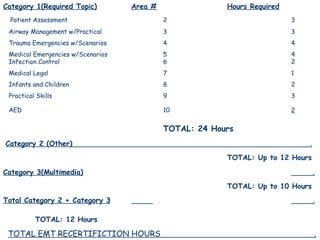
Emergency Medical Services (EMS) evolved from early battlefield medical care during wars to today's organized community response systems. EMS aims to provide immediate care to patients with sudden illness or injury. Over time, advances like motorized ambulances, helicopter evacuations, paramedic training programs, and emphasis on pre-hospital trauma care improved patient outcomes. The 1966 White Paper and Highway Safety Act prompted the development of standardized EMS education, systems, and oversight through agencies like the National Highway Safety Administration.