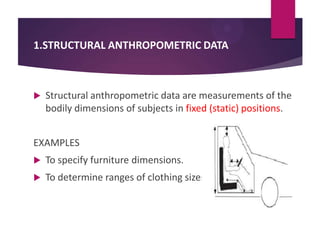
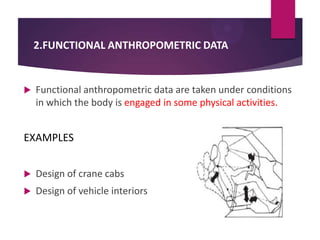
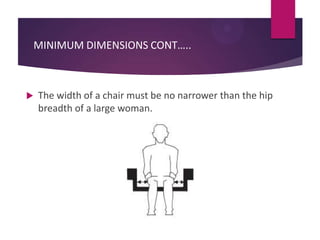
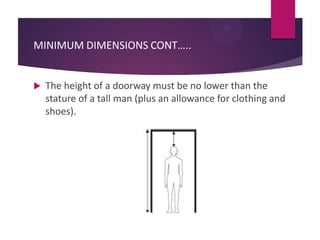
This document discusses applications of anthropometry, which is the measurement of the human body. It begins by defining anthropometry and describing the scope of the seminar. It then explains the two types of anthropometric data - structural and functional - and provides examples. Some key applications of anthropometric data discussed are equipment and facility design, determining dimensions, and defining workspaces. Measuring various body dimensions allows the fitting of tasks to individuals and the design of products for variability in body sizes. In conclusion, the use of anthropometry can increase accuracy, reduce fatigue and injuries, and improve comfort and productivity.