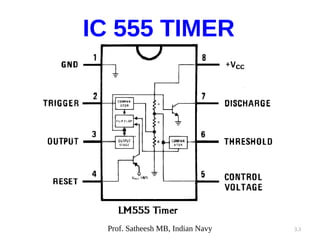
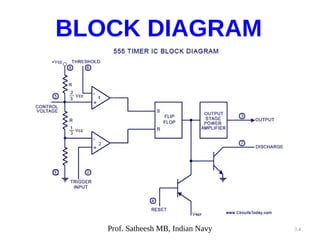
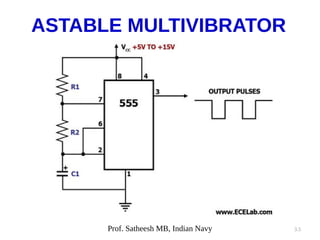
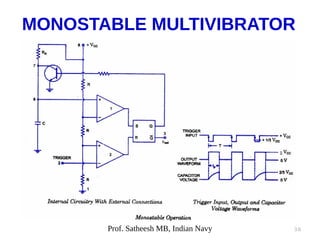
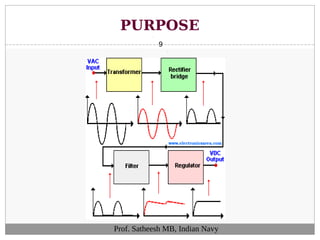
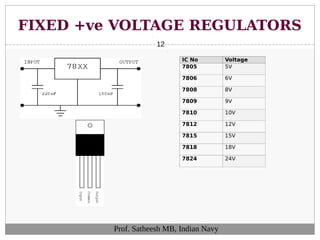
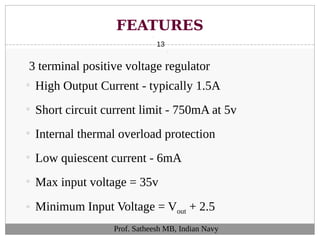
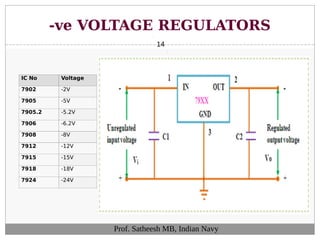
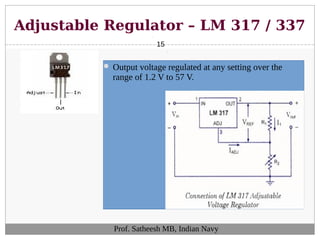
The document discusses integrated circuit voltage regulators. It describes IC voltage regulators as circuits that supply constant voltage regardless of load current changes. It classifies regulators as multi-pin types like the LM 723C or 3-pin types like the 78/79XX series. The document lists common fixed positive voltage regulators like the 7805 and negative voltage regulators like the 7905. It also discusses the adjustable LM317 positive and LM337 negative regulators and their ability to output any voltage from 1.2V to 57V. Performance parameters like line and load regulation, temperature stability, ripple rejection and quiescent current are defined.