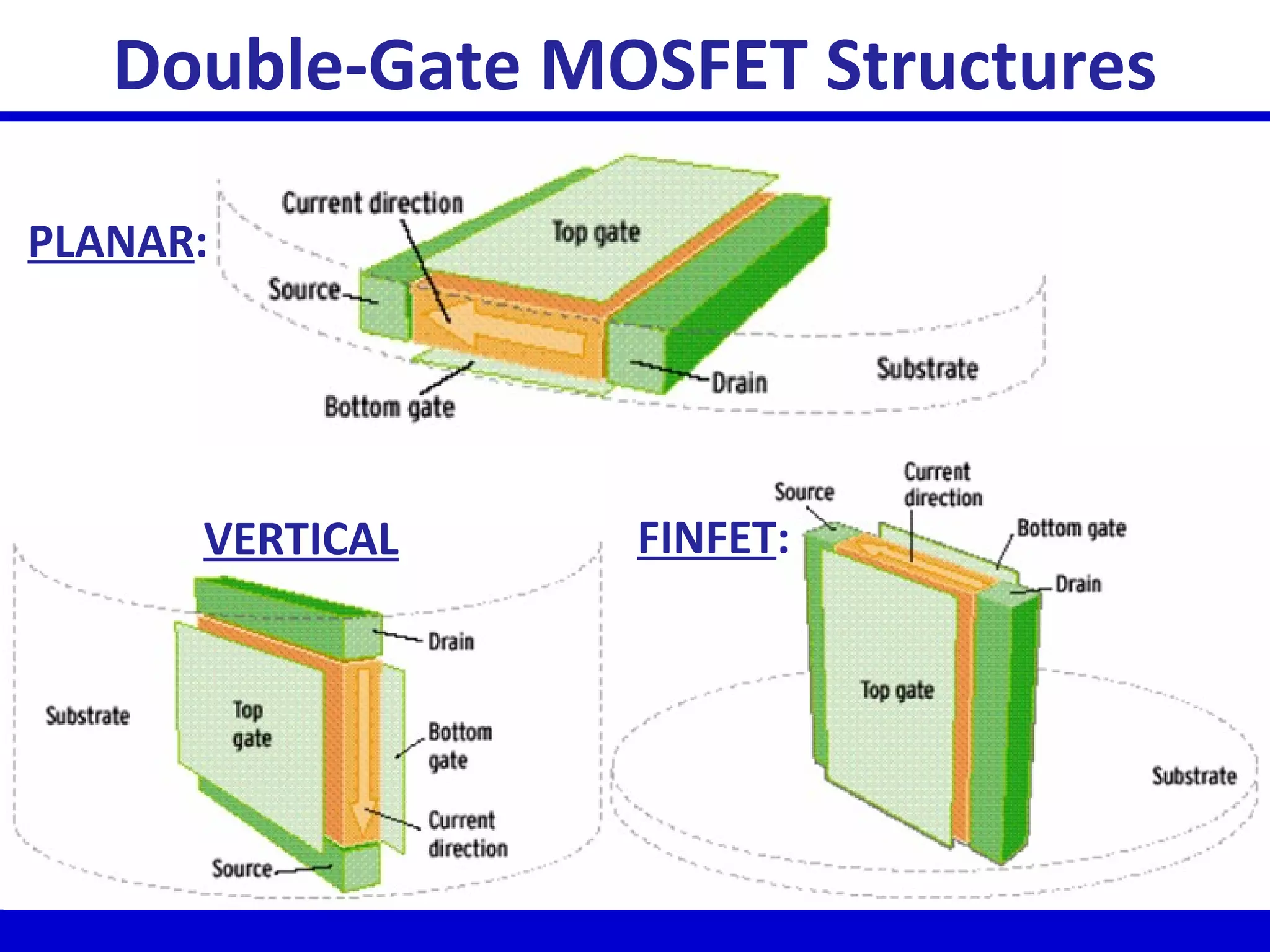
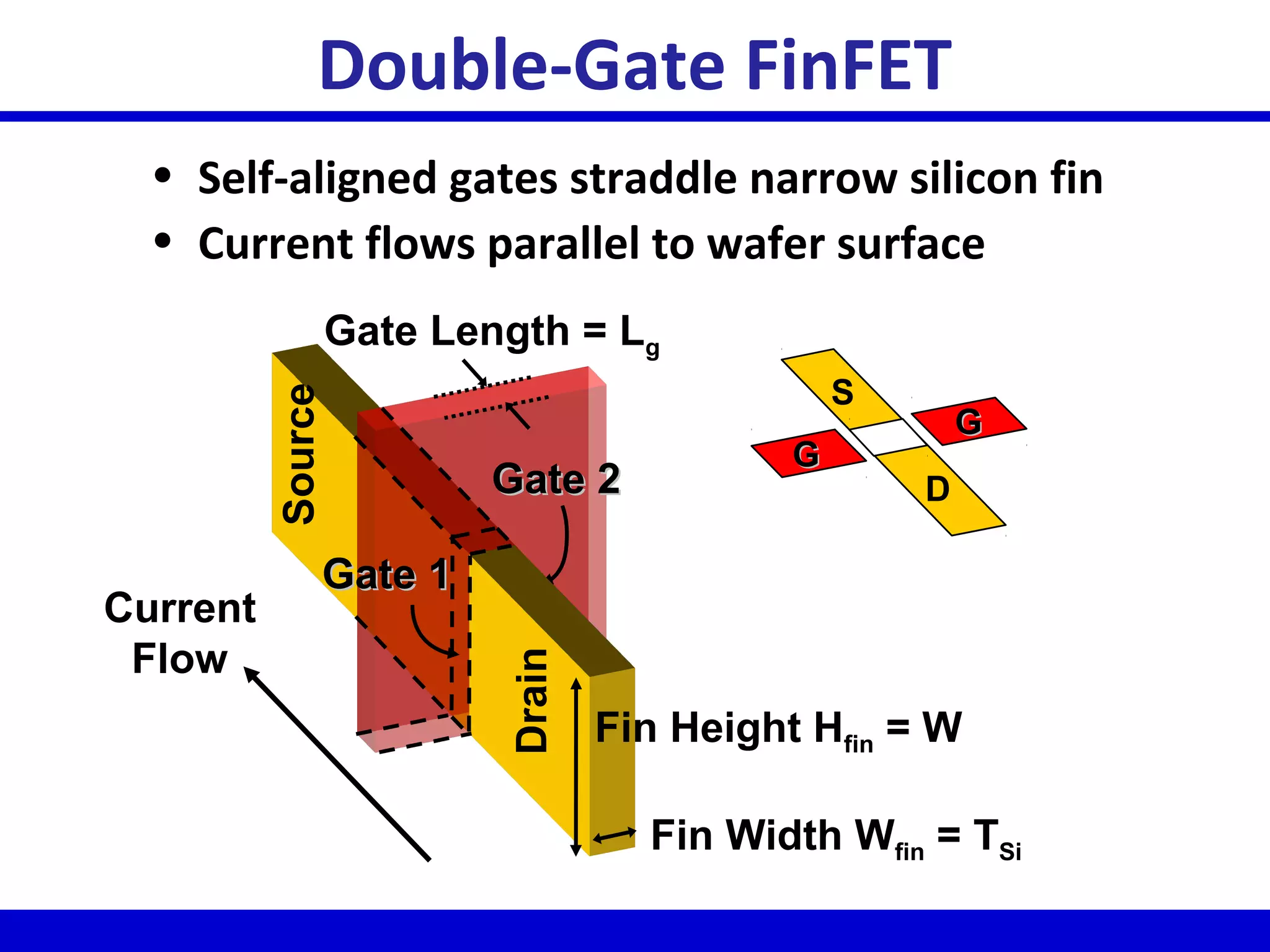
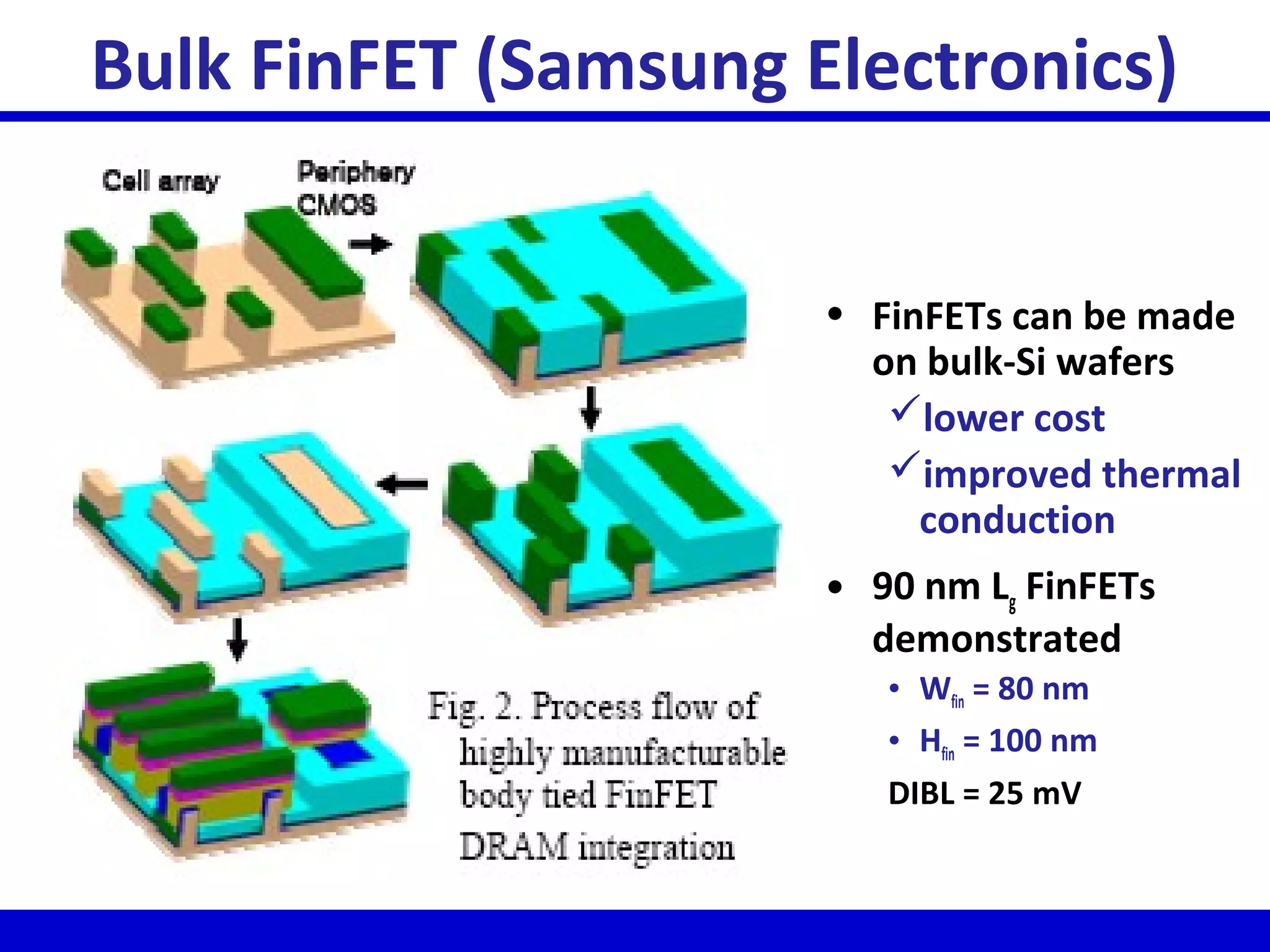
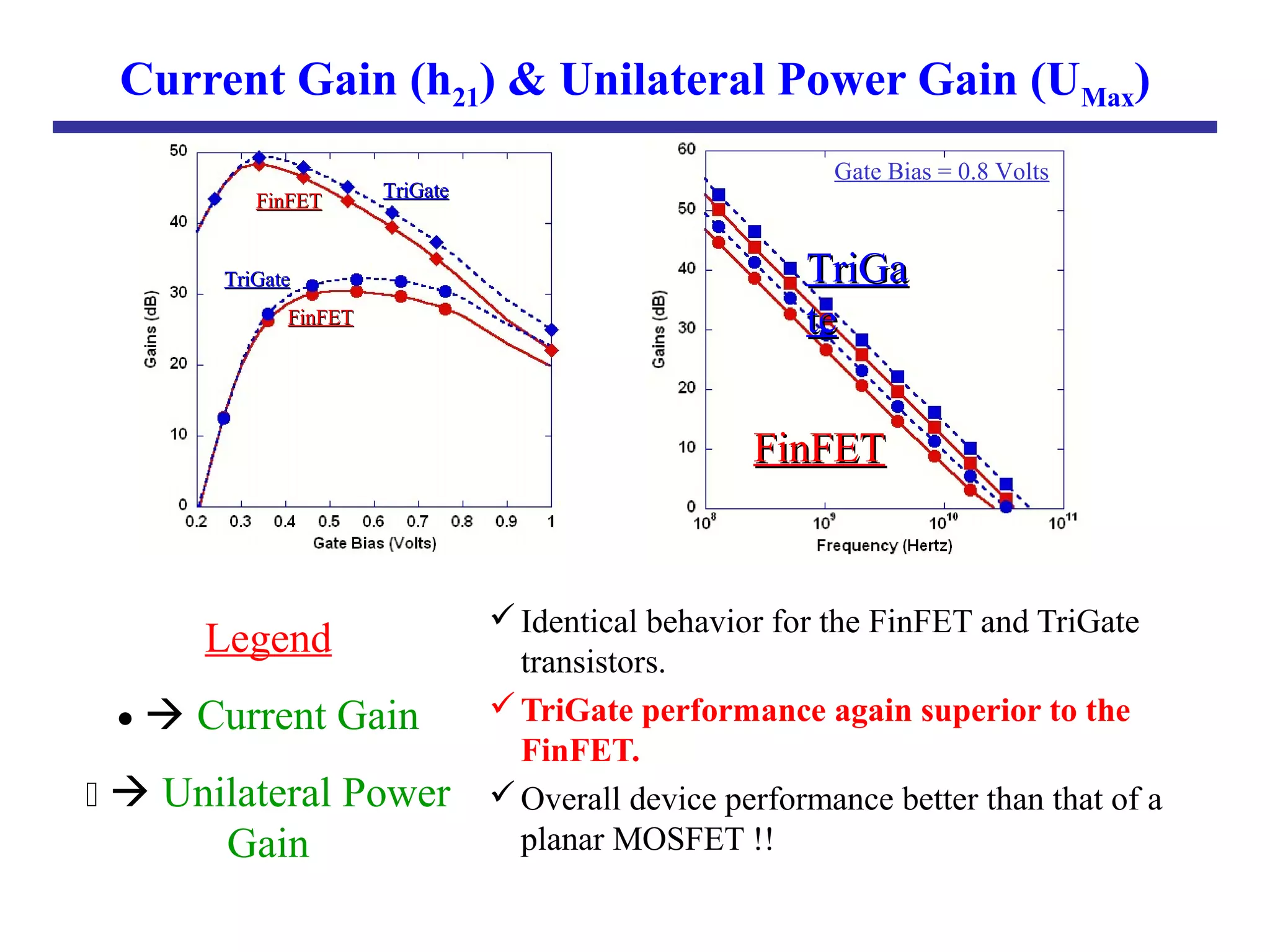
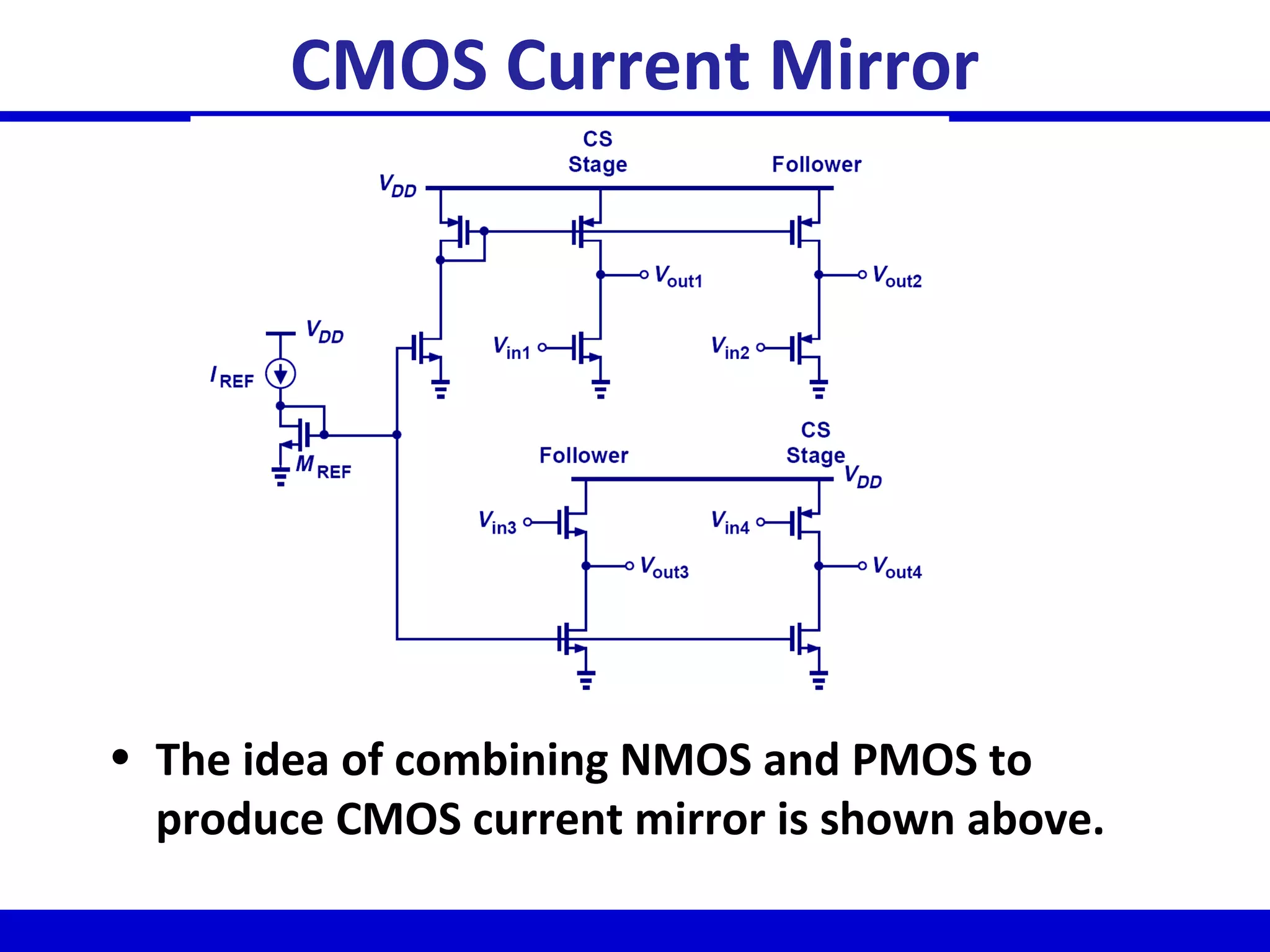
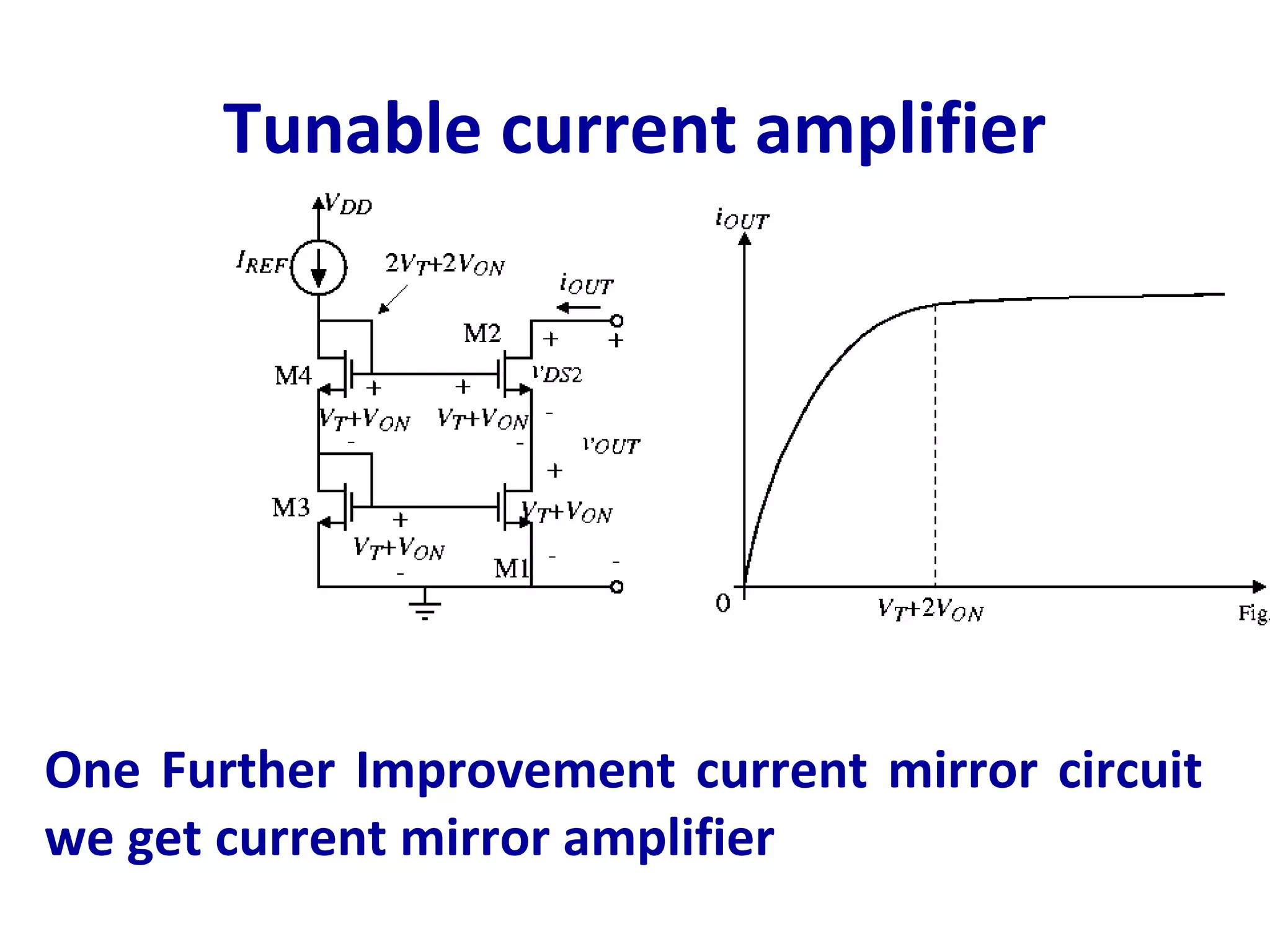
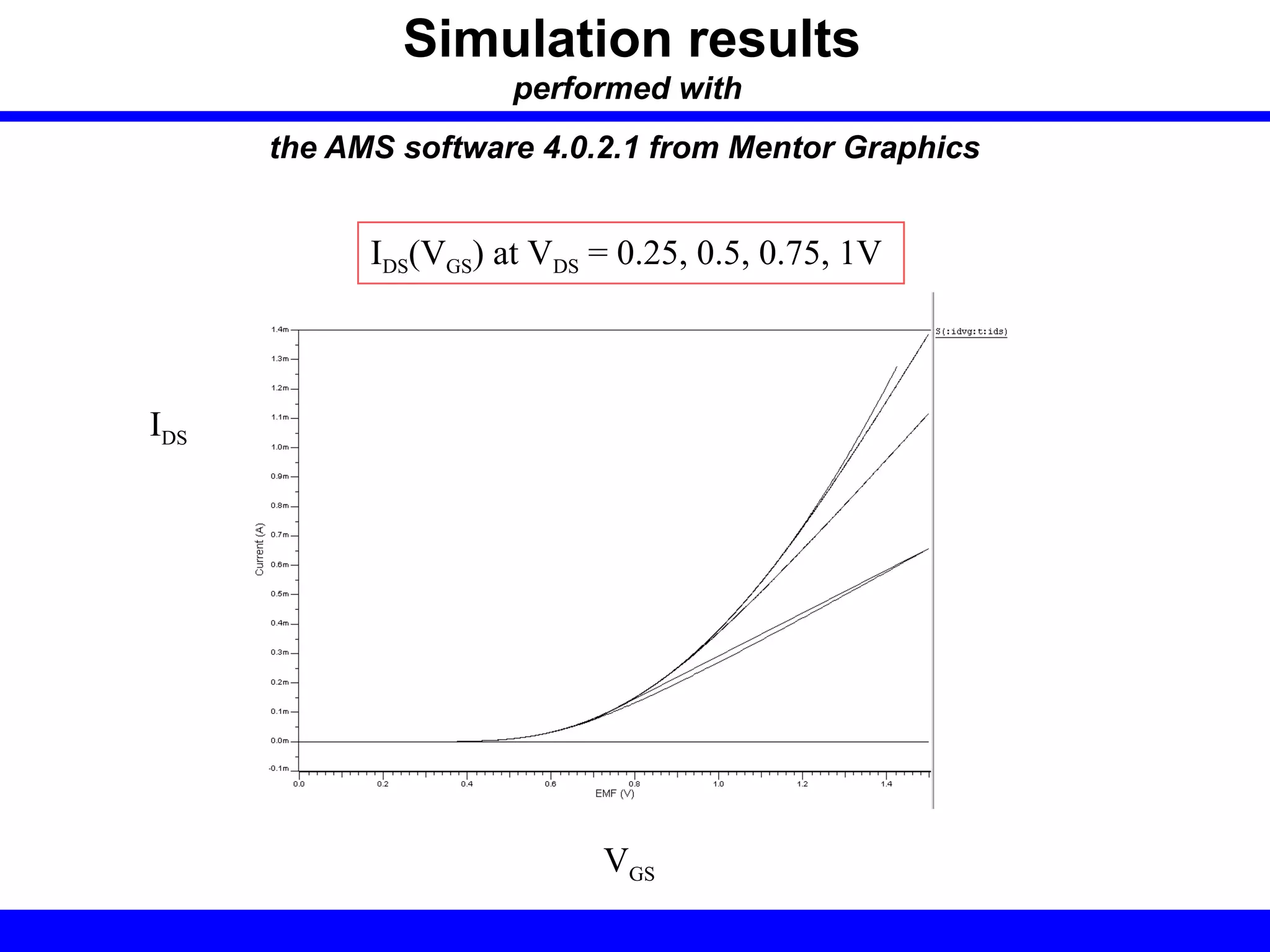
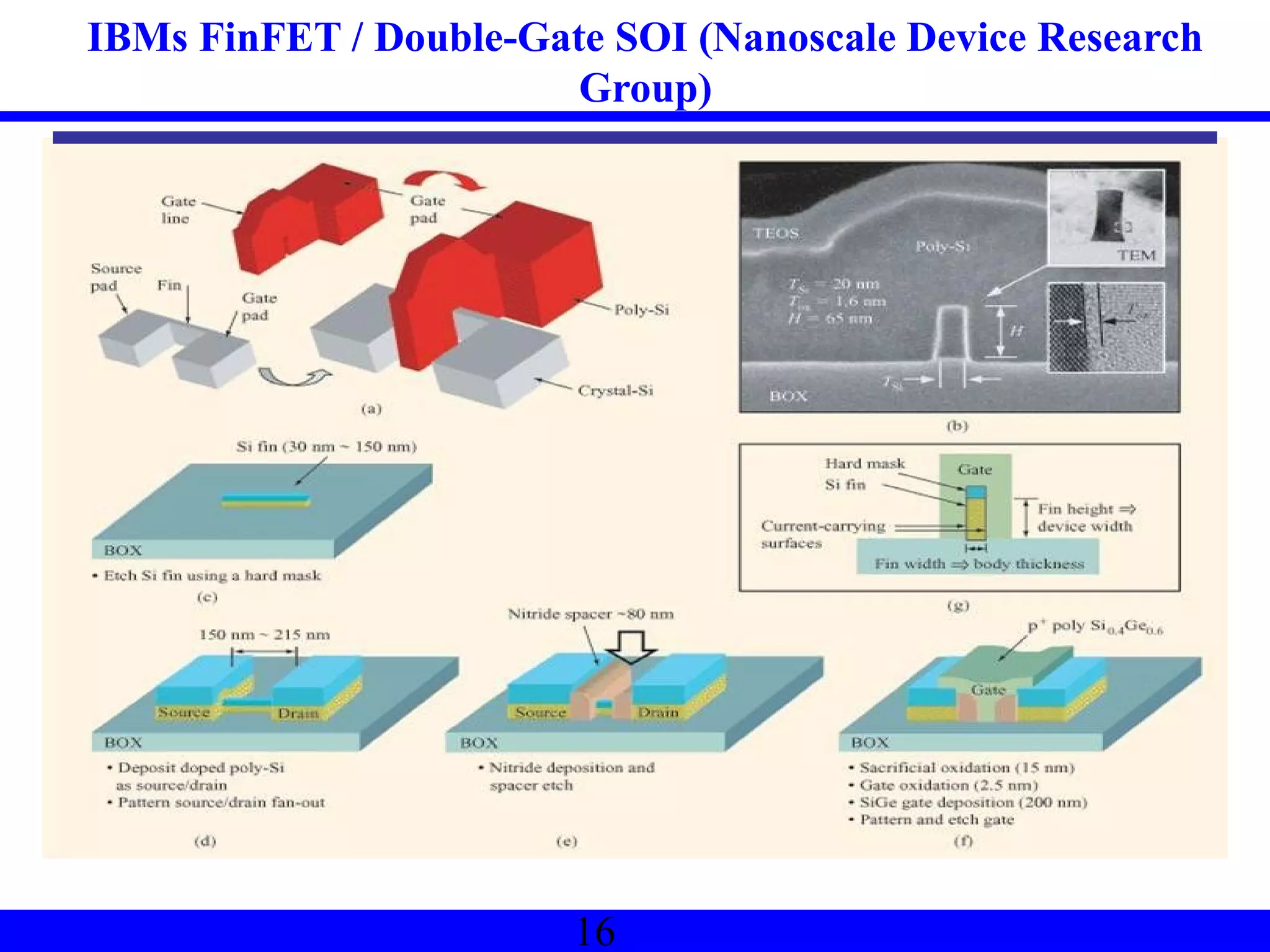
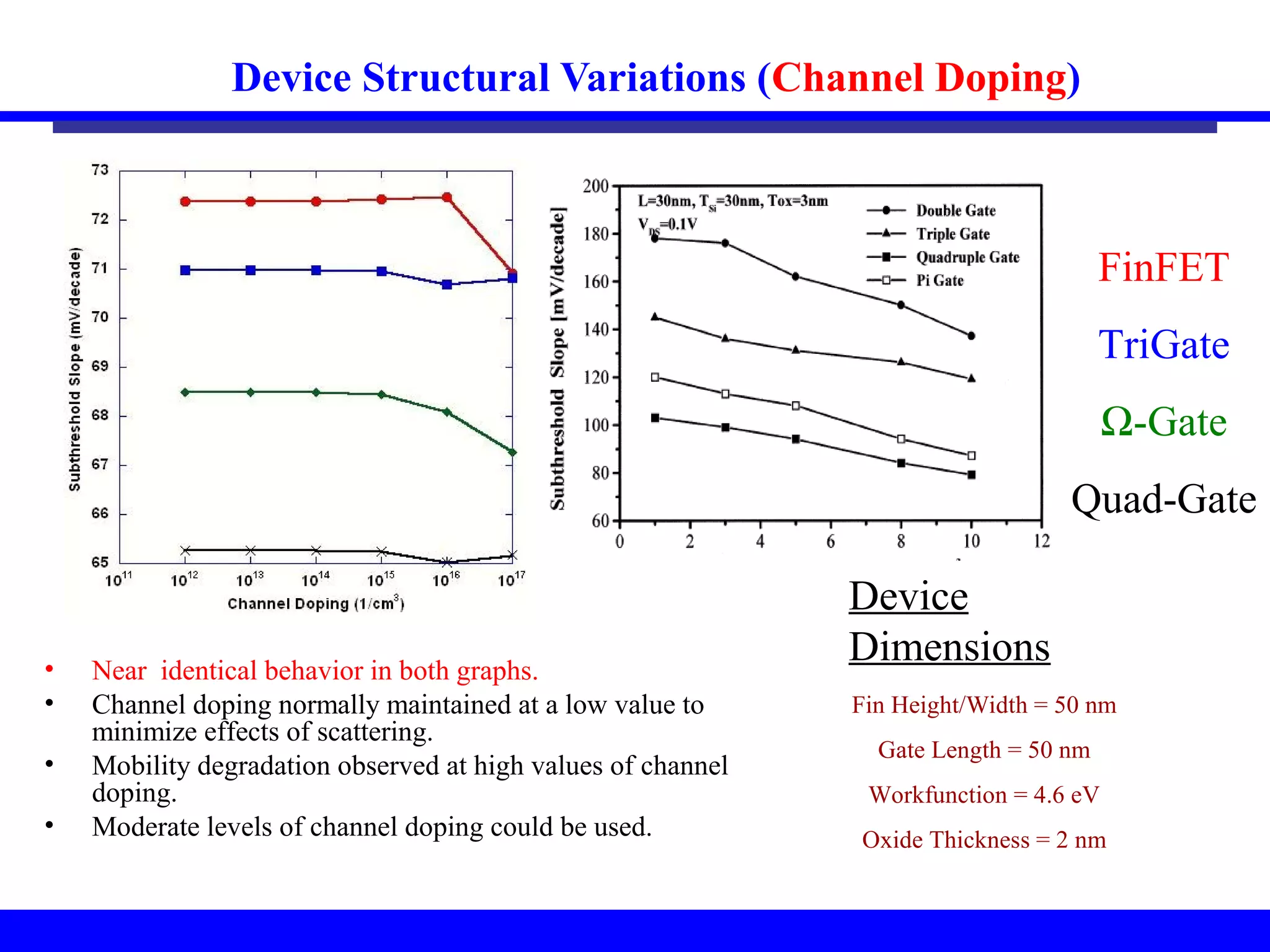
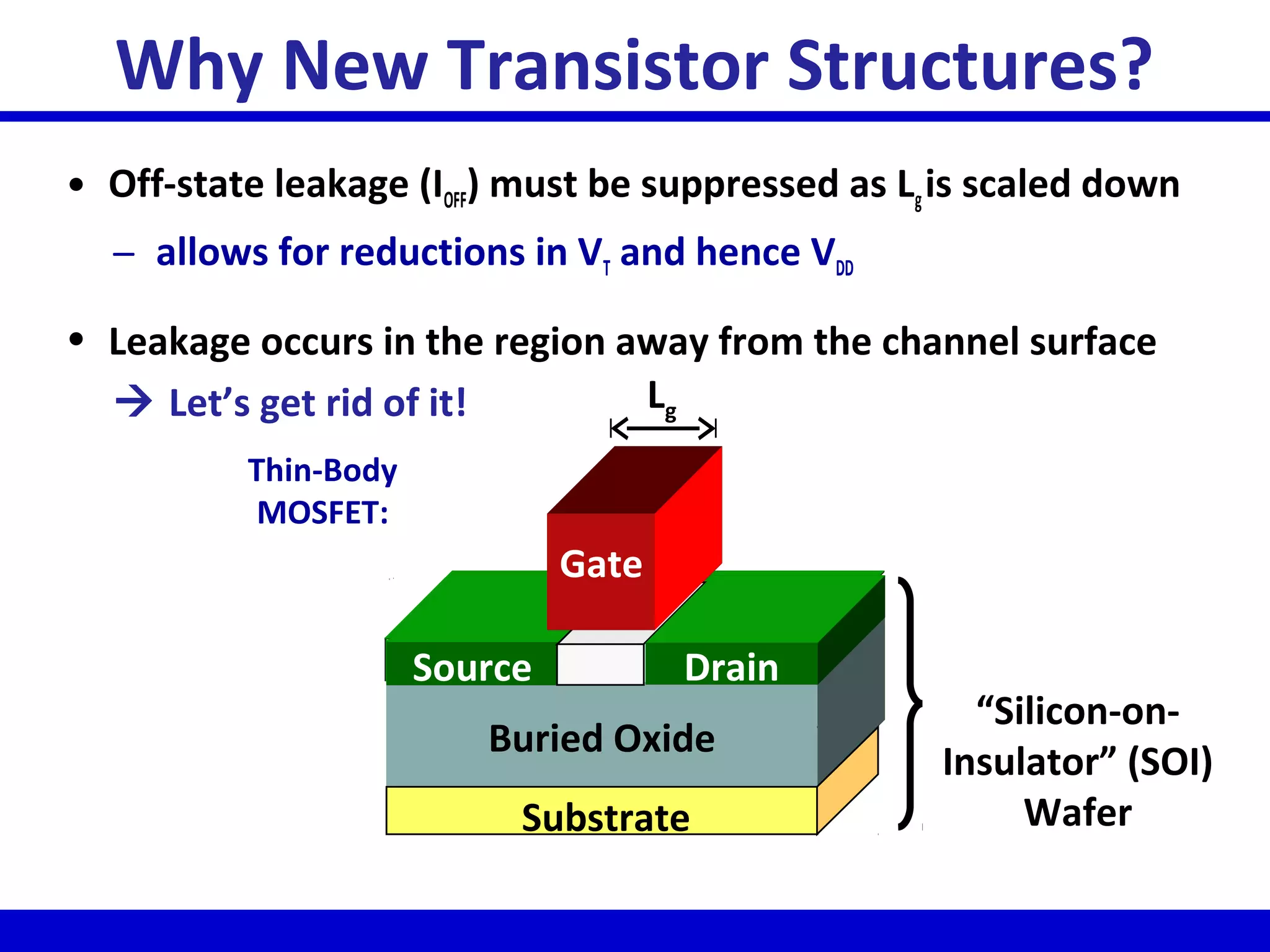
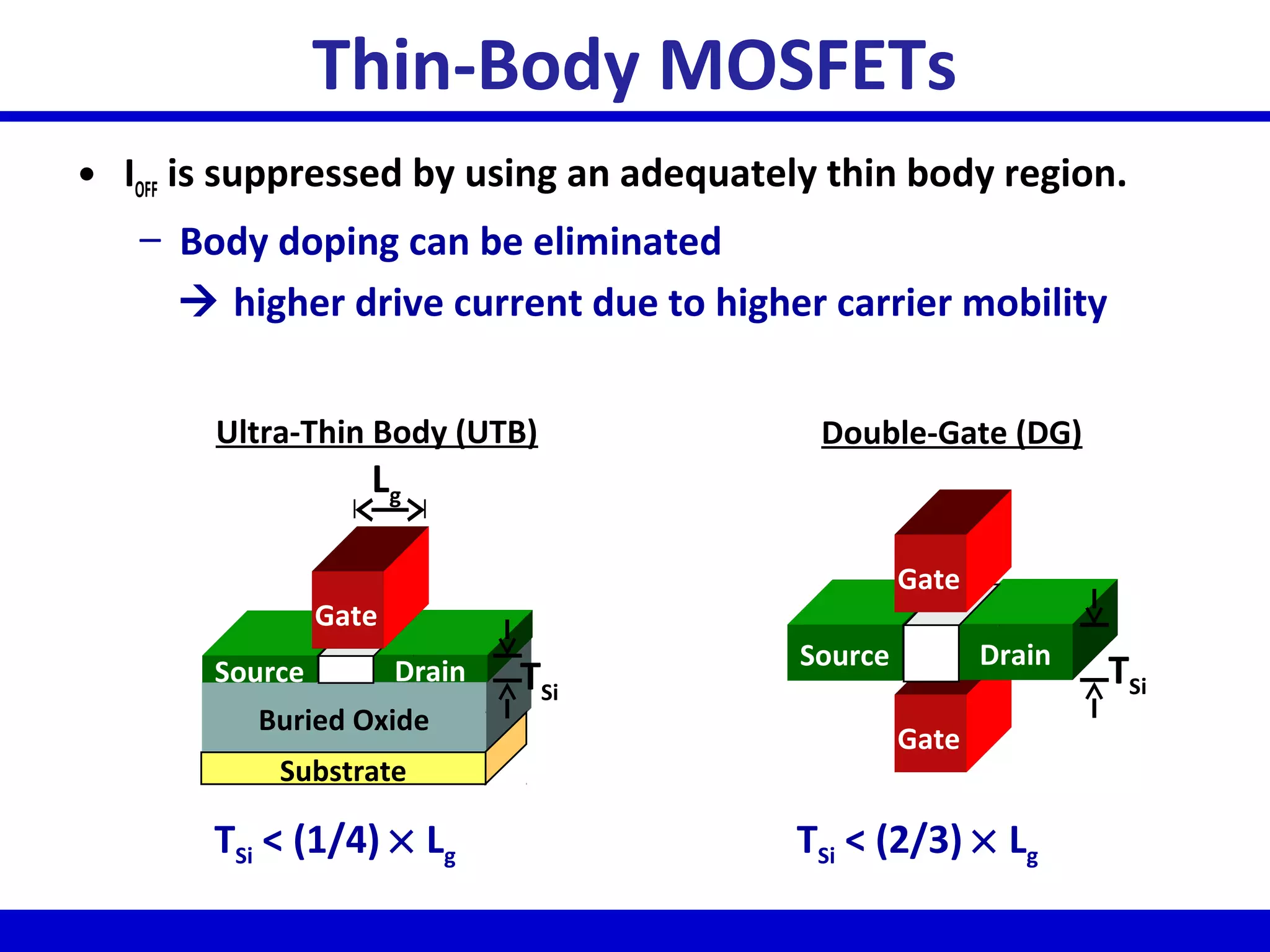
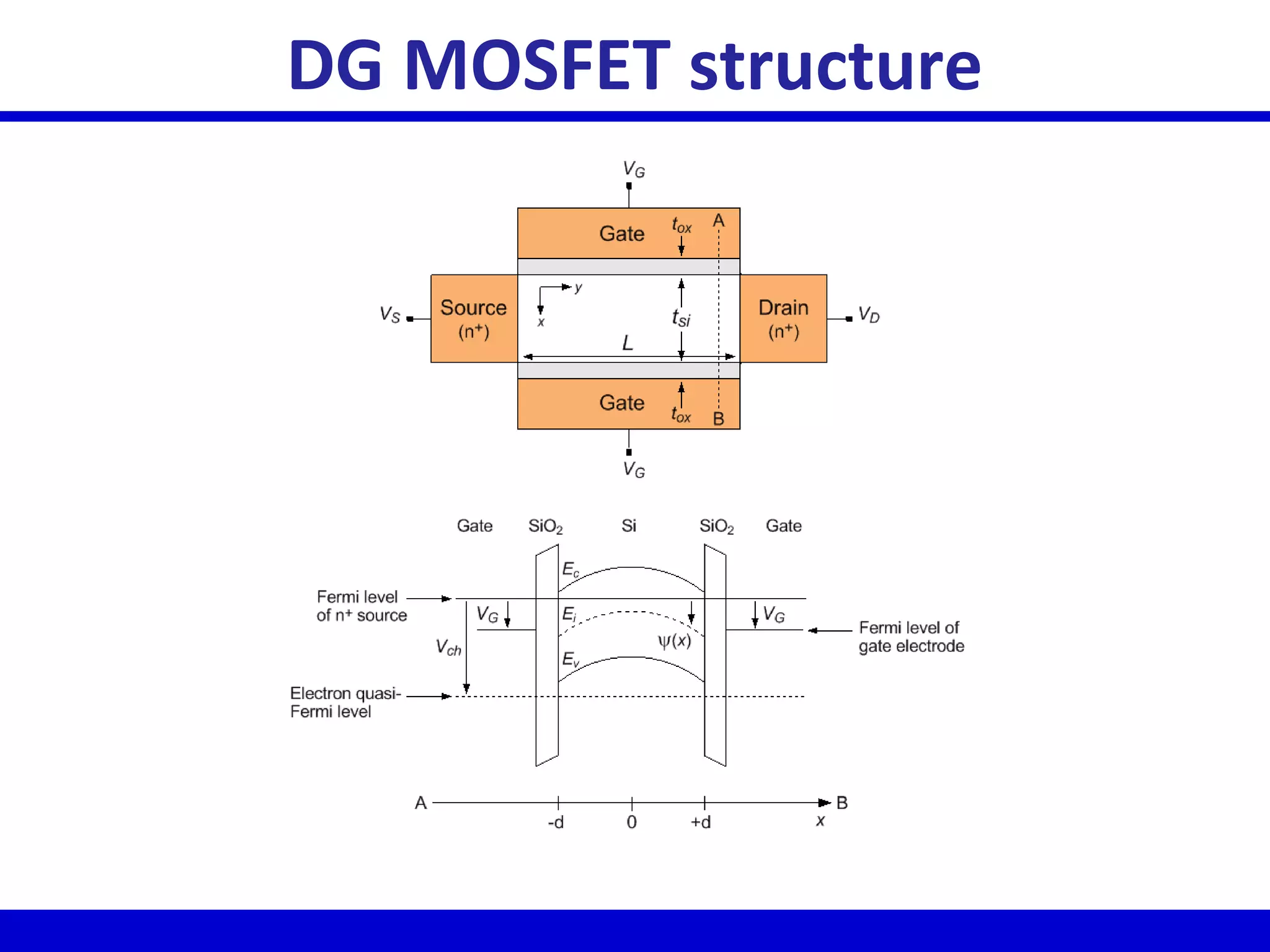
Nano-scale double-gate MOSFETs can be used in low power tunable current mode applications. Silicon-on-insulator technology reduces junction capacitance and leakage compared to bulk silicon, enabling continued device scaling. Double-gate MOSFETs suppress off-state leakage by using an adequately thin body region without body doping, allowing higher drive currents. Simulation results show identical behavior for FinFET and TriGate transistors in terms of current gain and unilateral power gain, with TriGate performance superior to FinFET. Future work includes modeling p-channel devices, understanding design constraints from fabrication tolerances, and investigating microwave characteristics.


![Effect of TSi on OFF-state Leakage
IOFF = 19 µA/µmIOFF = 2.1 nA/µm
Leakage Current
Density [A/cm2
]
@ VDS = 0.7 V
106
10-1
3x102
0.0
4.0
8.0
12.0
16.0
20.0
G
G
S D
G
G
S D
Si Thickness [nm]
Lg = 25 nm; tox,eq = 12Å
TSi = 10 nm TSi = 20 nm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rm-170803064844/75/Rm-naatchammai-vlsi-paper-ppt-7-2048.jpg)