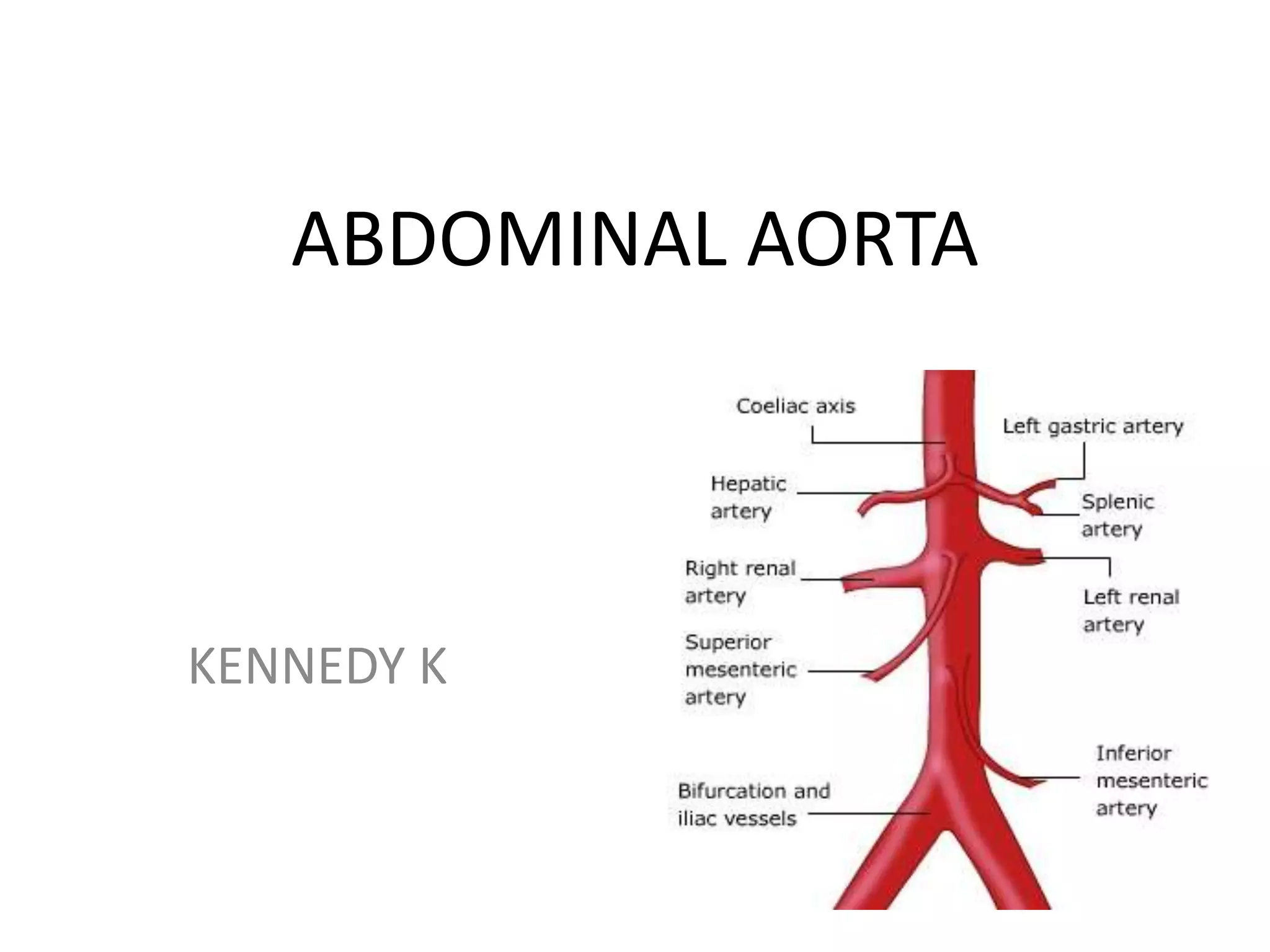
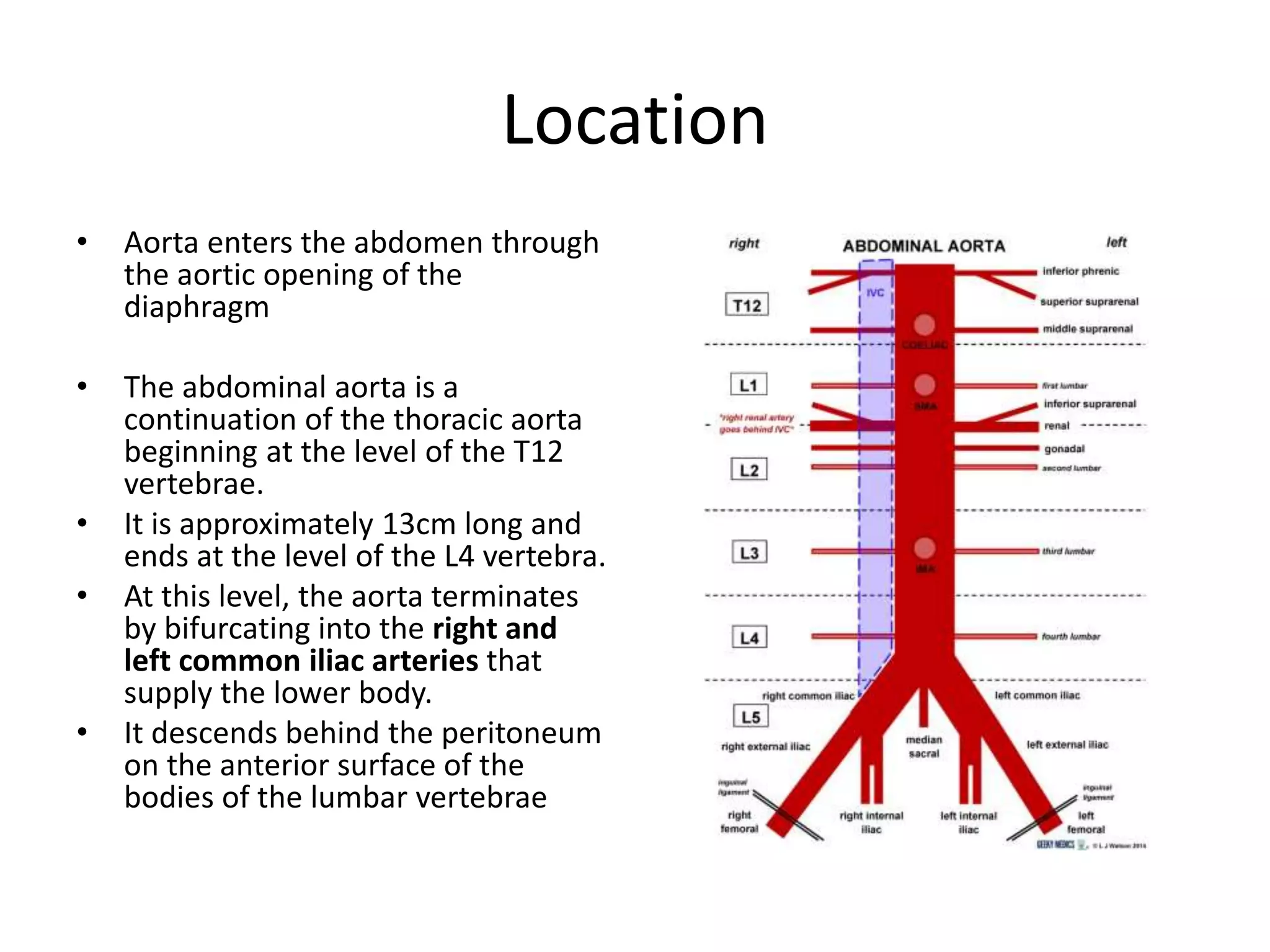
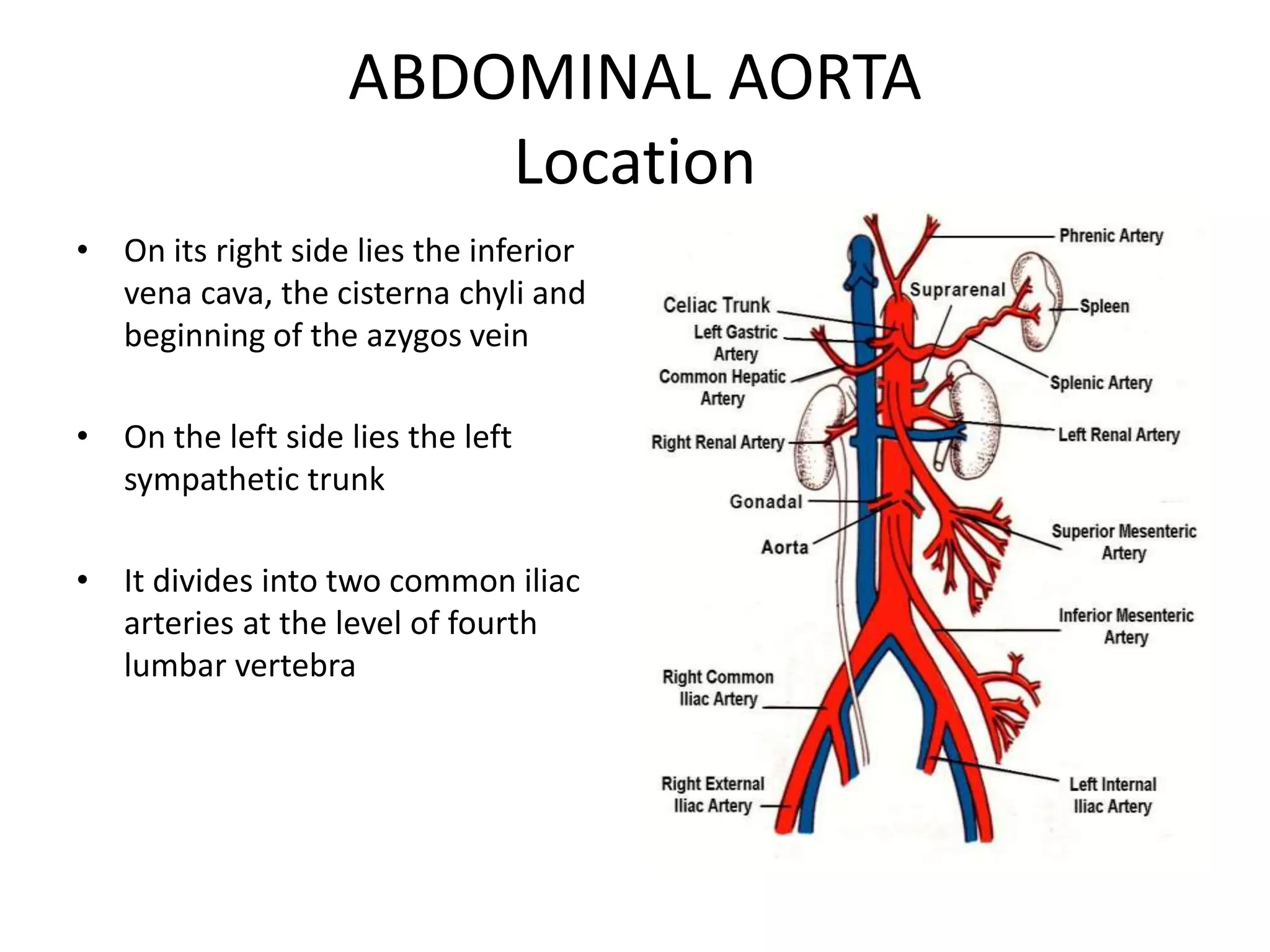
The abdominal aorta begins at the T12 vertebrae as a continuation of the thoracic aorta. It descends behind the peritoneum on the anterior surface of the lumbar vertebrae and ends by bifurcating into the common iliac arteries at L4. It has 9 branches that supply the abdominal viscera and walls. The three major anterior branches are the celiac artery, superior mesenteric artery, and inferior mesenteric artery, which supply the foregut, midgut, and hindgut respectively.