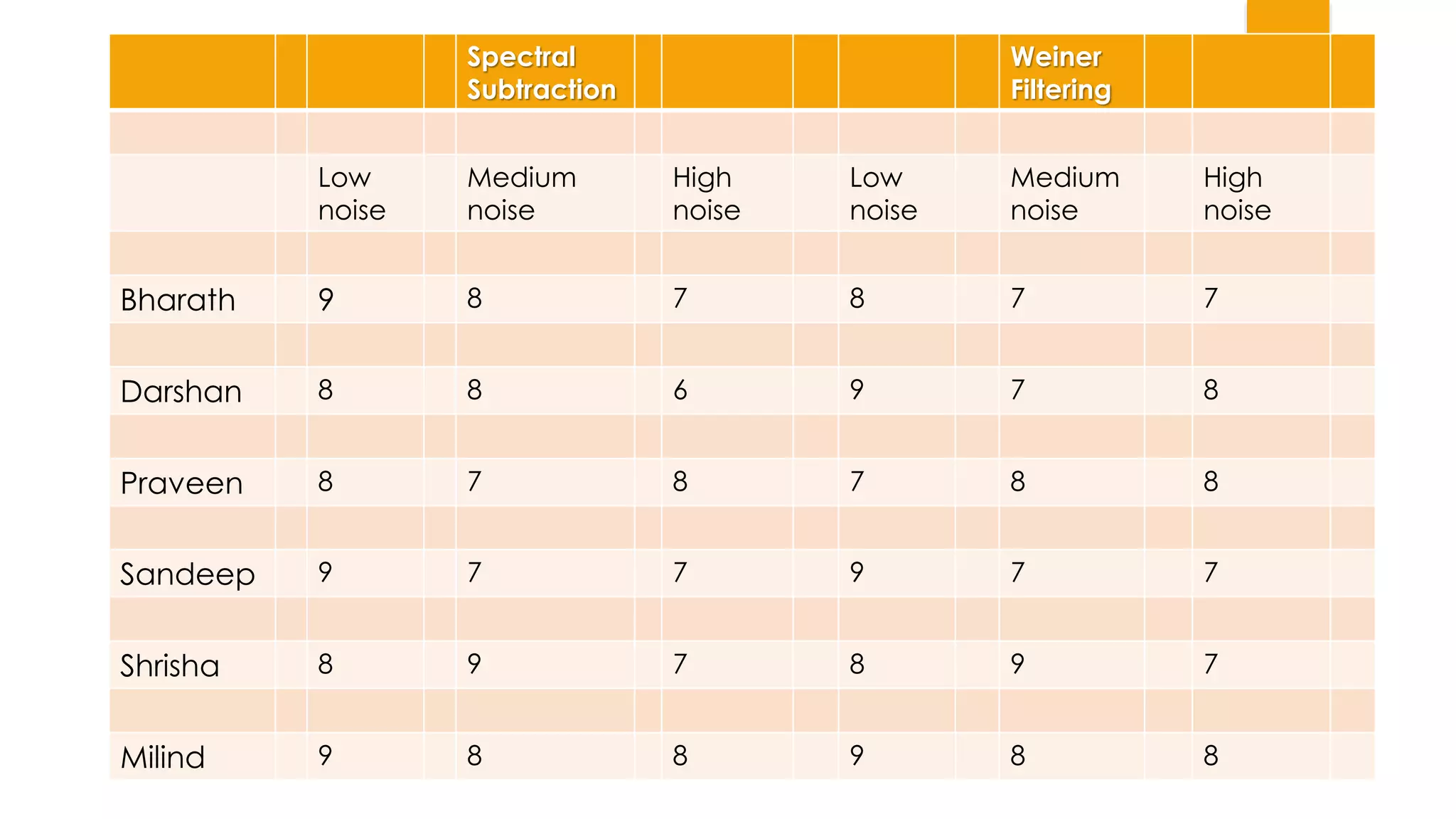
This document summarizes research on applying speech enhancement techniques including spectral subtraction and Wiener filtering. The goals were to examine and simulate these techniques in Matlab. The techniques were tested on speech degraded by additive noise at different signal-to-noise ratios. Spectral subtraction removes noise by subtracting noise spectrum estimates from the degraded speech spectrum. Wiener filtering suppresses noise by multiplying the speech spectrum by a frequency response. Both techniques performed similarly at low noise, but Wiener filtering performed better at higher noise levels. Future work could include automatic noise detection and adaptation to changing noise.