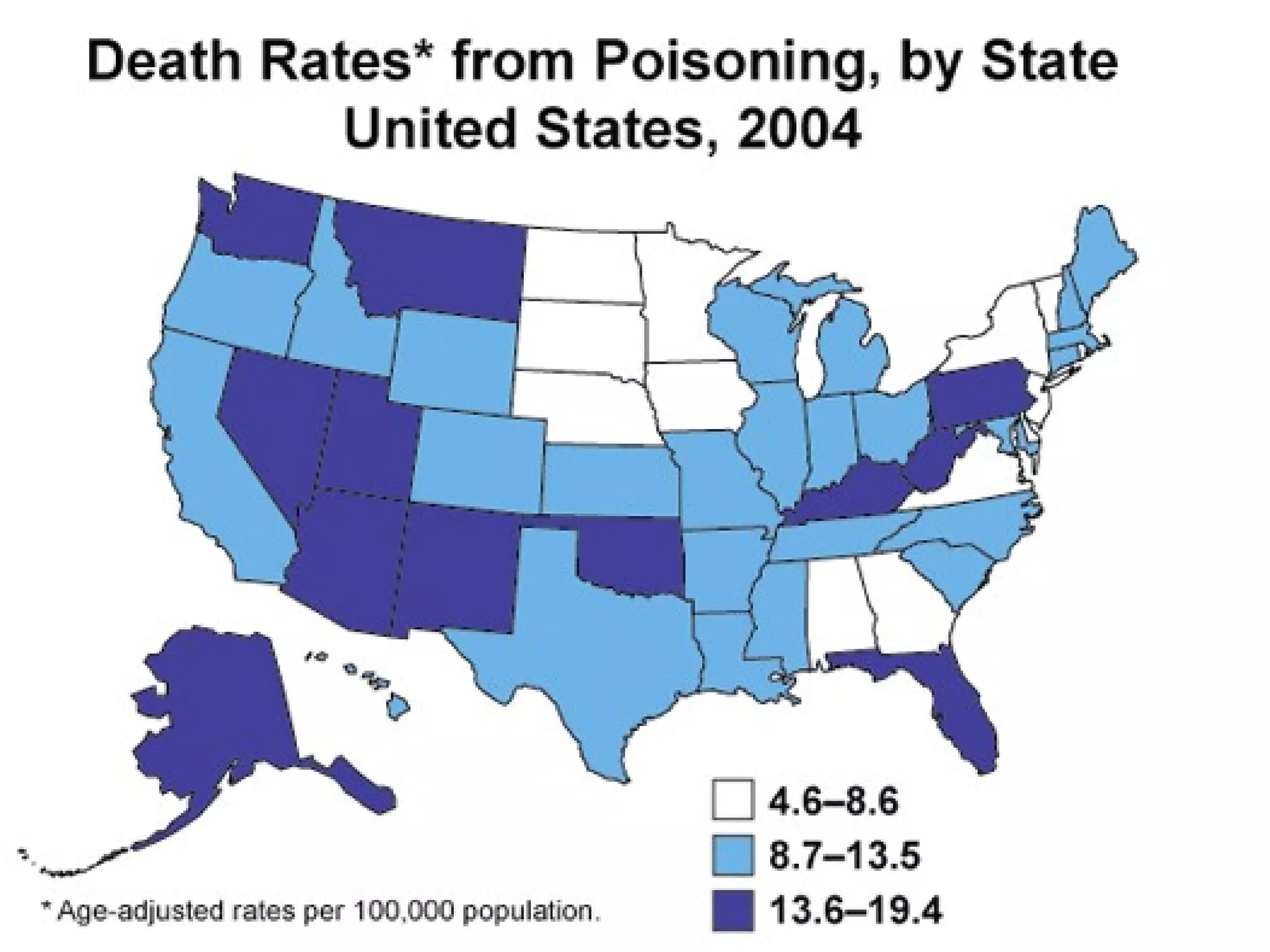
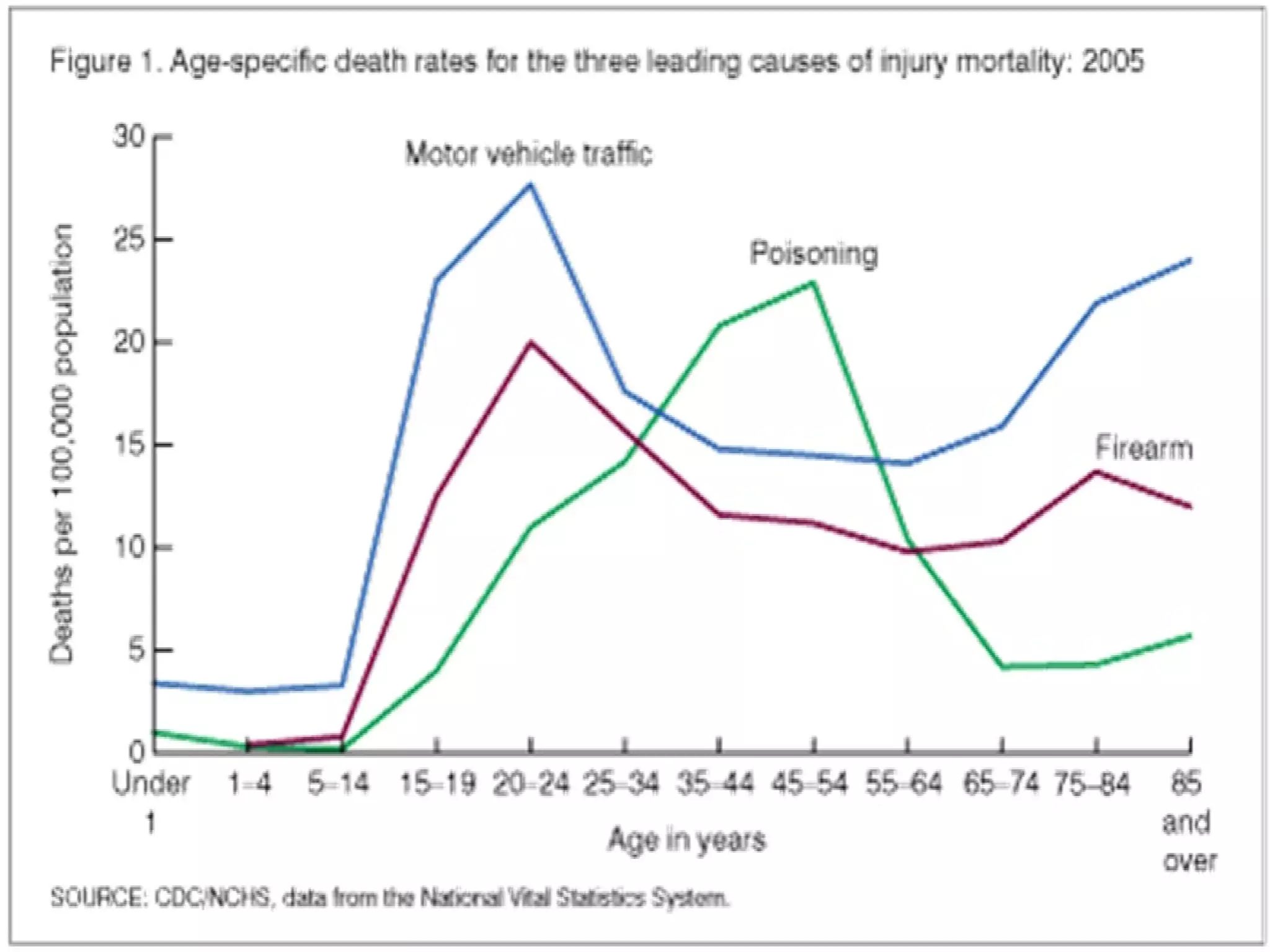
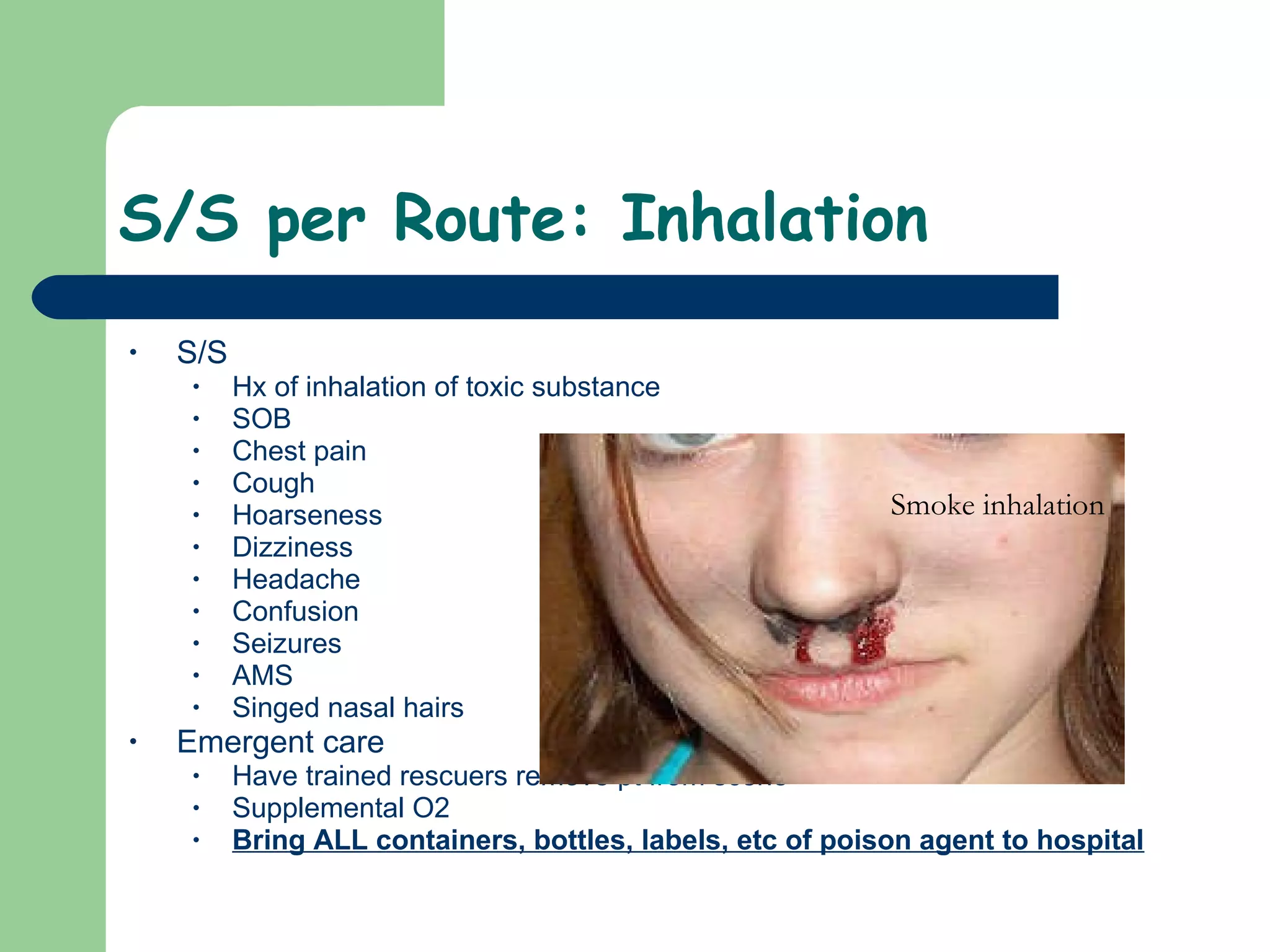
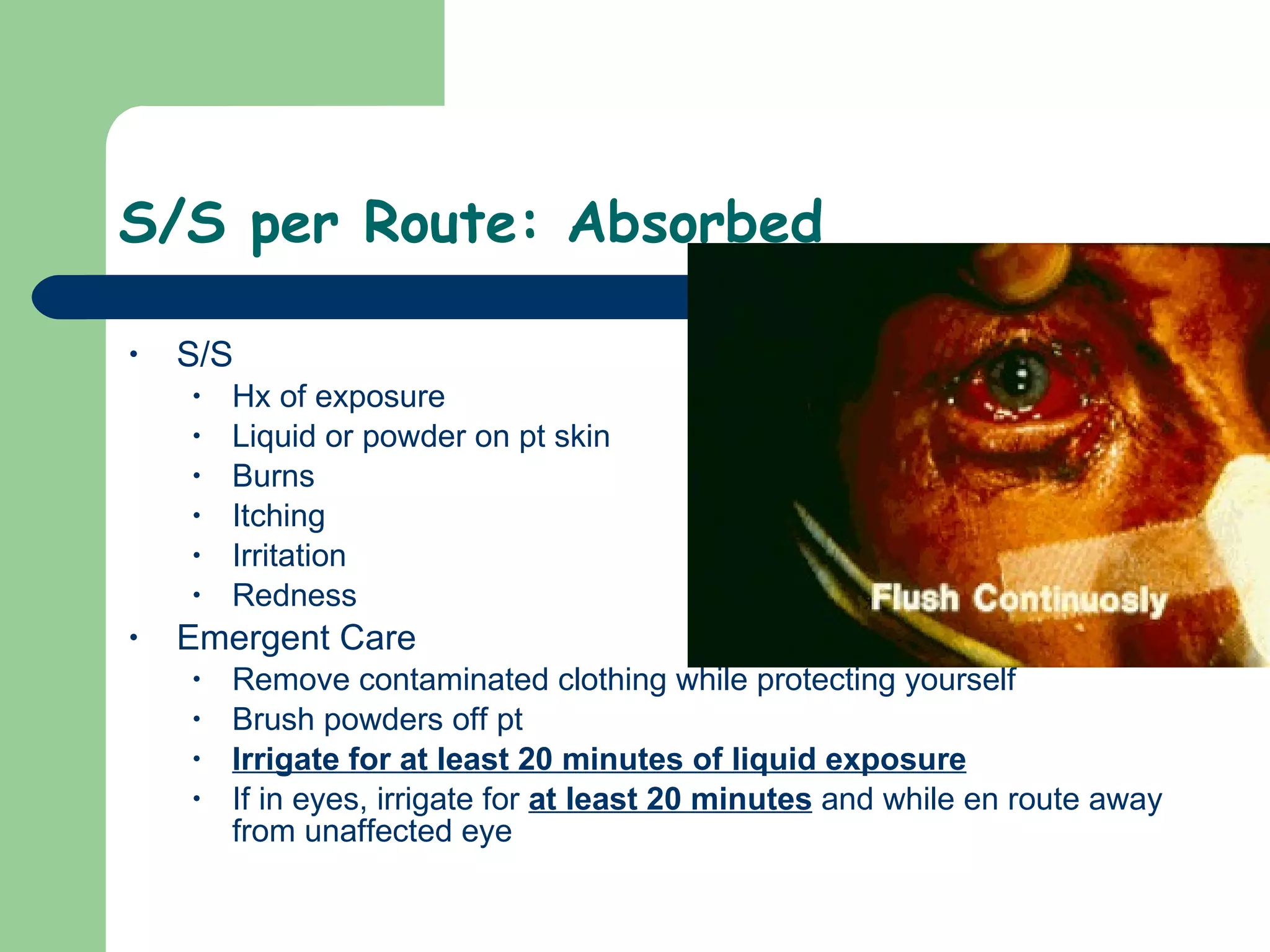
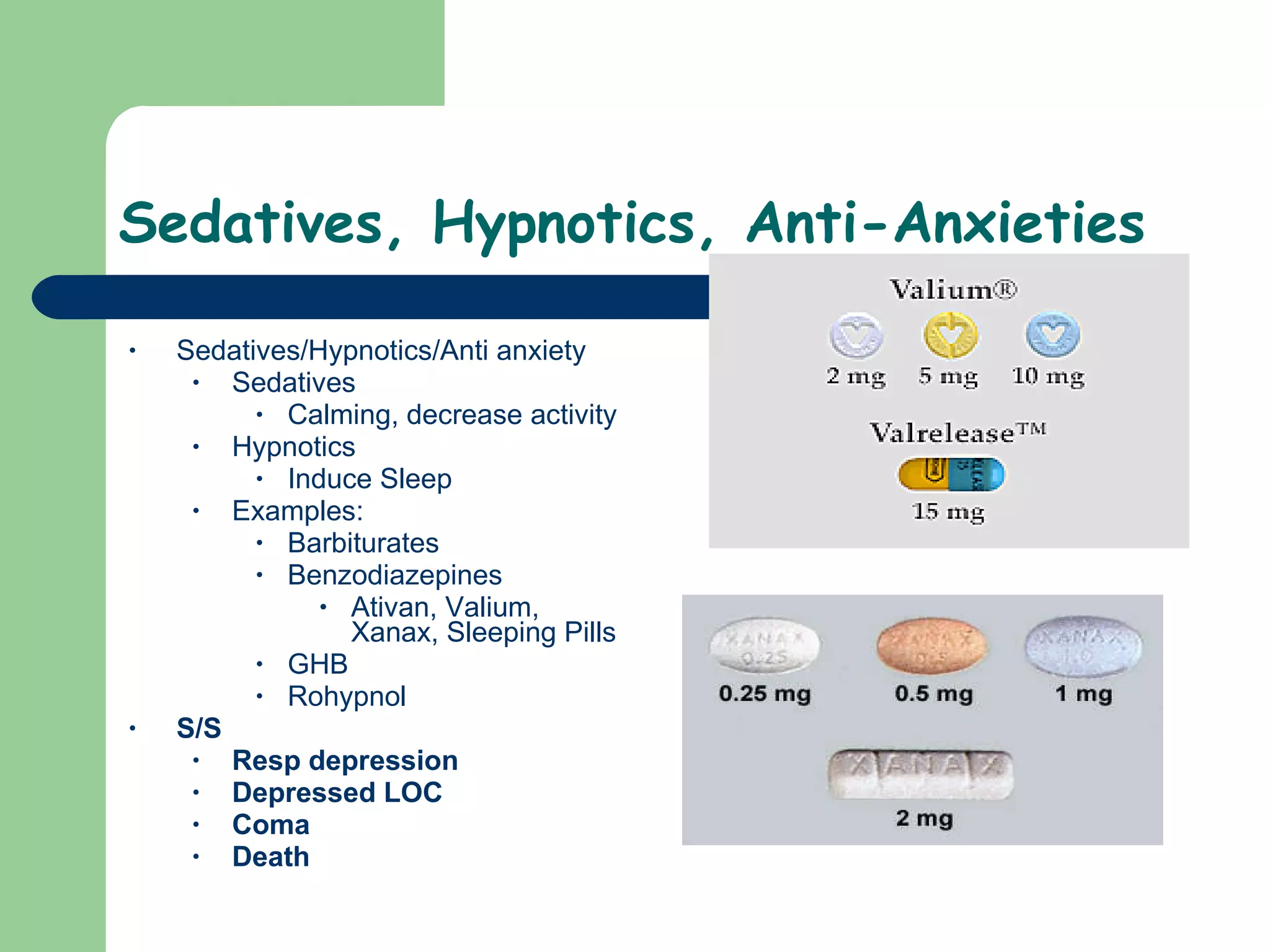
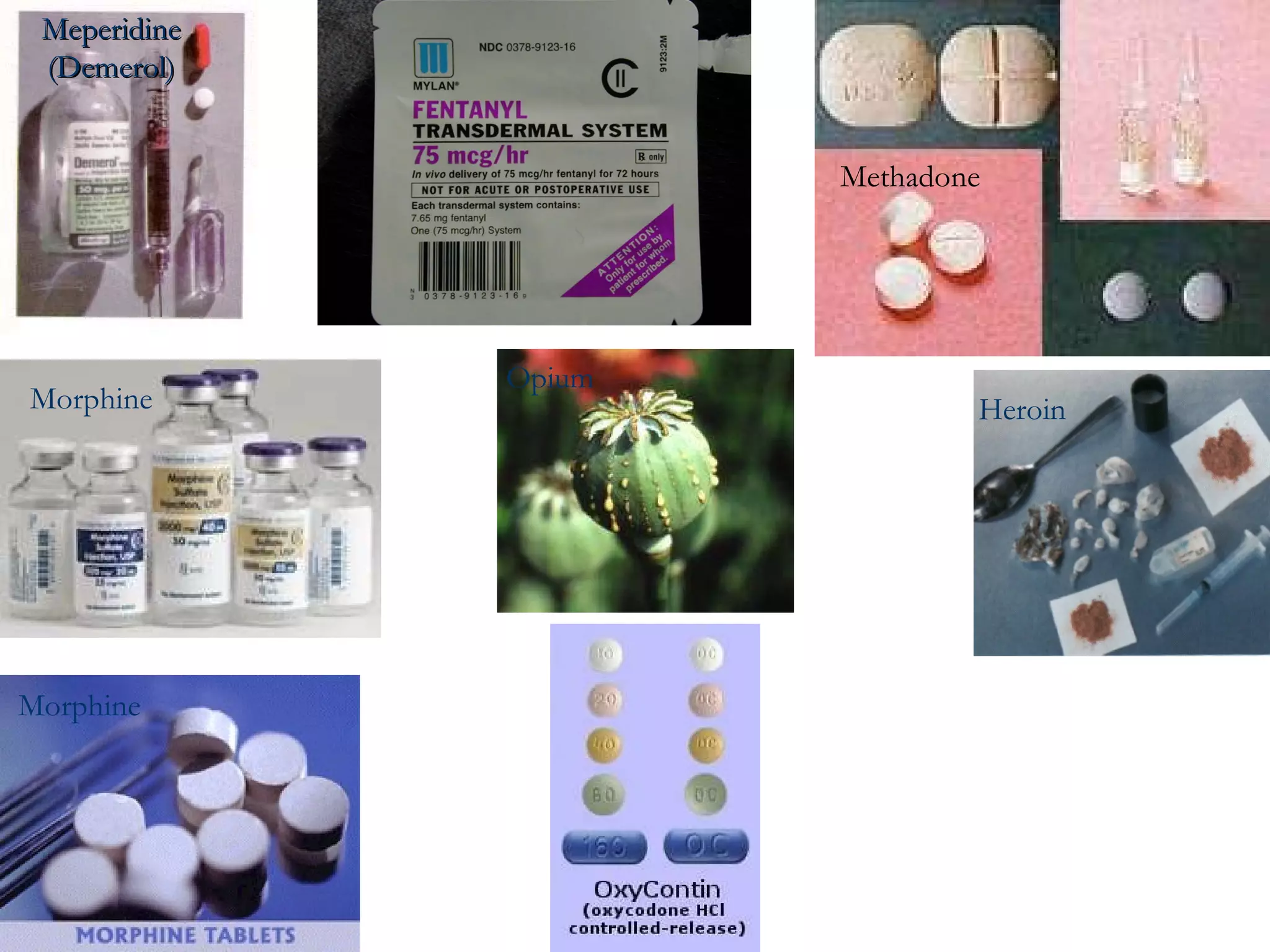
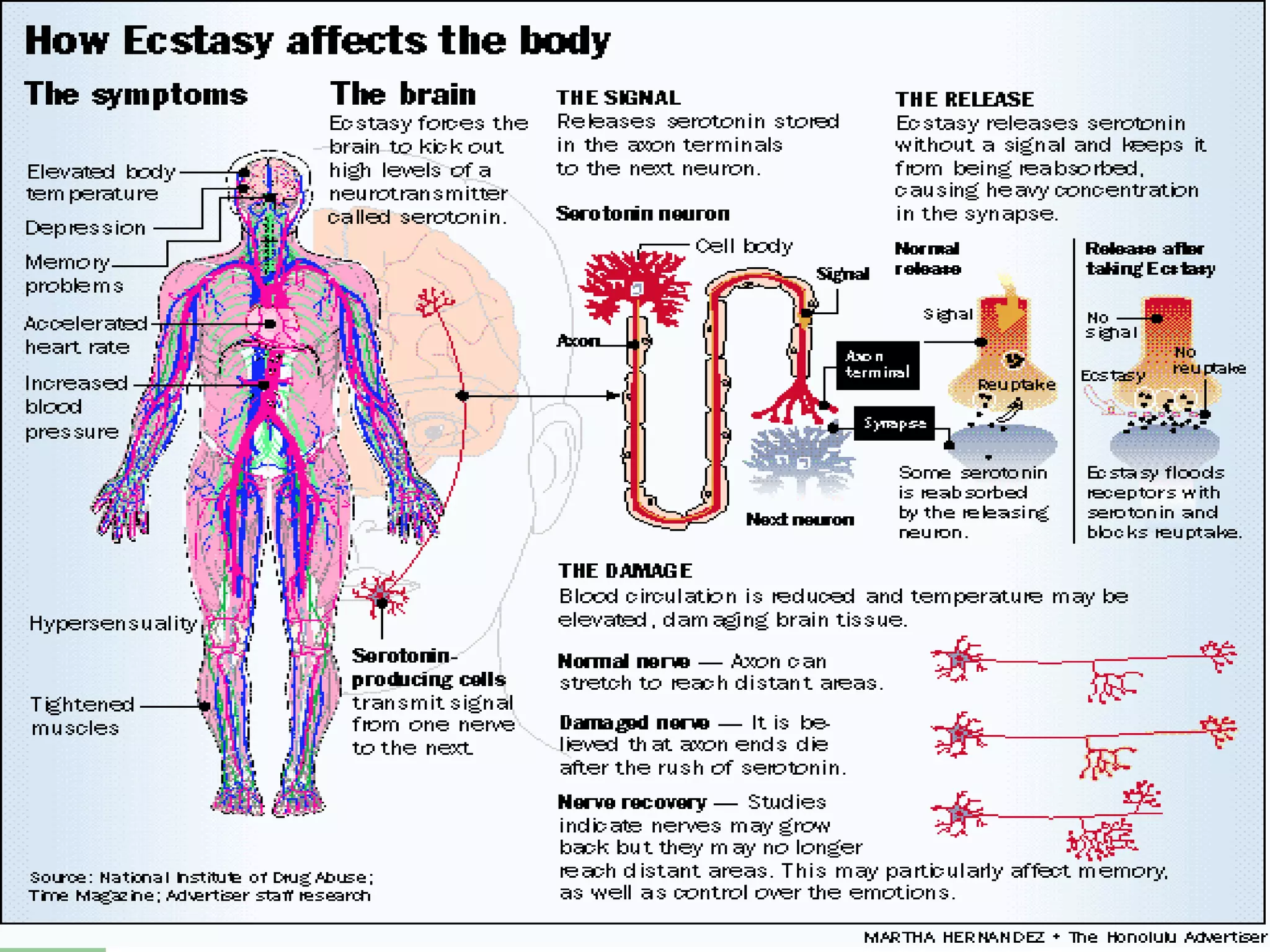
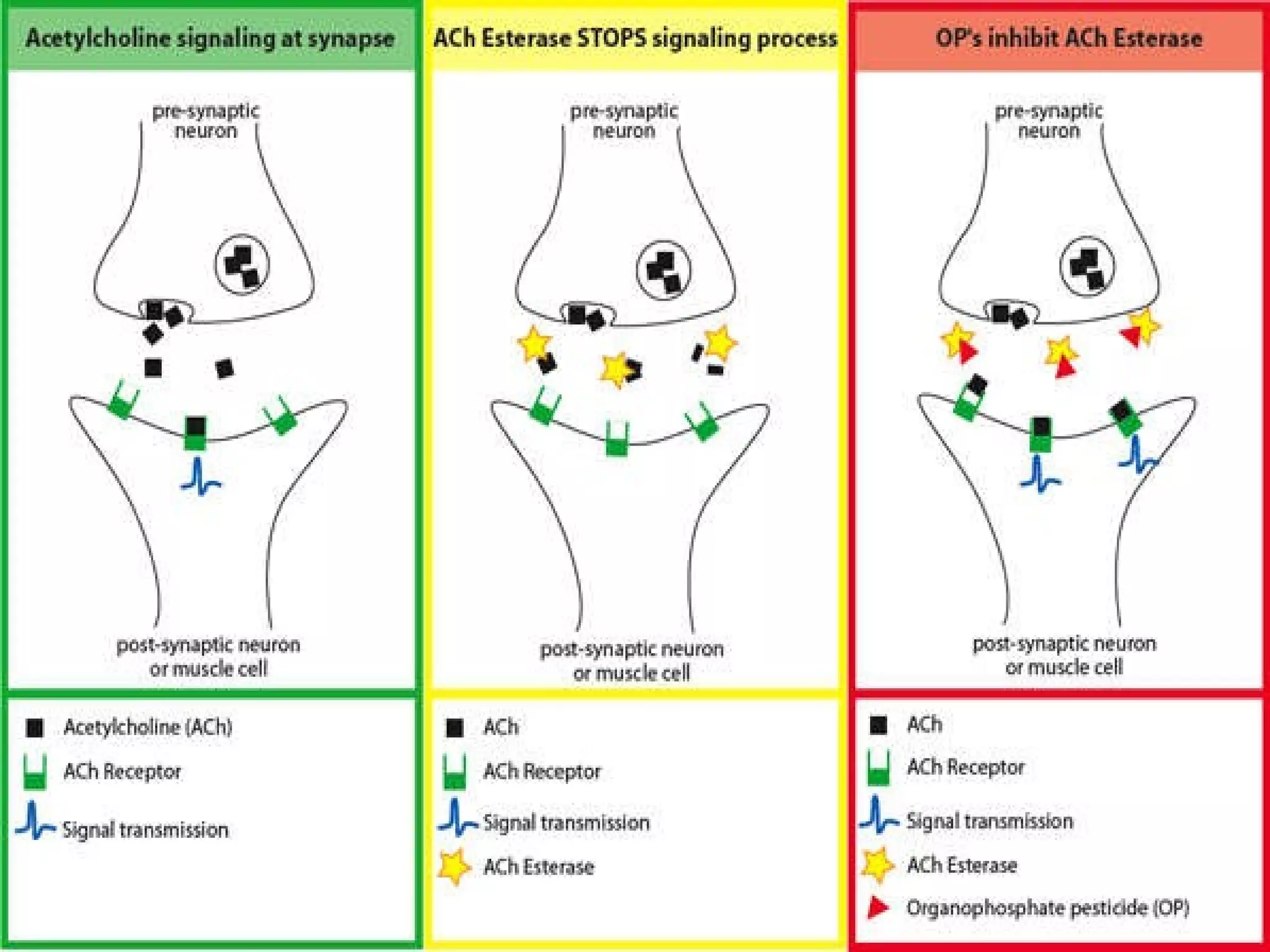
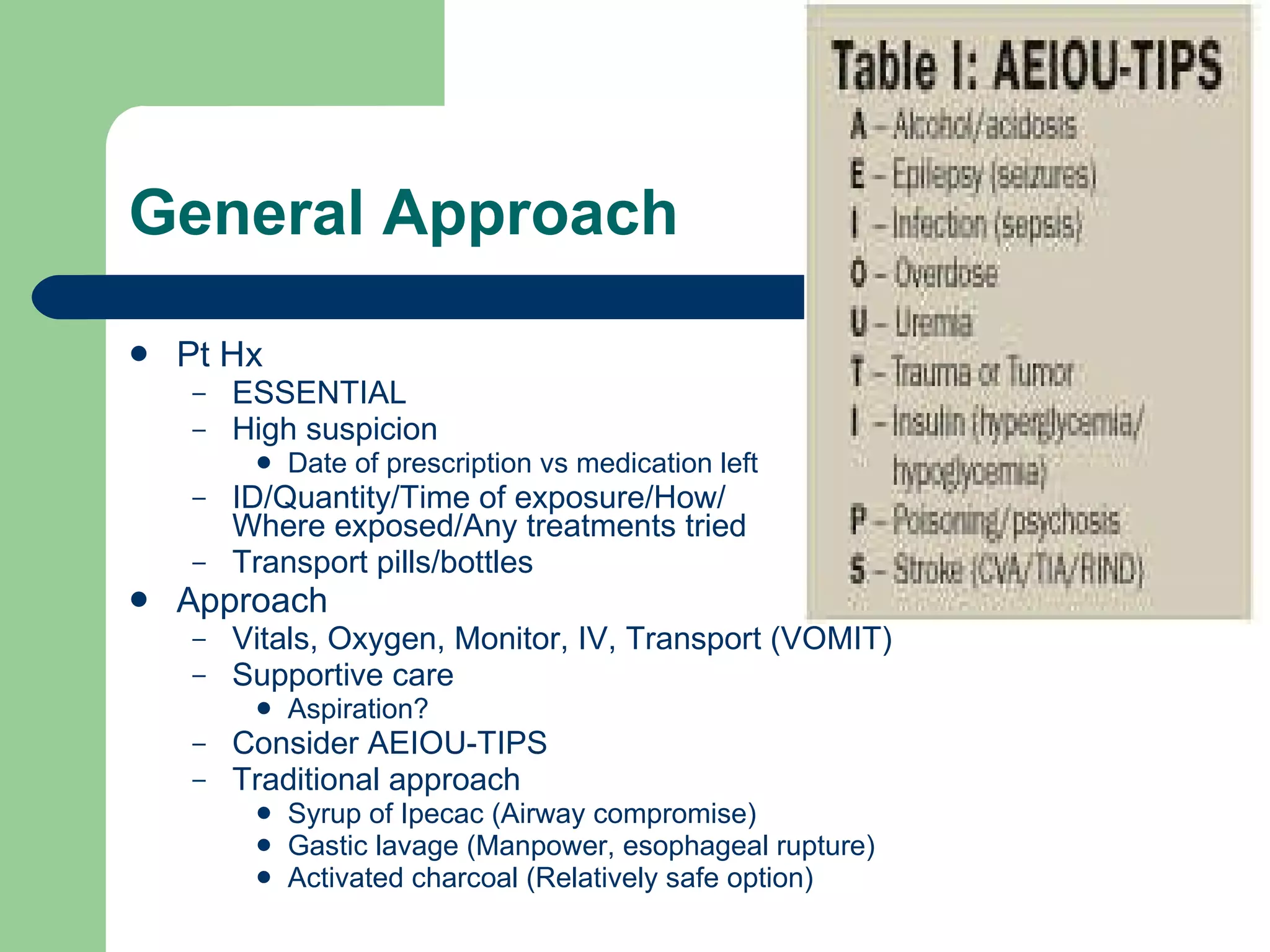
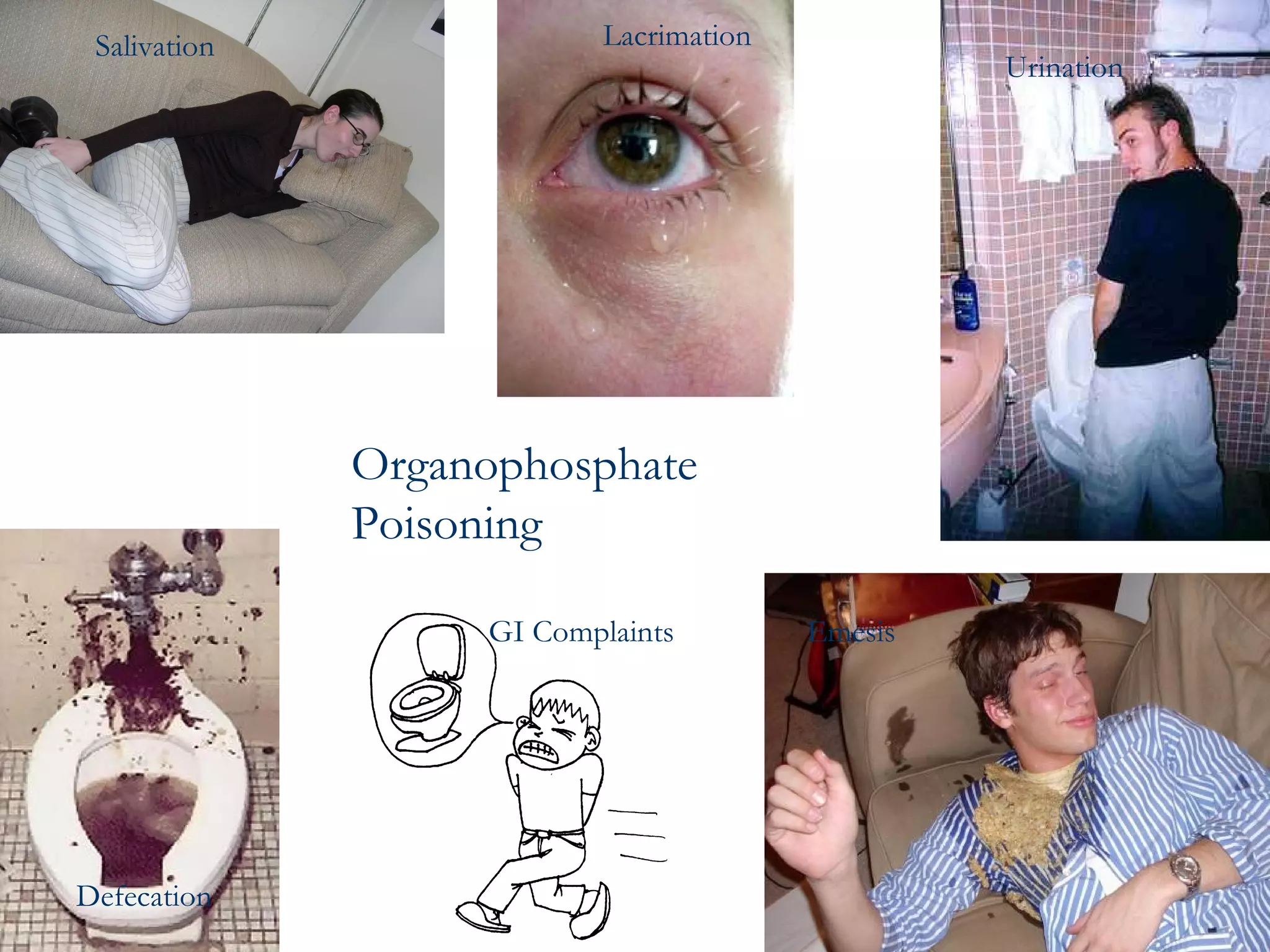
This document provides information on poisoning and overdose, including types of exposures, signs and symptoms by route of exposure, specific toxins, assessment considerations, management strategies, and activated charcoal administration. It discusses ingestion, inhalation, absorption, and injection as routes of exposure. Common toxins described include sedatives, opioids, stimulants, alcohol, analgesics, organophosphates, and food poisoning. Assessment involves considering the substance, amount, and time of exposure. Management focuses on airway control, ventilation, absorption prevention, and symptom treatment. Activated charcoal is indicated for ingestions to bind toxins and prevent absorption.