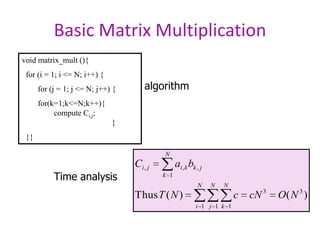
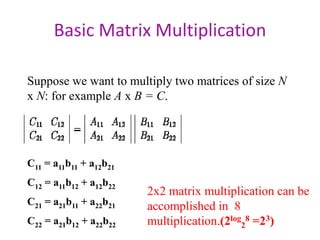
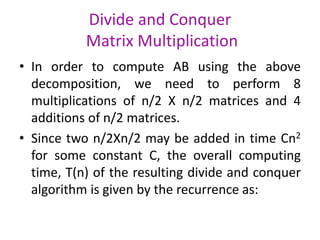
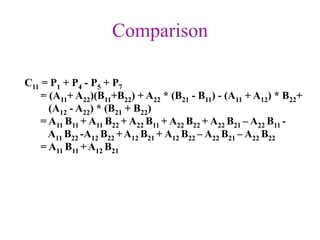
Strassen's algorithm improves on the basic matrix multiplication algorithm which runs in O(N3) time. It achieves this by dividing the matrices into sub-matrices and performing 7 multiplications and 18 additions on the sub-matrices, rather than the 8 multiplications of the basic algorithm. This results in a runtime of O(N2.81) using divide and conquer, providing an asymptotic improvement over the basic O(N3) algorithm.