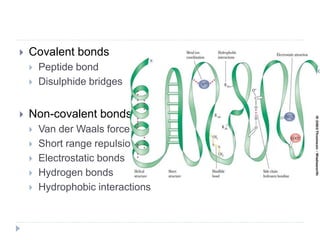
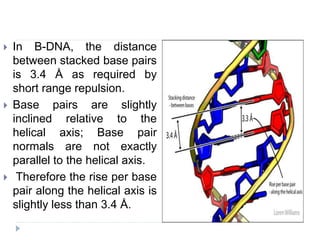
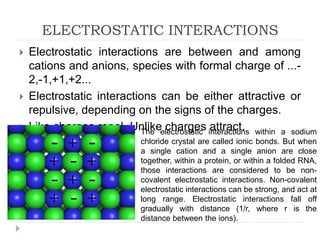
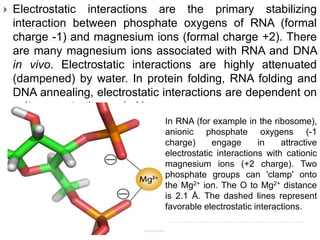
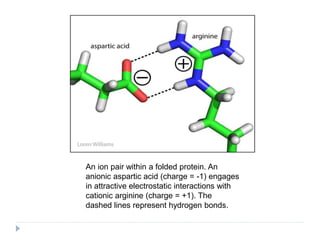
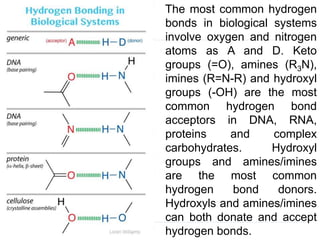
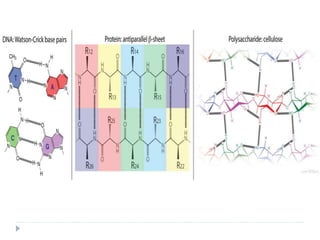
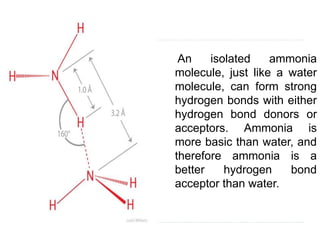
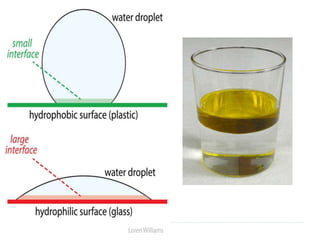
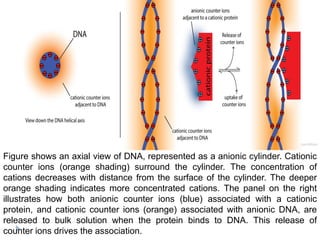
Covalent bonds, peptide bonds, and disulfide bridges stabilize protein structures through strong covalent interactions. Non-covalent interactions like van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonds, electrostatic interactions, and hydrophobic effects also contribute to protein stability. These non-covalent interactions are weaker than covalent bonds but work together in large numbers to stabilize a protein's native conformation. Perturbations can disrupt this delicate balance of interactions and cause protein denaturation.