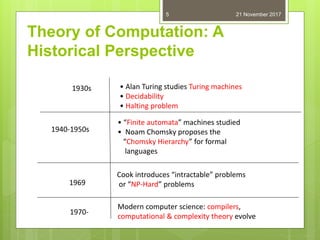
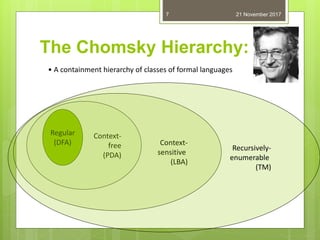
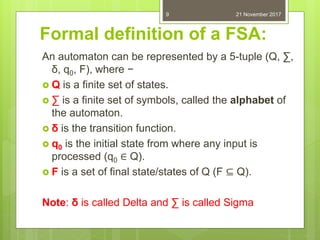
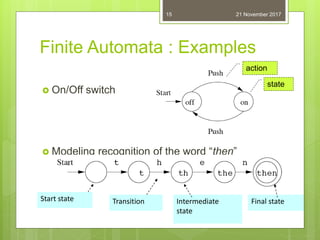
The document introduces automata theory, focusing on abstract computing devices called automata and their historical significance, particularly the contributions of Alan Turing and the development of the Chomsky hierarchy. It explains the fundamentals of languages, grammars, and finite state machines, including their classifications into deterministic and non-deterministic types. The applications of finite automata in various fields such as digital circuits, compilers, and pattern recognition are also discussed.