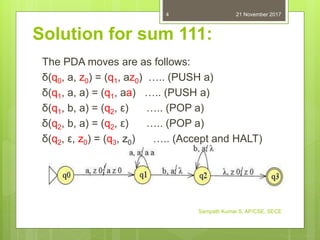
The document discusses deterministic pushdown automata (DPDA) and provides examples of DPDAs that accept specific languages. It begins by defining DPDA as a PDA that has at most one choice of move in any state, as opposed to a non-deterministic PDA. It then gives an example of a DPDA that accepts the language L={anbn|n>1} and explains its transition function. Finally, it lists several other language recognition problems and invites the reader to design DPDAs to solve them.


![Problems to discuss:
112. Design a PDA which accept the language
containing equal number of a’s and b’s over Σ={a,
b}.
113. Design a PDA which accepts L={anb2n|n>1}
114. Design a PDA which accepts L={a3bncn|n>0}
115. Design a PDA which accepts L={wcwr|w
(a+b)*}
116. Design a PDA which accepts the set of
balanced parenthesis. ([{()}])
21 November 2017
Sampath Kumar S, AP/CSE, SECE
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-171121155335/85/3-4-deterministic-pda-5-320.jpg)



