Catalysts increase the rate of chemical reactions without being consumed. They work by lowering the activation energy of reactions. Catalytic reactions can be either homogeneous, where reactants and catalysts are in the same phase, or heterogeneous, where they are in different phases. Catalytic reactions are also classified based on their effect - positive catalysts increase reaction rate, negative catalysts decrease it, auto-catalytic reactions use a reaction product as the catalyst, and induced catalytic reactions cause a reaction not otherwise possible.


![The chemical phenomenon which is influenced by a substance or a set of substances
that remains unchanged at the end of the phenomenon is called catalytic reaction. The
influencing substances are called catalyst.
For example - In Fischer-Tropsch synthesis Ru is used as a catalyst.
(2n+1)H2 + n CO + [Ru] = CnH(2n+2) + H2O + [Ru]
A catalyst increases the forward reaction as well as backward reaction and reduces the
activation energy of a reaction corresponding to the non catalytic reaction of the
reactants.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hrmchaudhari-180920174951/85/Catalytic-Reaction-3-320.jpg)
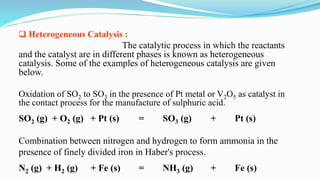
![A)According to the phase of reactant, product and
catalyst
Catalytic reaction are of 2 types which are as follow :
Homogeneous Catalysis:
The reactants and catalyst remain in the same
phase.
For example – In the decomposition of excited NO3* , NO2 is used as
catalyst.
NO3 *(g) + [NO2(g) ] = NO*(g) + O2 (g) + [NO2(g)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hrmchaudhari-180920174951/85/Catalytic-Reaction-4-320.jpg)

![ Positive Catalytic Reaction:
The typical catalytic reaction on which
the rate of the reaction is increased.
For example – In the production of Oxygen from Potassium chlorate,
Manganese oxide acts as a positive Catalyst.
KClO3 + [MnO2] = KCl + O2 + [MnO2]
Negative Catalytic Reaction:
The catalytic reaction on which the rate of
the reaction is decreased.
For example – Production of Sodium sulfate from the oxidation of
Sodium sulfide solution is hampered by the presence of ethyl alcohol.
Na2SO3 + O2 + [C2H5OH] = Na2SO4 + [C2H5OH]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hrmchaudhari-180920174951/85/Catalytic-Reaction-7-320.jpg)



