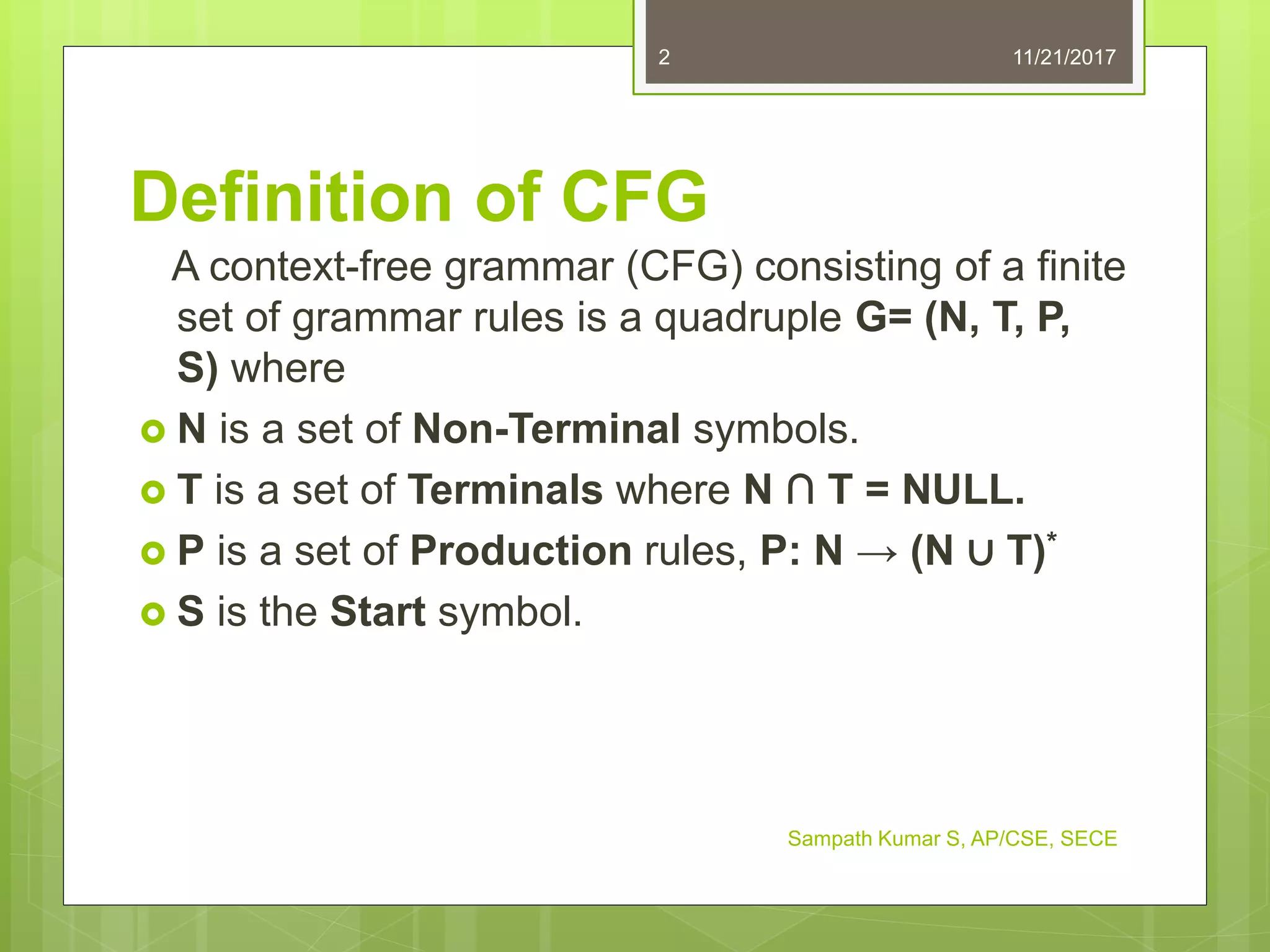
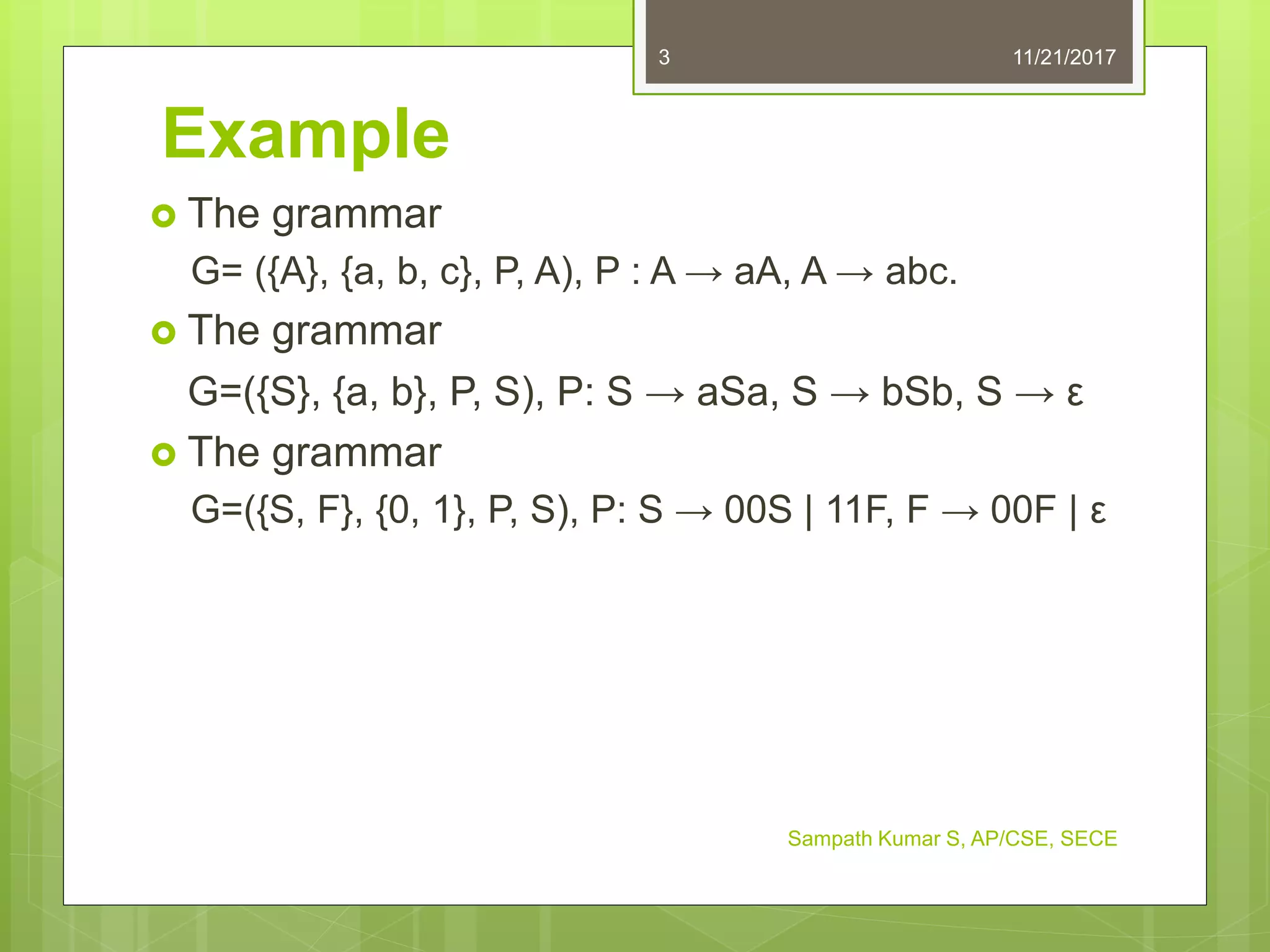
The document discusses context-free grammars and languages. It defines a context-free grammar as a quadruple consisting of non-terminal symbols, terminals, production rules, and a start symbol. Examples of context-free grammars are provided. Problems involving constructing context-free grammars for various languages are listed, along with their answers.