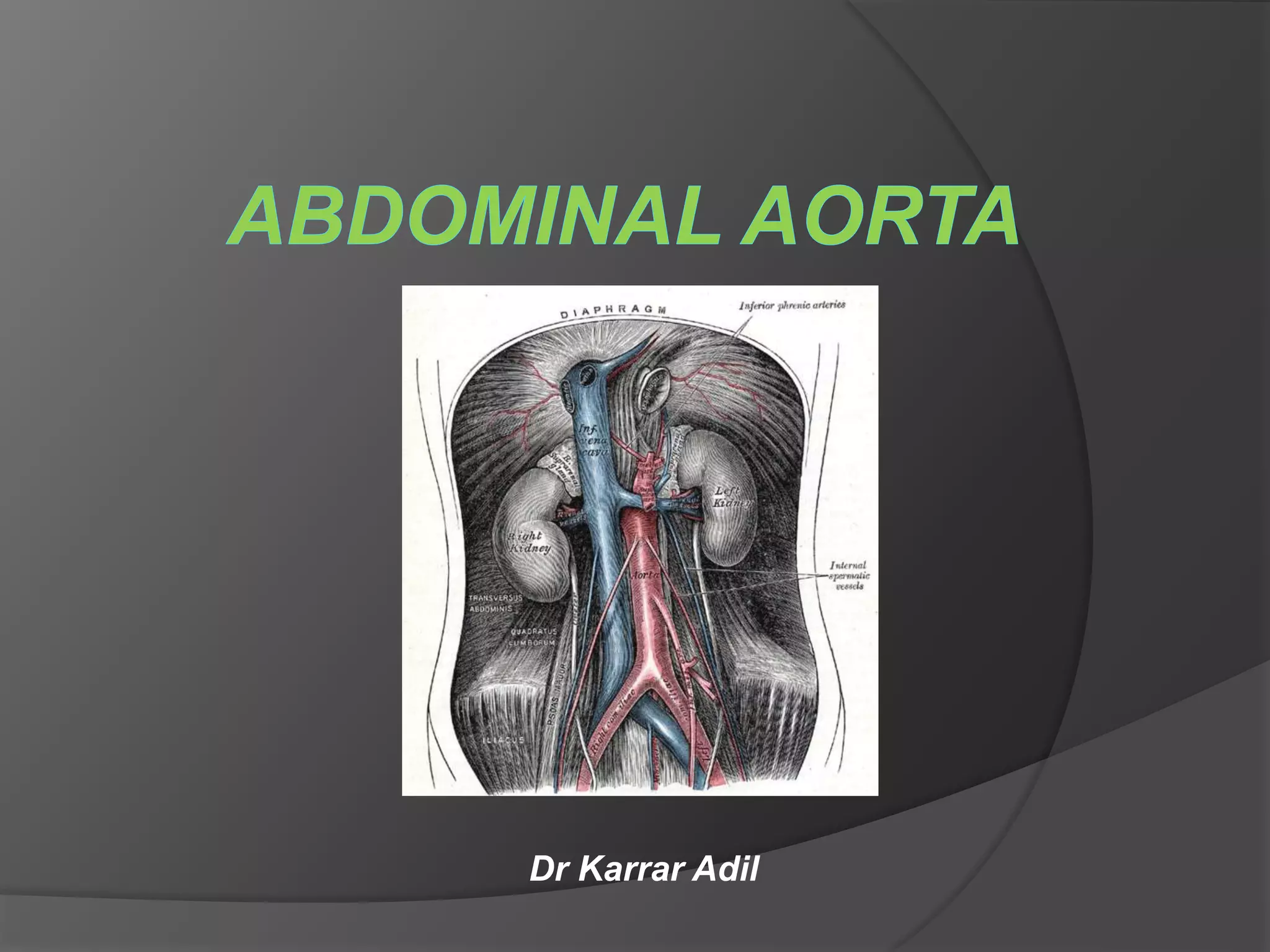
The abdominal aorta begins at the diaphragm and ends by bifurcating into the common iliac arteries. It has various branches that supply blood to abdominal organs. Abdominal aortic aneurysm is a localized dilation of the abdominal aorta over 50% of its normal diameter, most commonly occurring in the infrarenal aorta. Aneurysms are usually asymptomatic but the risk of rupture increases with size. Rupture is a medical emergency while asymptomatic aneurysms over 5.5 cm are repaired surgically or through endovascular graft placement to prevent rupture. Medical management focuses on risk factor modification for small asymptomatic aneurysms.