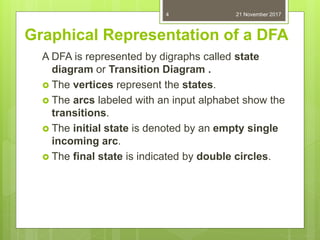
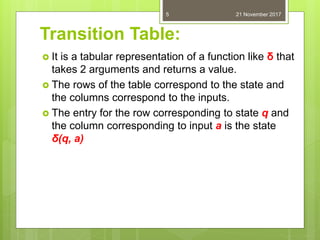
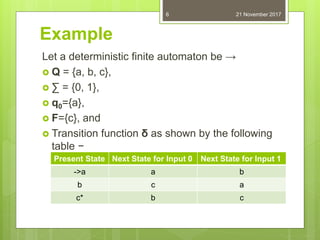
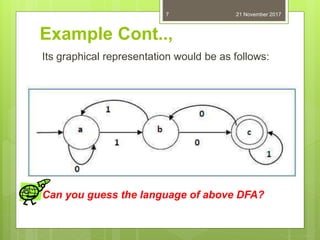
This document defines and provides examples of deterministic finite automata (DFAs). It begins by defining a DFA as a finite state machine where the transition function is deterministic. Formally, a DFA is defined as a 5-tuple consisting of a finite set of states, a finite input alphabet, a transition function, an initial state, and a set of final/accepting states. The document provides examples of representing DFAs using state diagrams and transition tables and discusses how to represent the extended transition function. It concludes by posing several problems about designing DFAs with certain language definitions.