Embed presentation
Downloaded 14 times

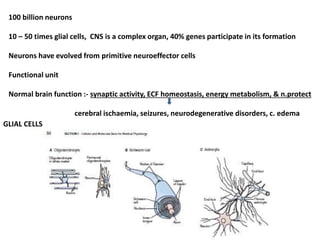


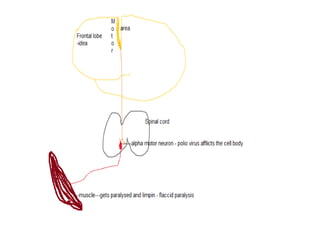
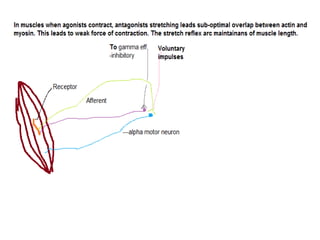
The document discusses neurophysiology and provides information on the brain and nervous system. It notes that the central nervous system contains around 100 billion neurons and 10-50 times as many glial cells. It also discusses different types of cells in the brain like motor neurons and glial cells. The document then outlines several neurological conditions, lesions, and their effects, including lower motor neuron paralysis from polio, upper motor neuron lesions causing changes to reflexes, and hypothalamic lesions potentially causing obesity.






