This document discusses different distributed computing system (DCS) models:
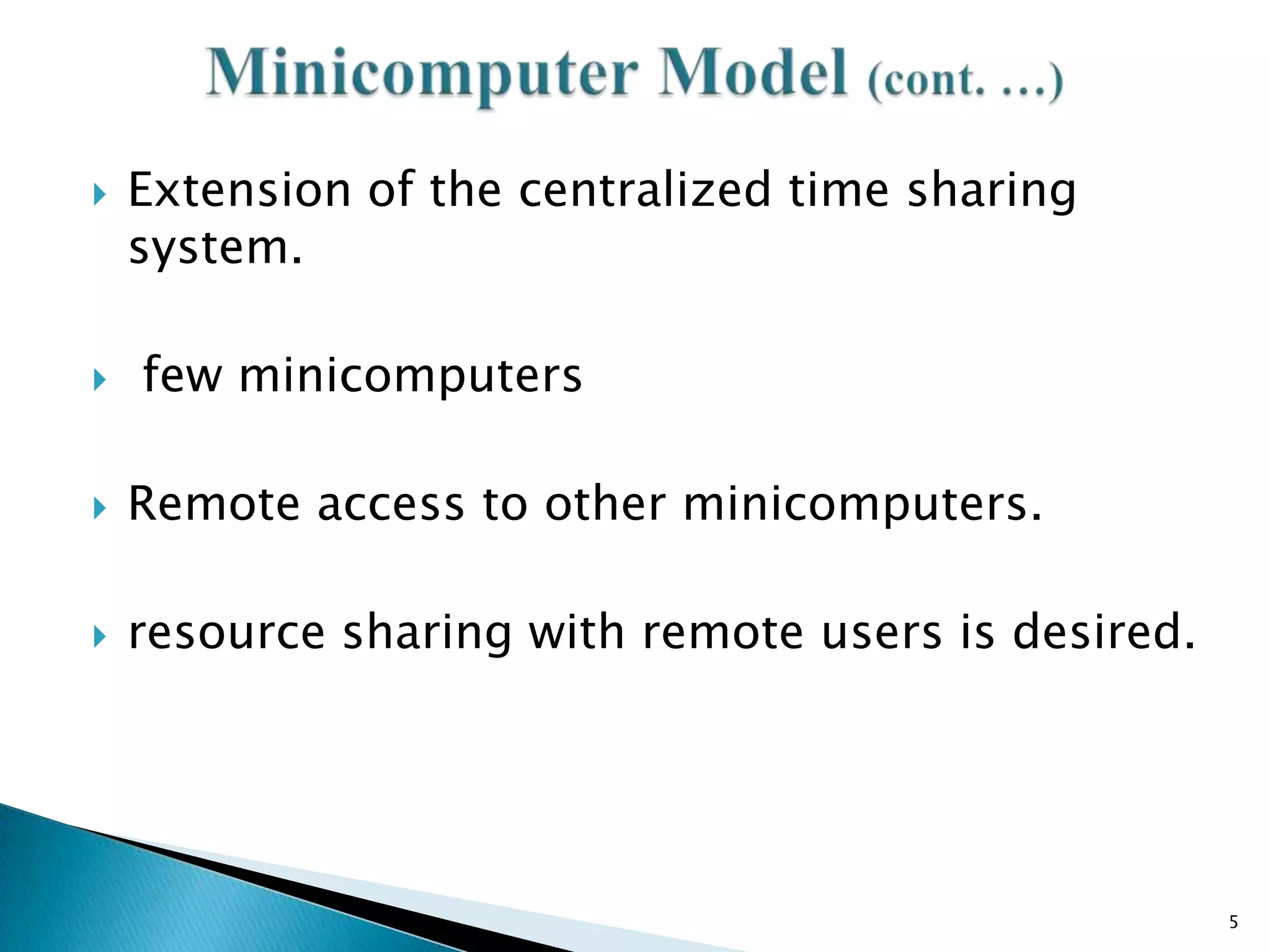
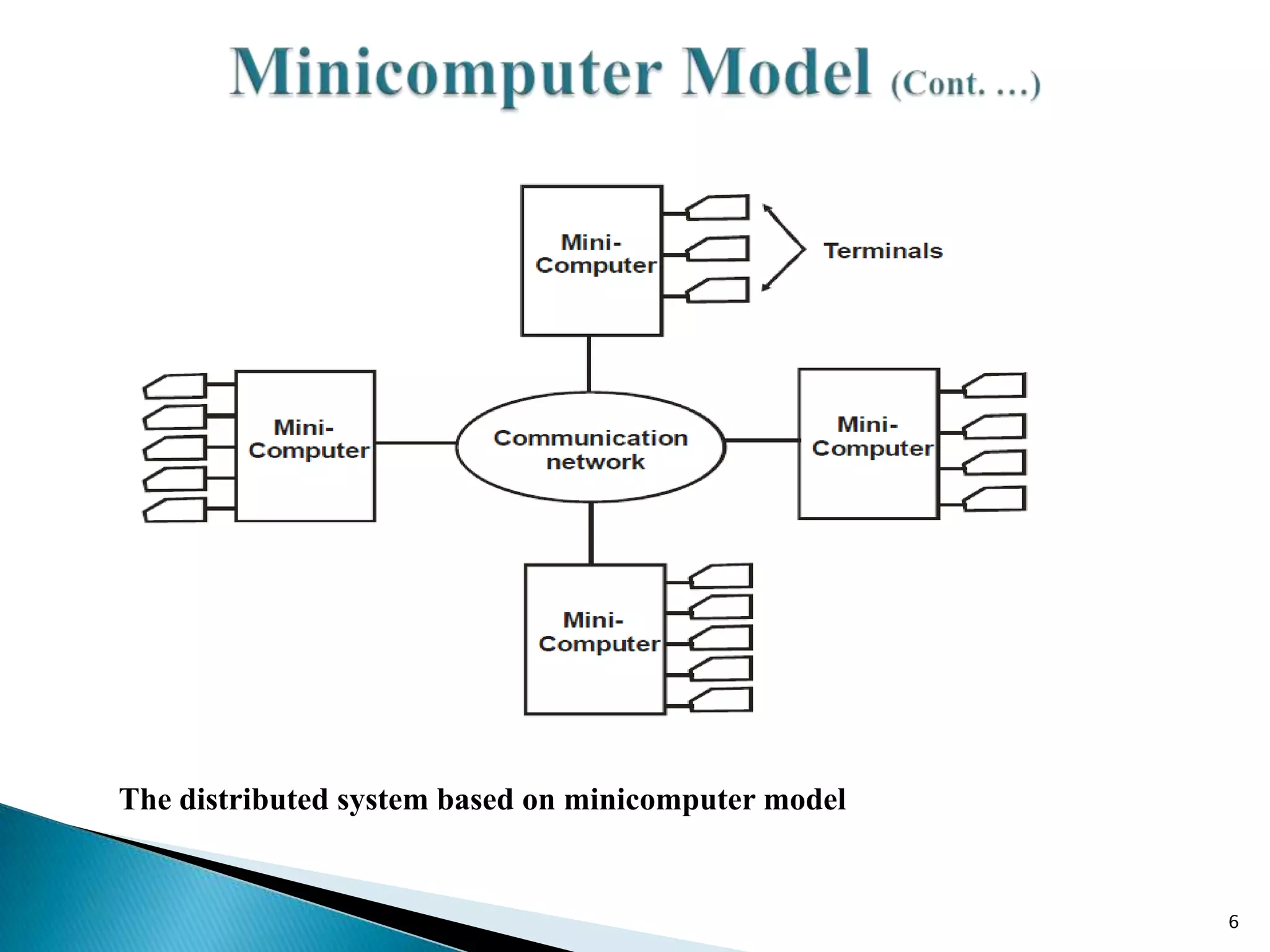
1. The minicomputer model consists of a few minicomputers with remote access allowing resource sharing.
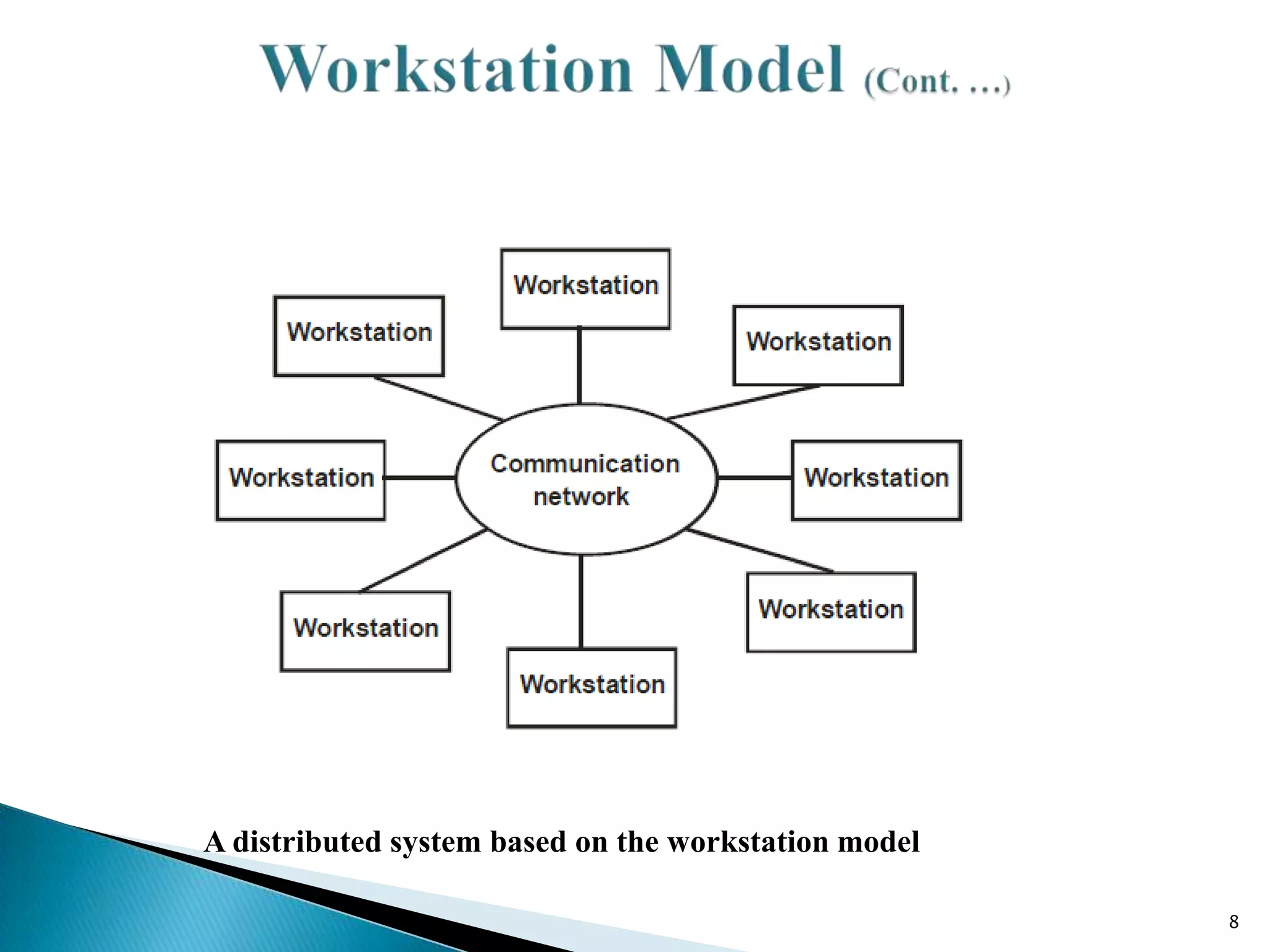
2. The workstation model consists of independent workstations scattered throughout a building where users log onto their home workstation.
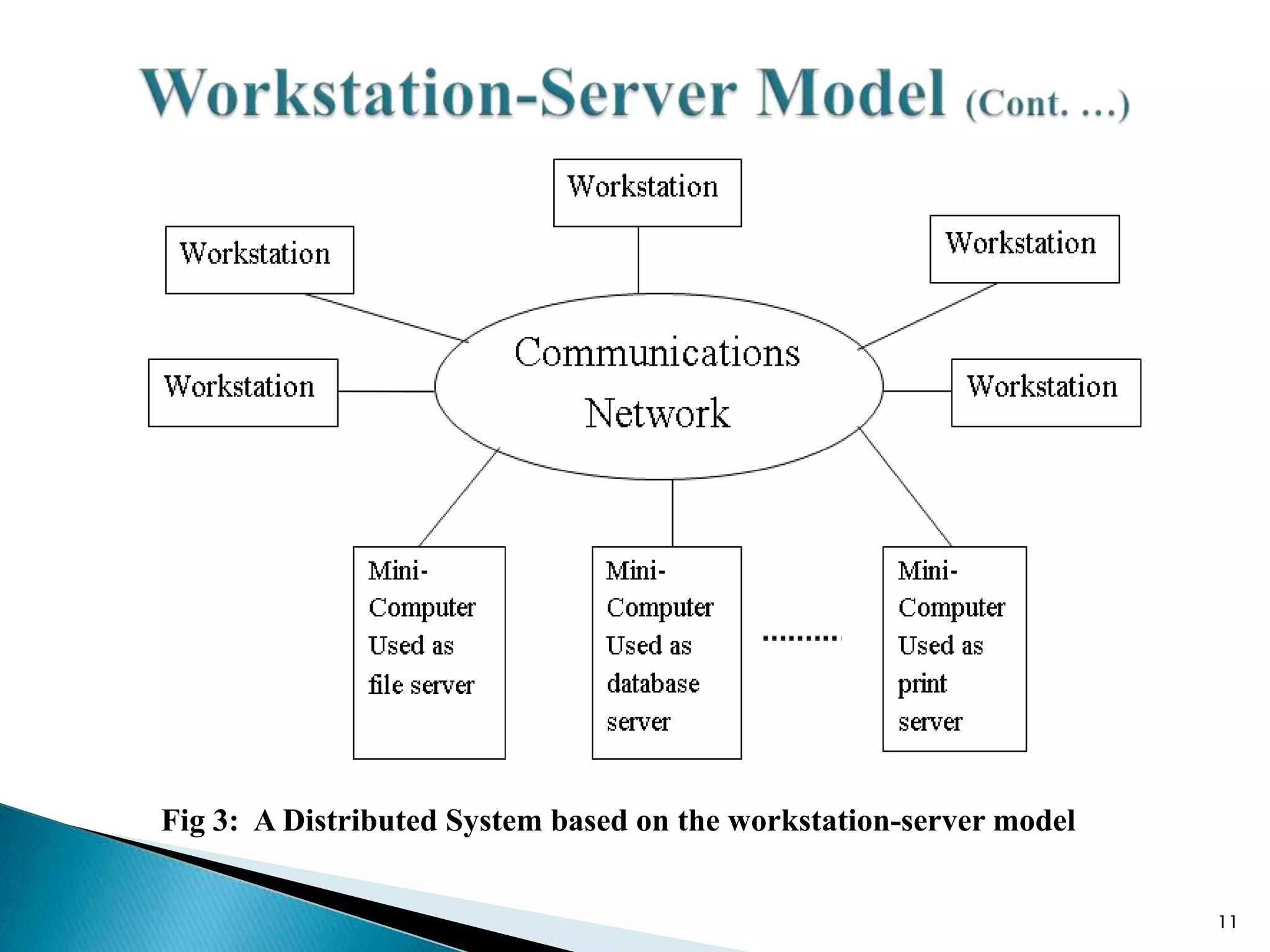
3. The workstation-server model includes minicomputers, diskless and diskful workstations, and centralized services like databases and printing.
It provides an overview of the key characteristics and advantages of different DCS models.