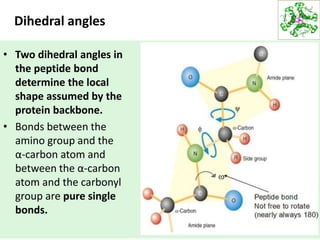
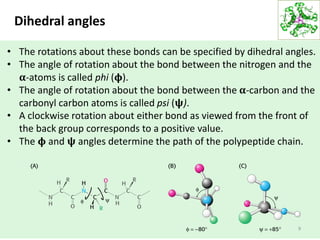
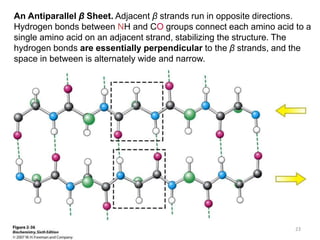
This lecture discusses protein structure and function, specifically focusing on secondary structure elements. It covers the conformations of peptide groups including cis and trans conformations, and dihedral angles phi and psi. Common secondary structures like alpha helices, beta sheets, and turns are described in detail. Alpha helices are stabilized by hydrogen bonds between amino acids four residues apart in the sequence. Beta sheets can be antiparallel or parallel depending on the direction of hydrogen bonding between strands. Turns and loops allow changes in the peptide chain direction. Amino acids have different preferences for forming these secondary structures.