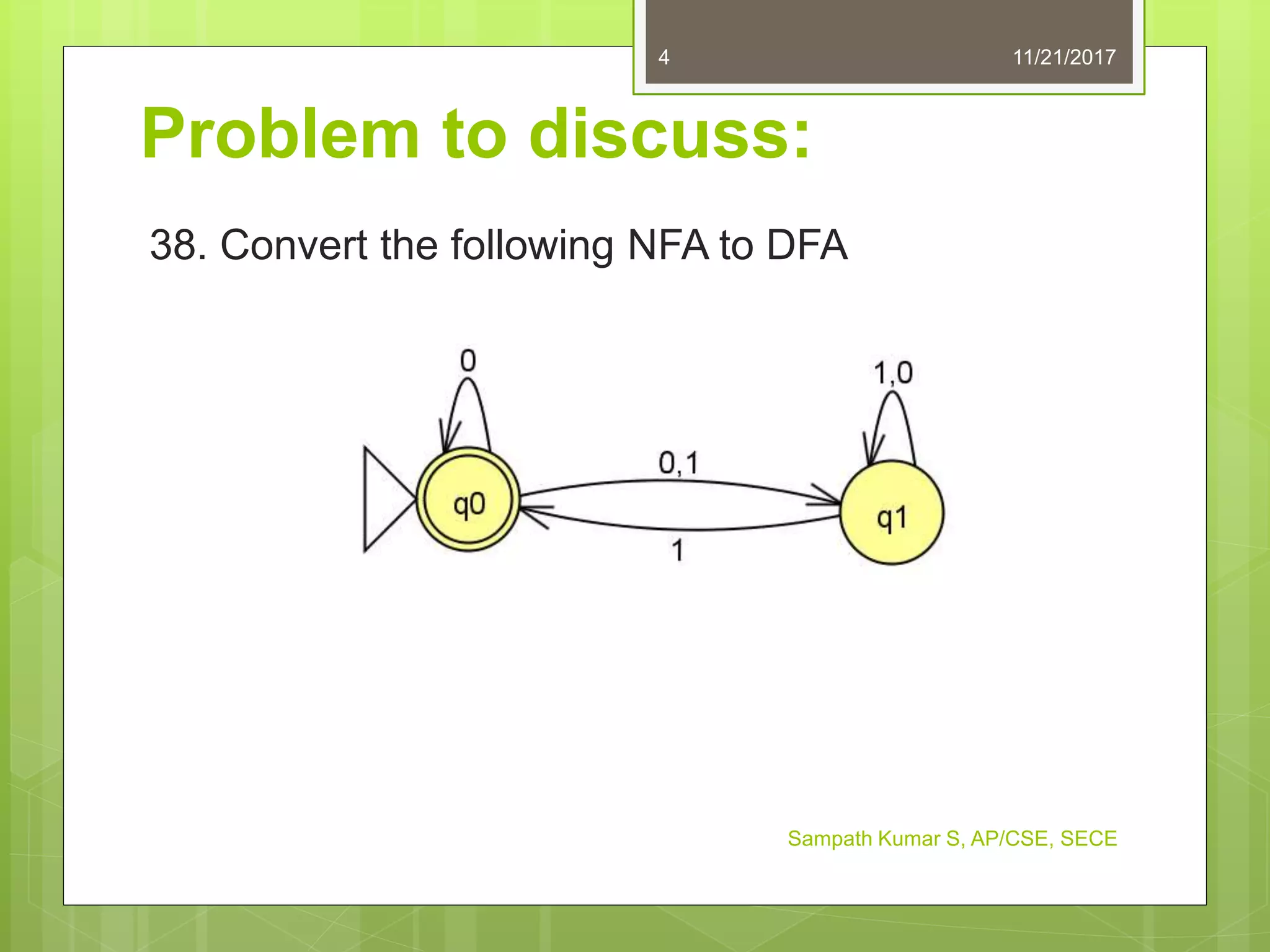
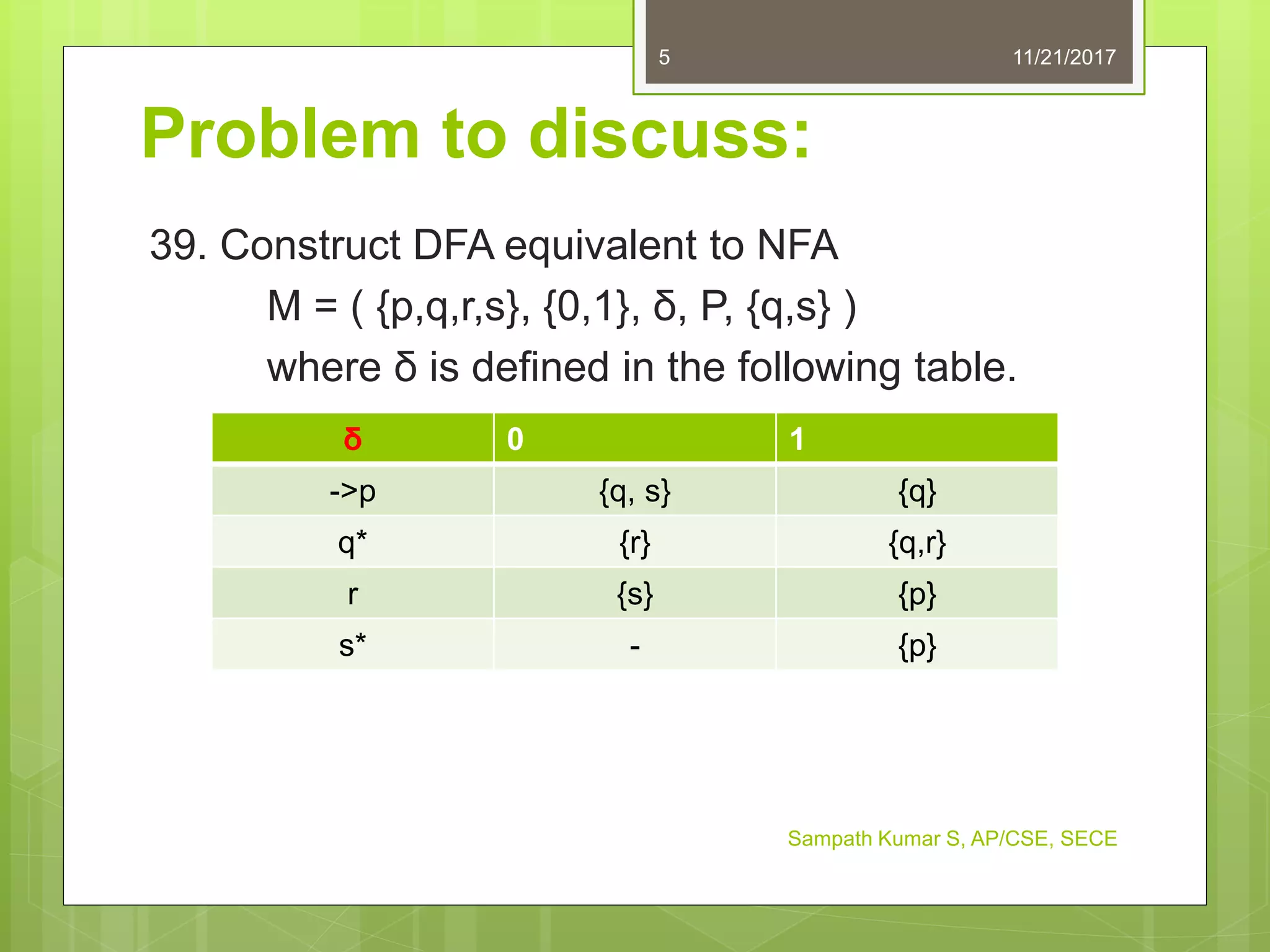
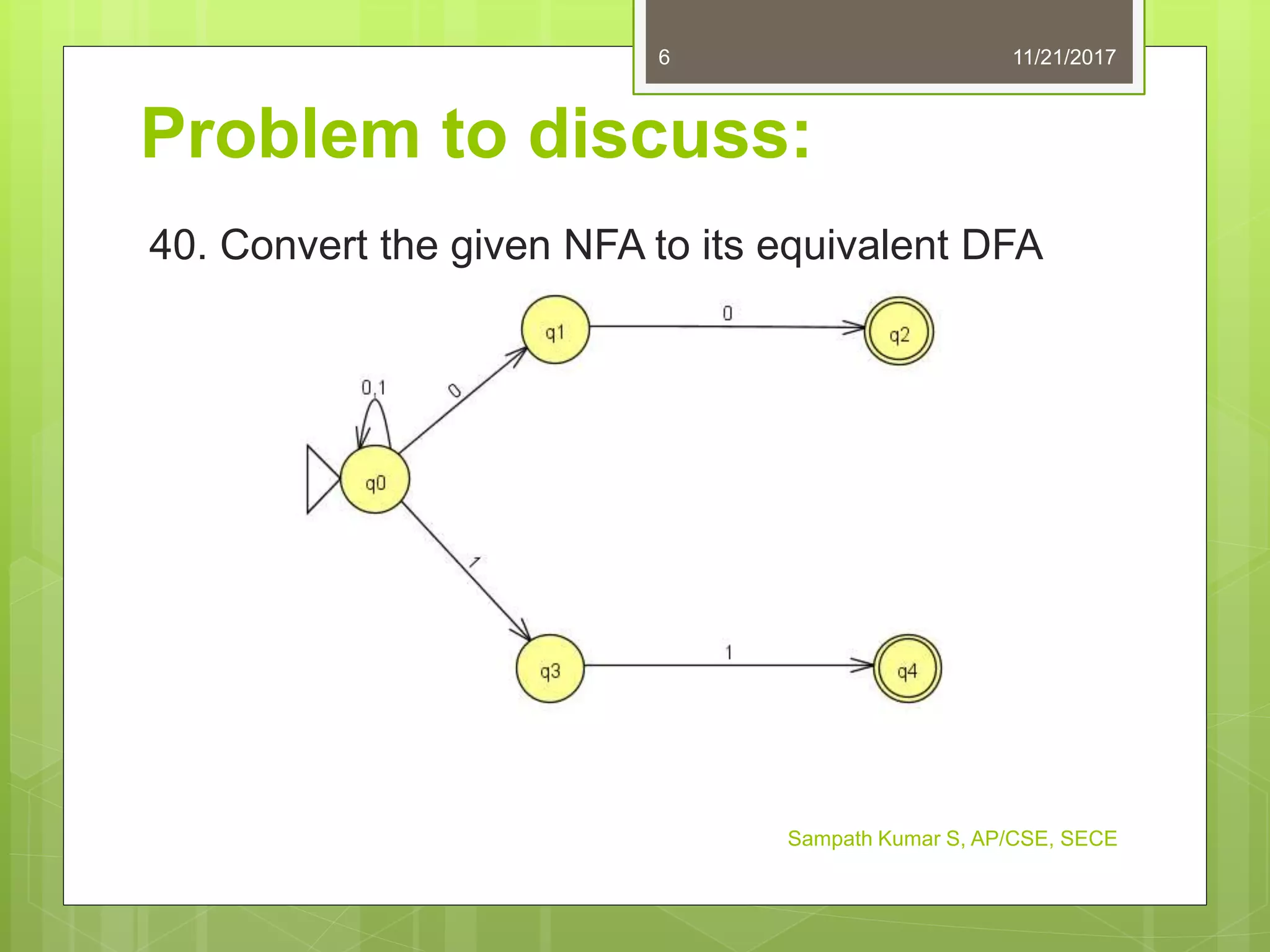
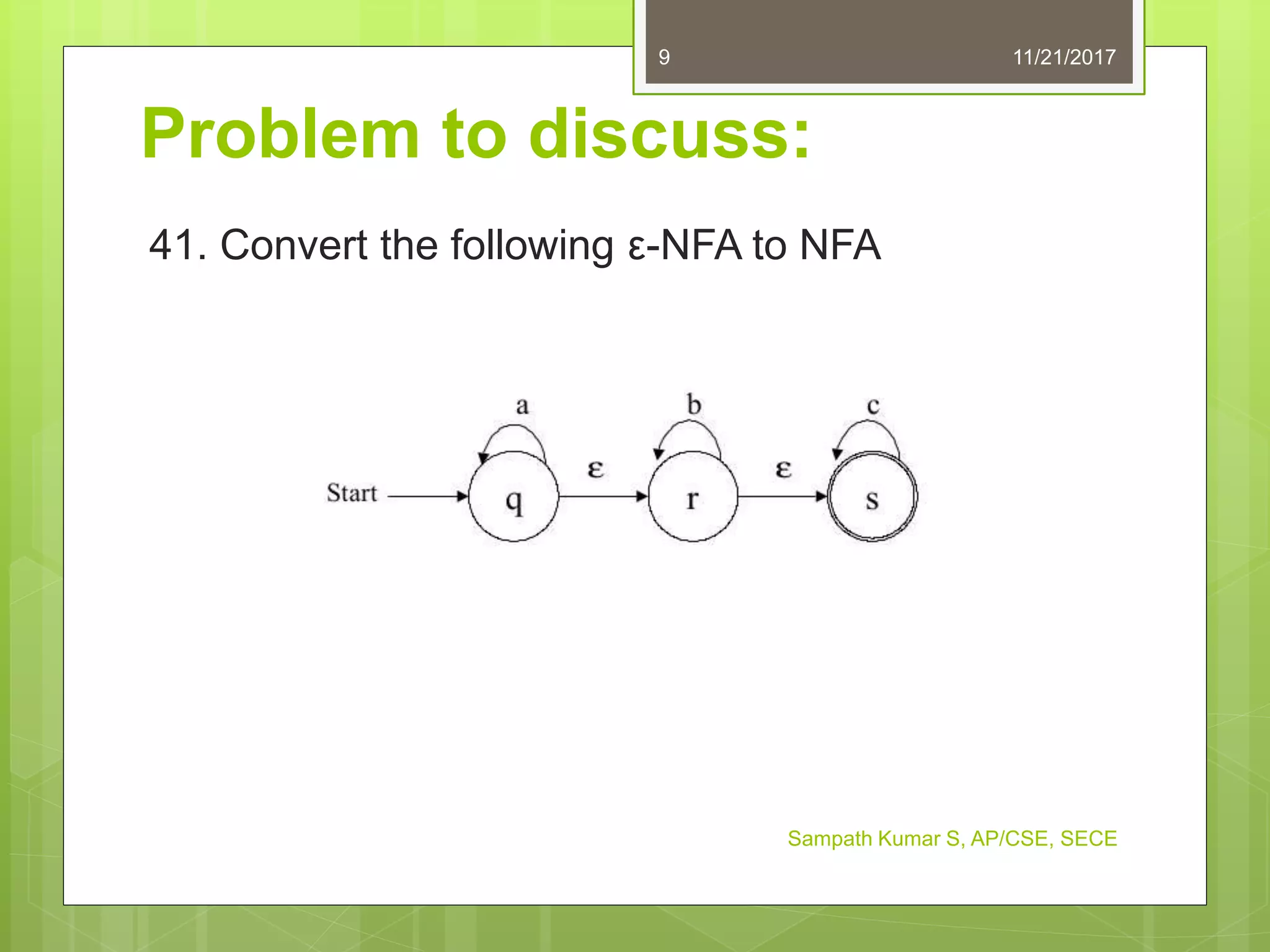
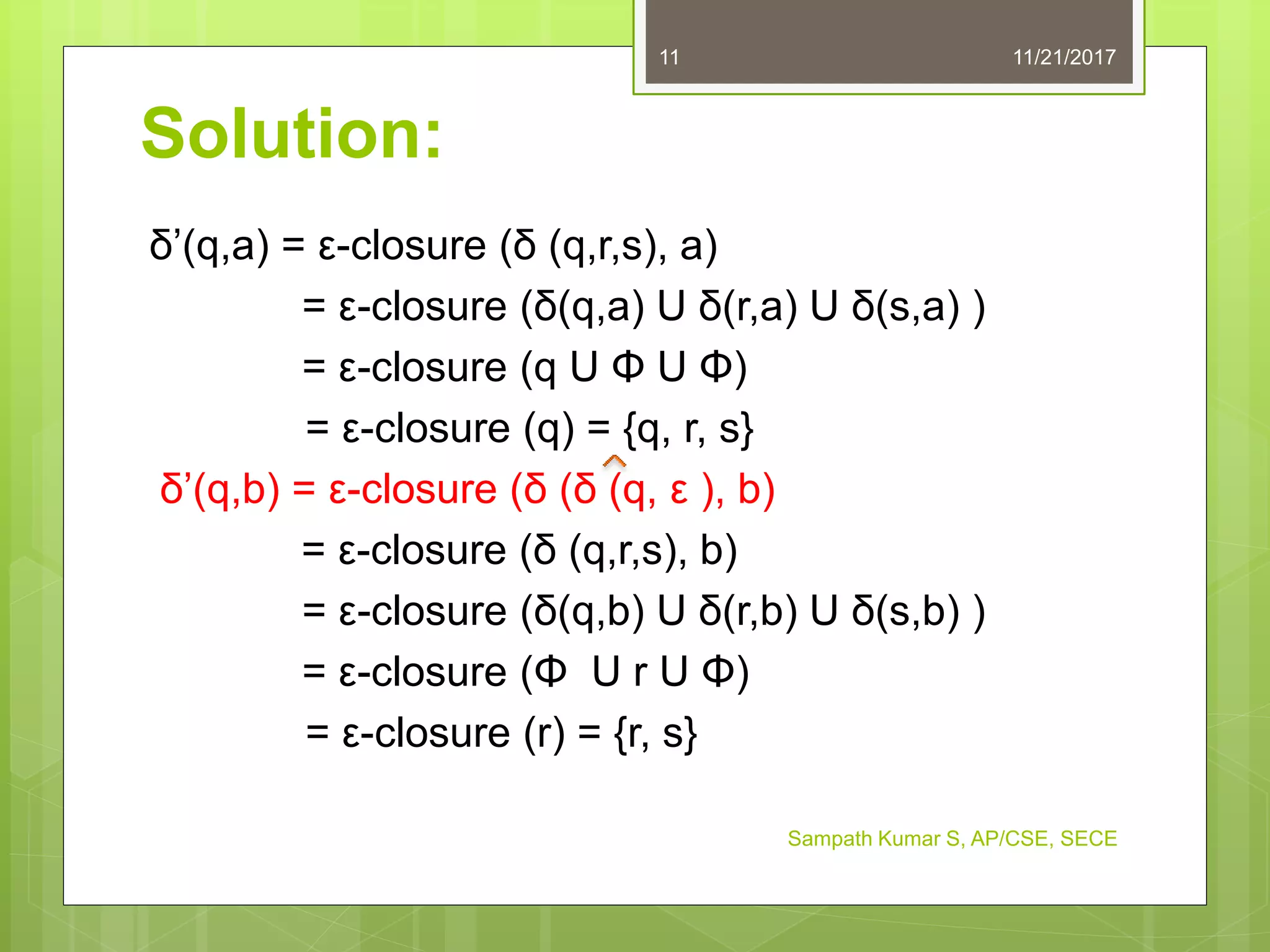
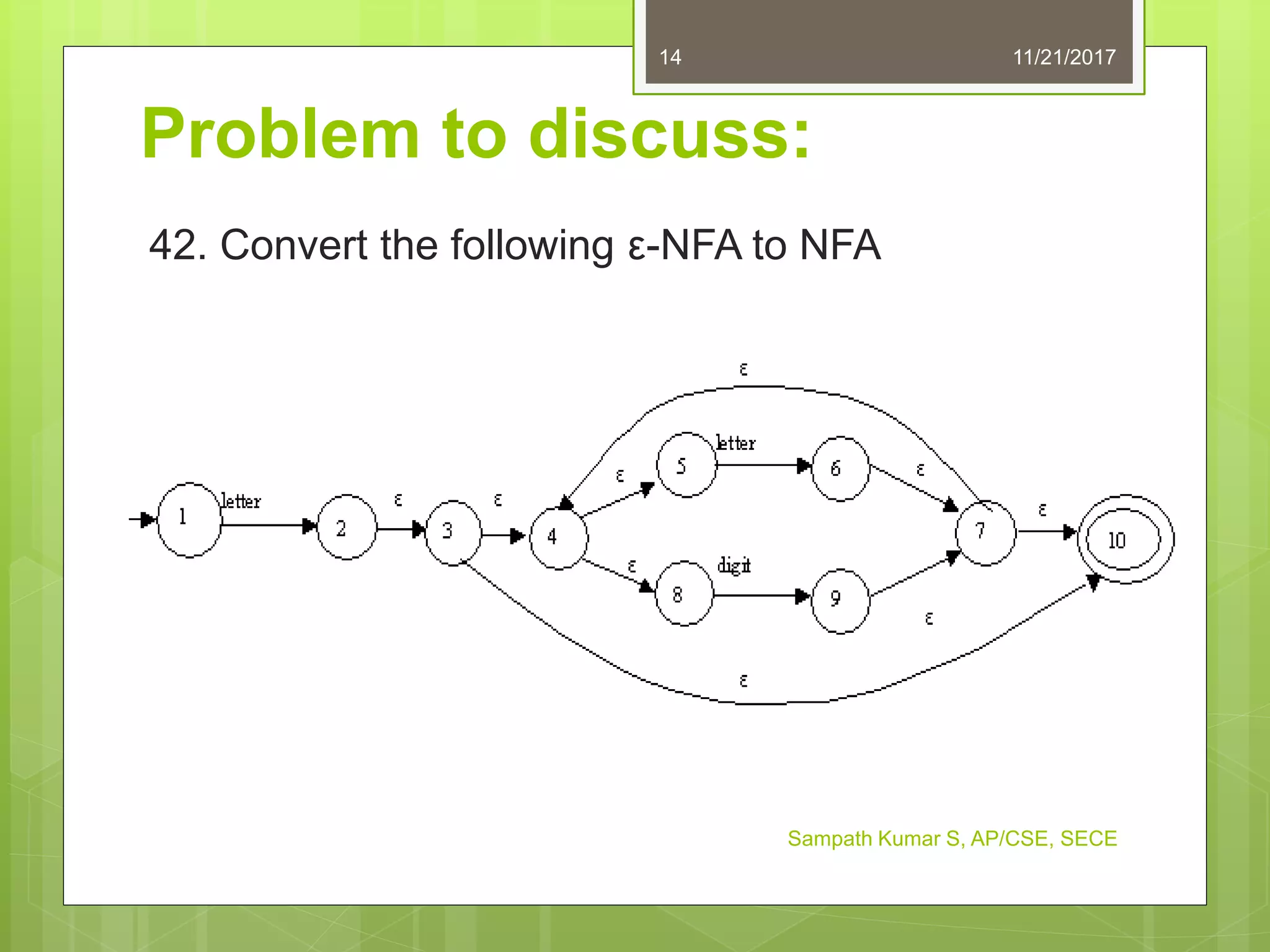
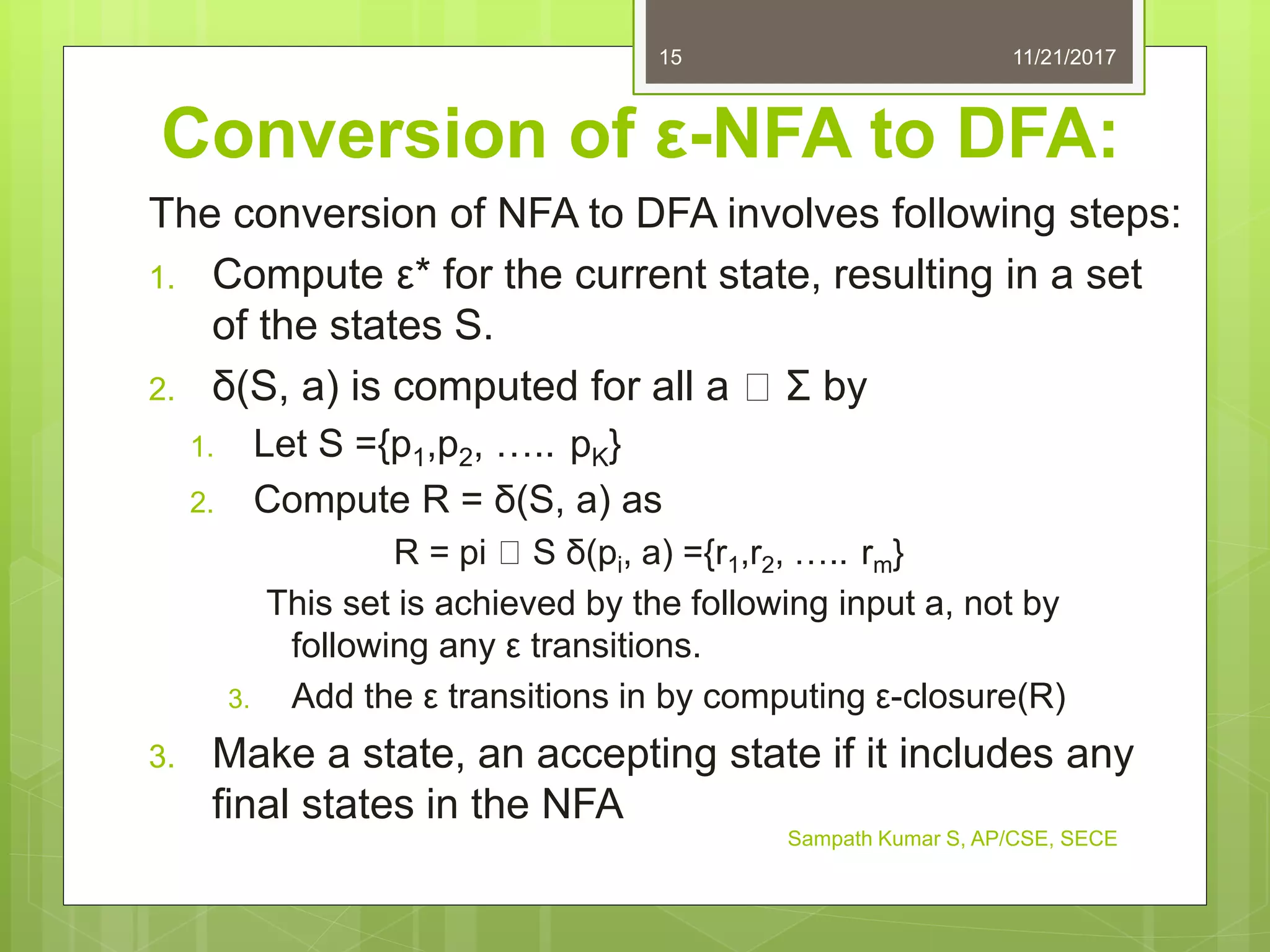
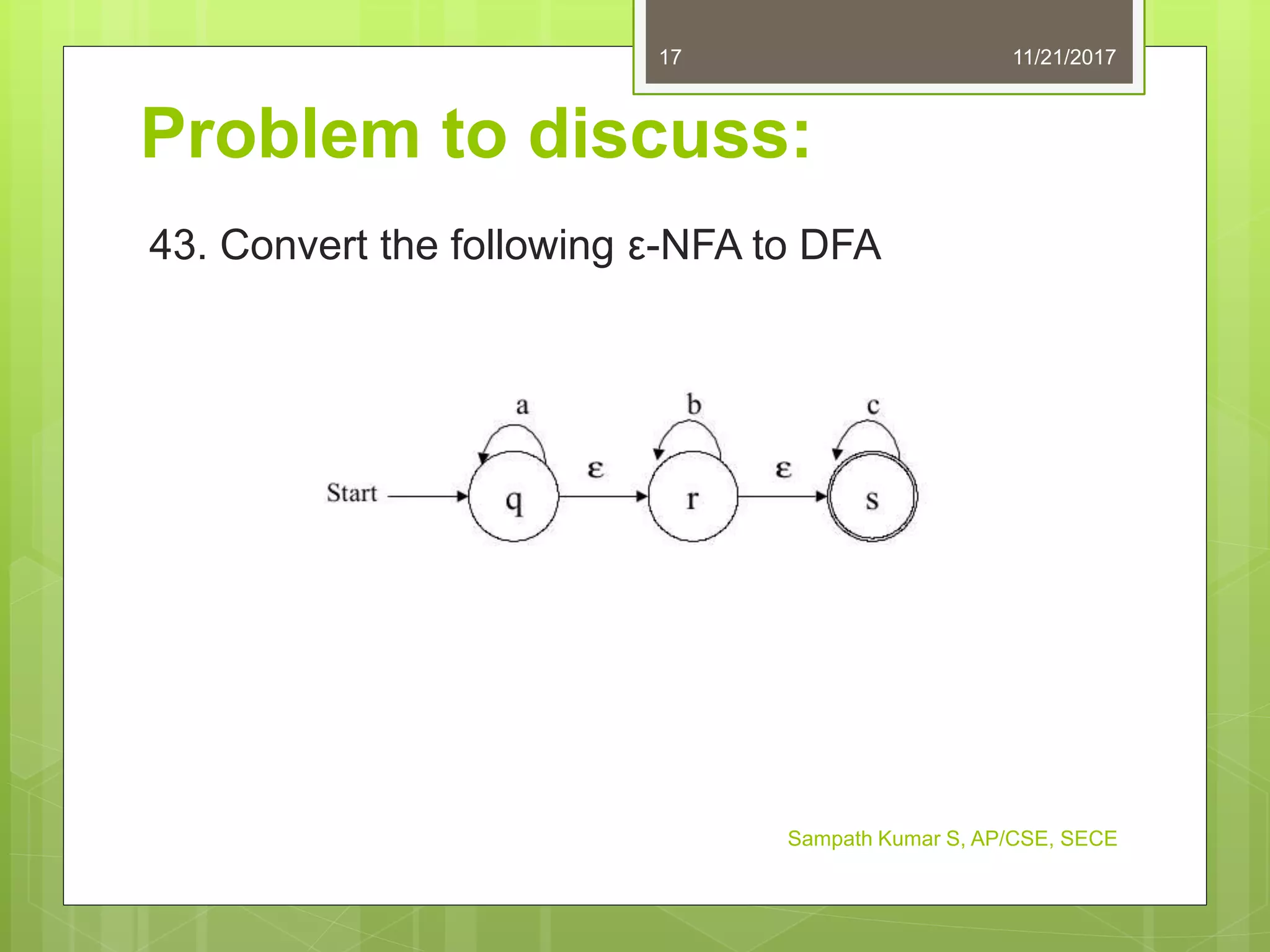
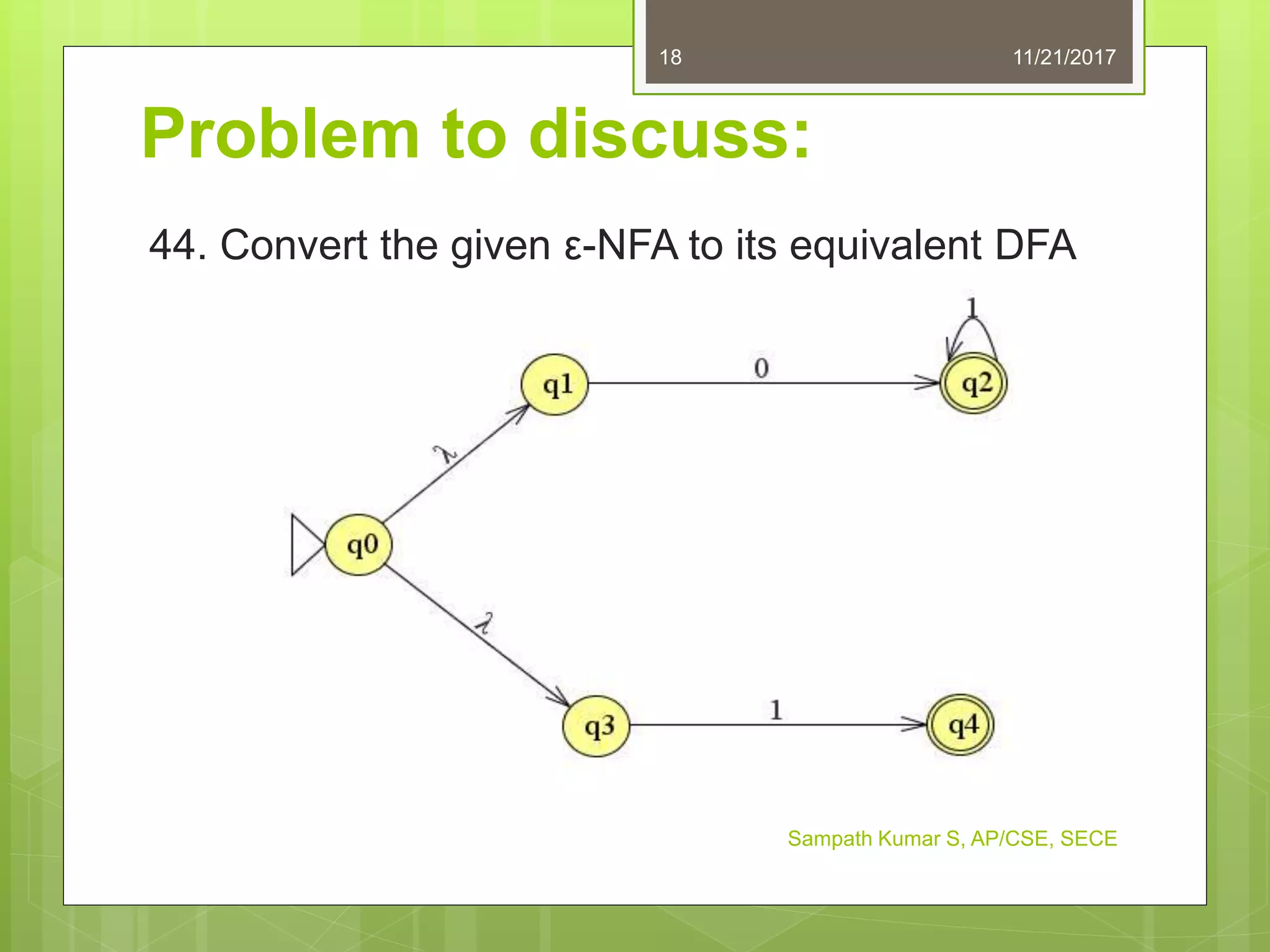
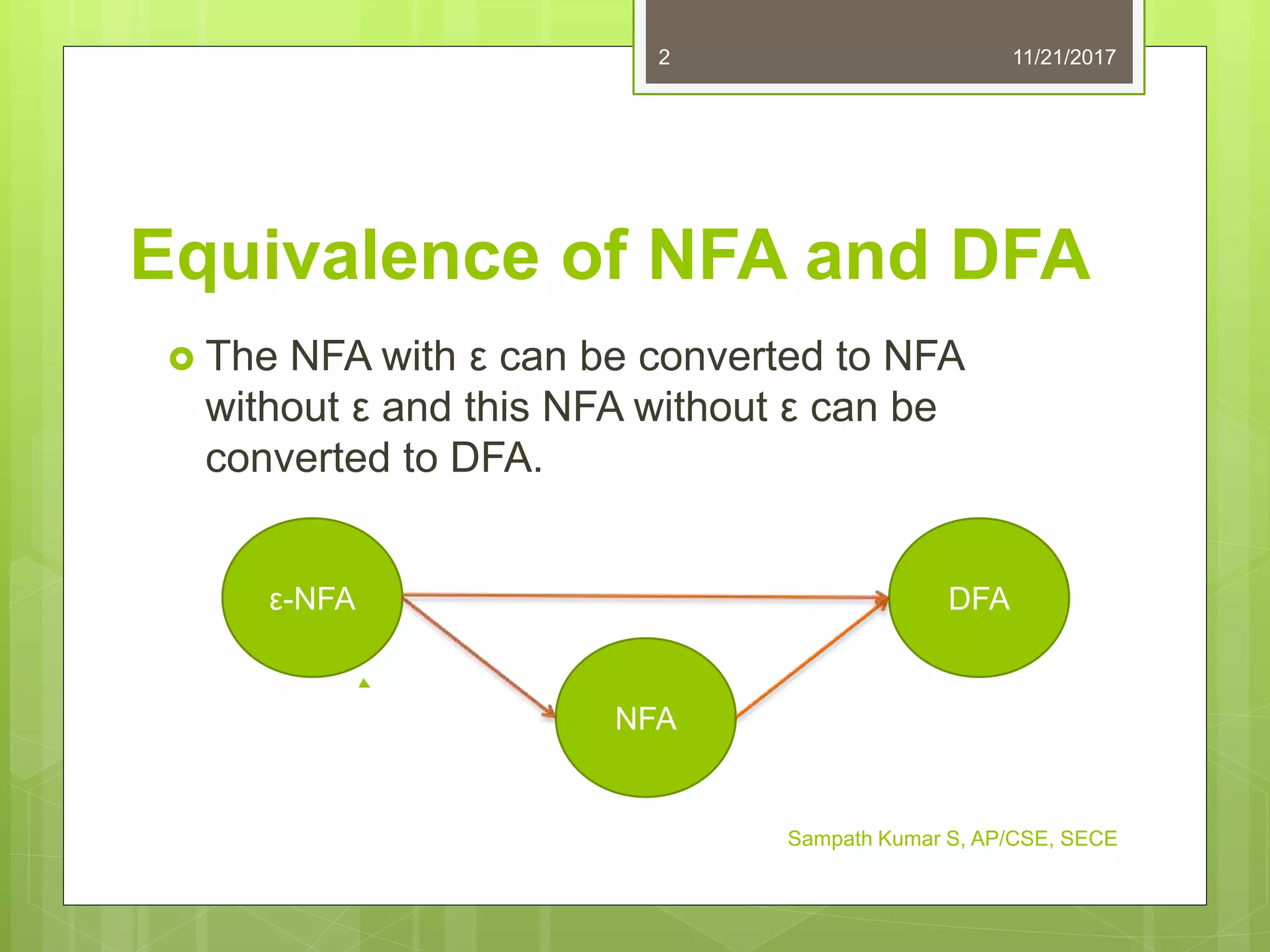
The document discusses the conversion of non-deterministic finite automata (NFA) to deterministic finite automata (DFA). It states that an NFA with epsilon transitions can first be converted to an NFA without epsilon transitions, which can then be converted to an equivalent DFA. The conversion of NFA to DFA involves constructing a DFA with up to 2^n states for an n-state NFA, with the same input alphabet and transition and acceptance functions based on the NFA. Examples are provided of converting epsilon NFAs to NFAs without epsilon transitions and NFAs to equivalent DFAs.

![Conversion of NFA to DFA:
The conversion of NFA to DFA involves following steps:
1. QD = 2Q
N. If NFA has n states. DFA at most have 2n
states.
2. Σn=ΣD
3. [q0]=[q0]
4. FD = A set of all the states of QD that contains at
least one of the final states of FN .
5. δD((q1,q2,q3),a)=
δn(q1,a) u δn(q2,a) u δn(q3,a) ={p1,p2,p3}
Add state [P1,P2,P3] to QD if it is not there
11/21/20173
Sampath Kumar S, AP/CSE, SECE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-171121153452/75/1-7-eqivalence-of-nfa-and-dfa-3-2048.jpg)