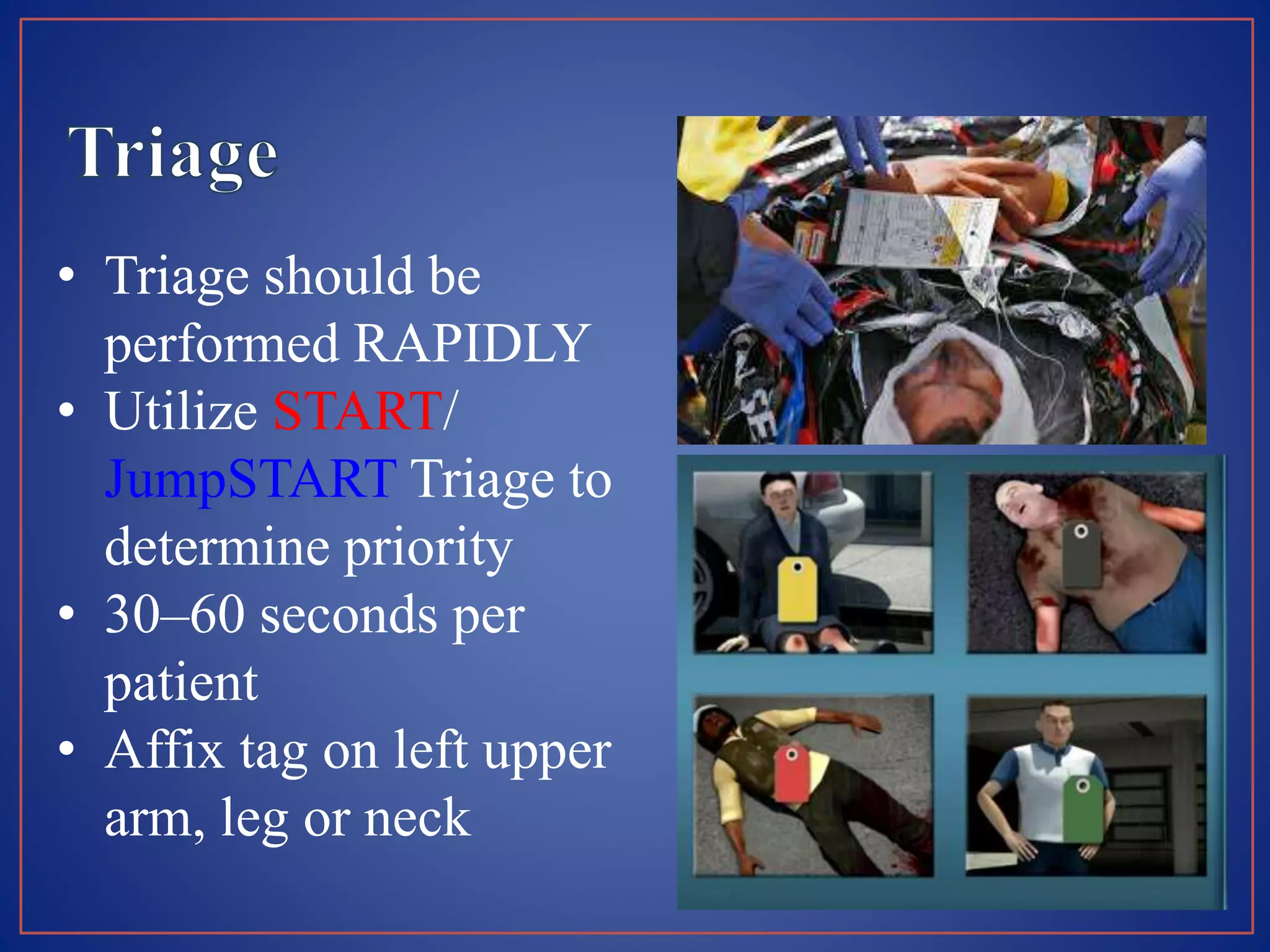
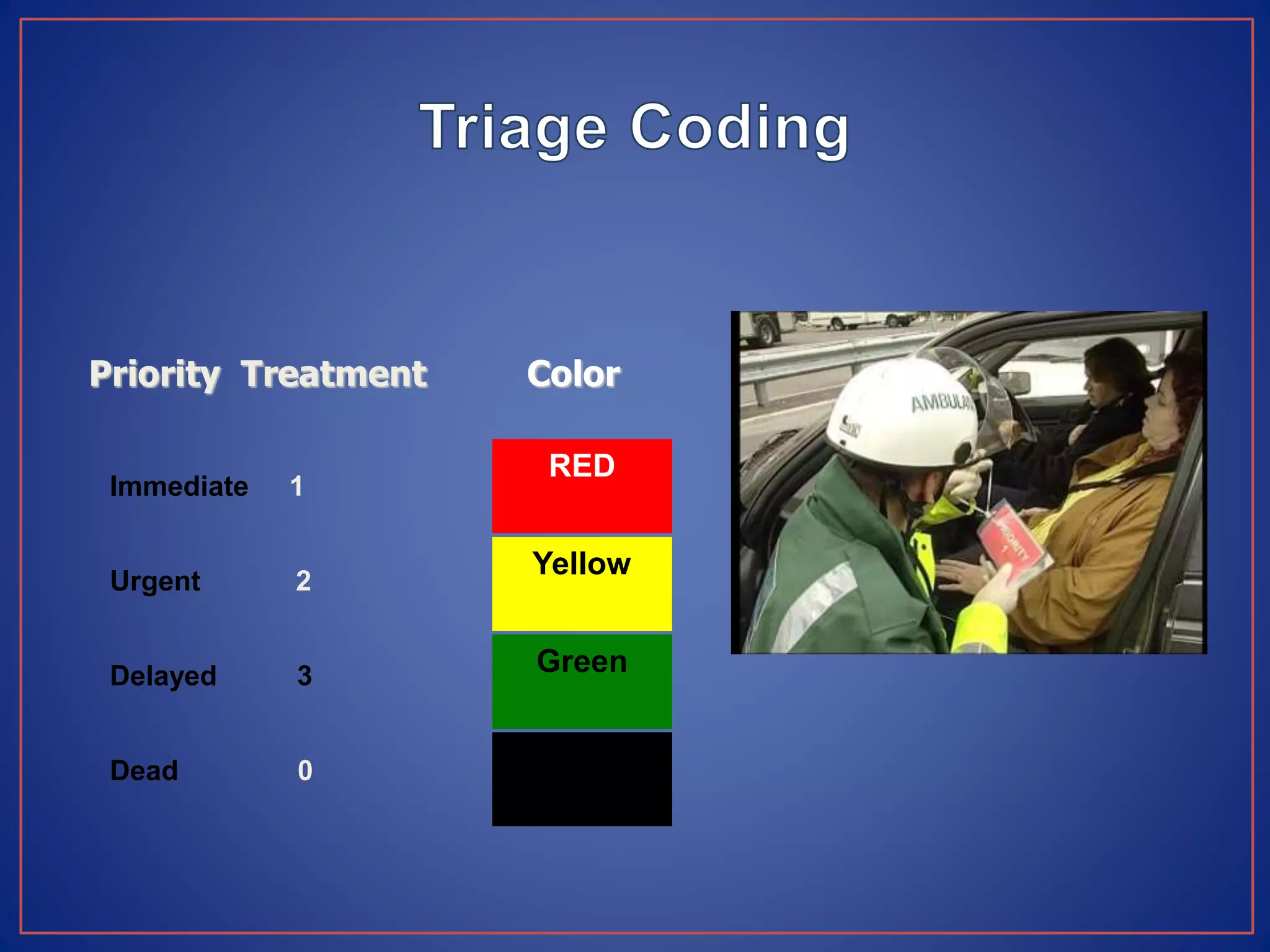
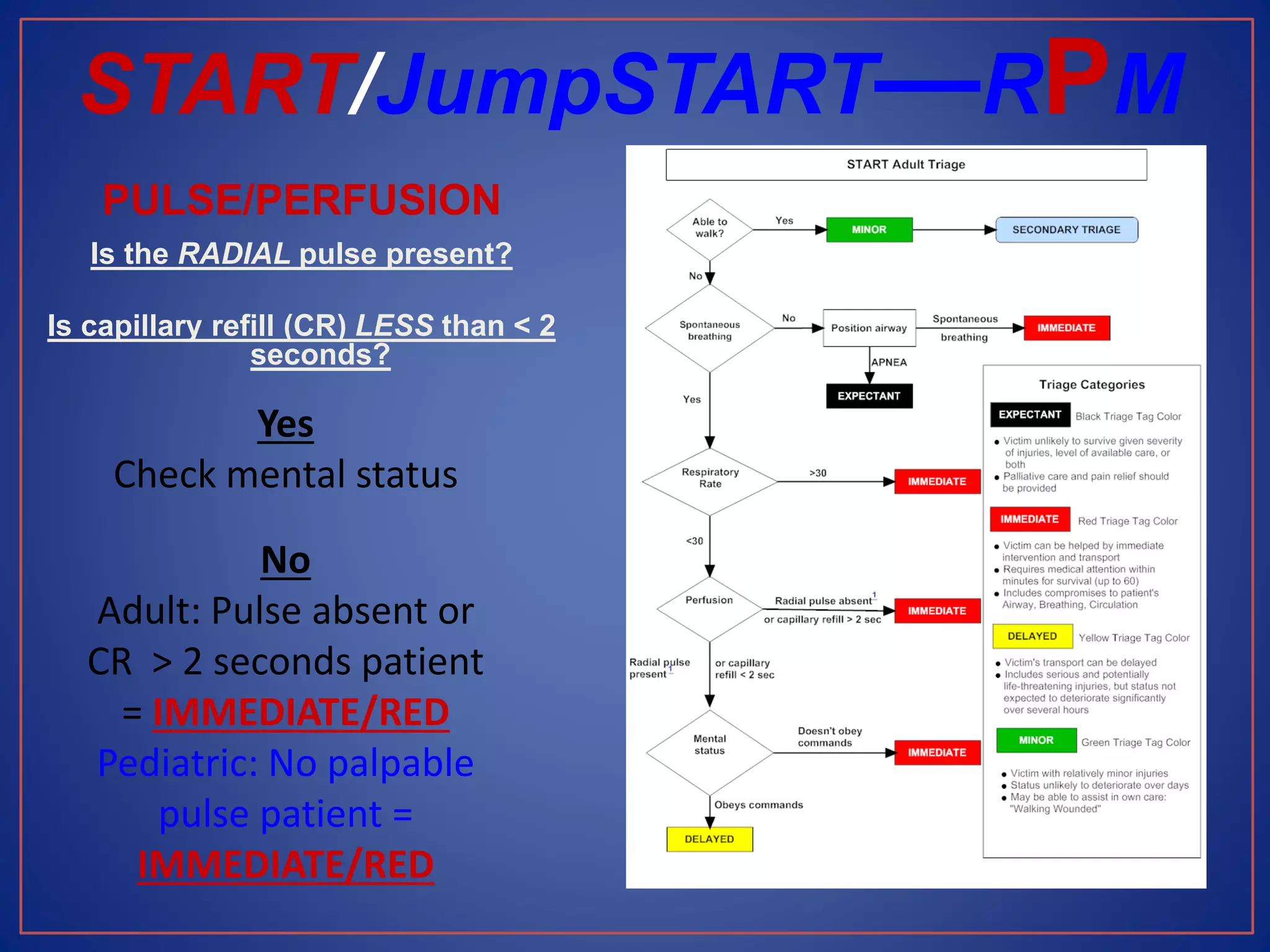
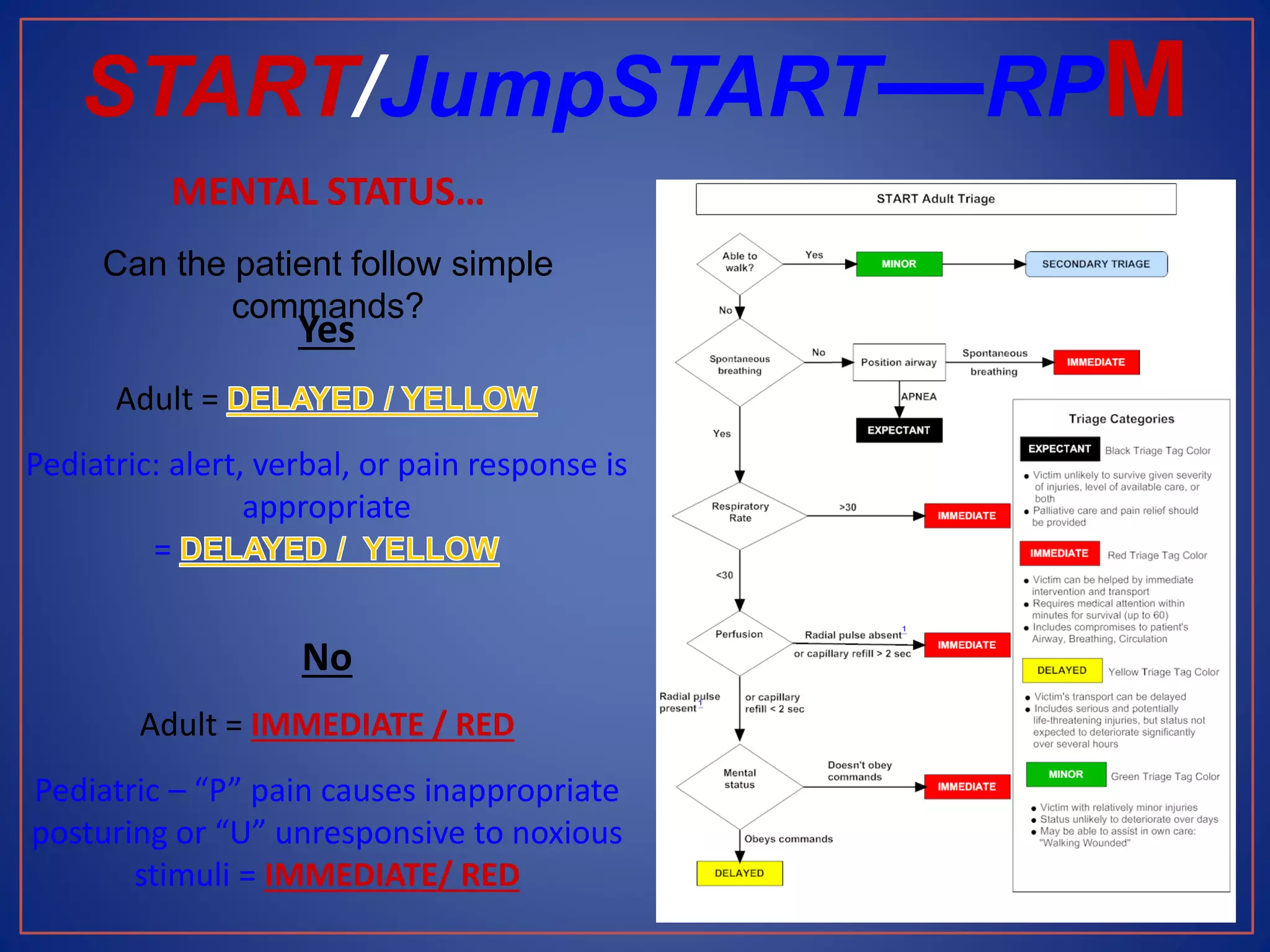
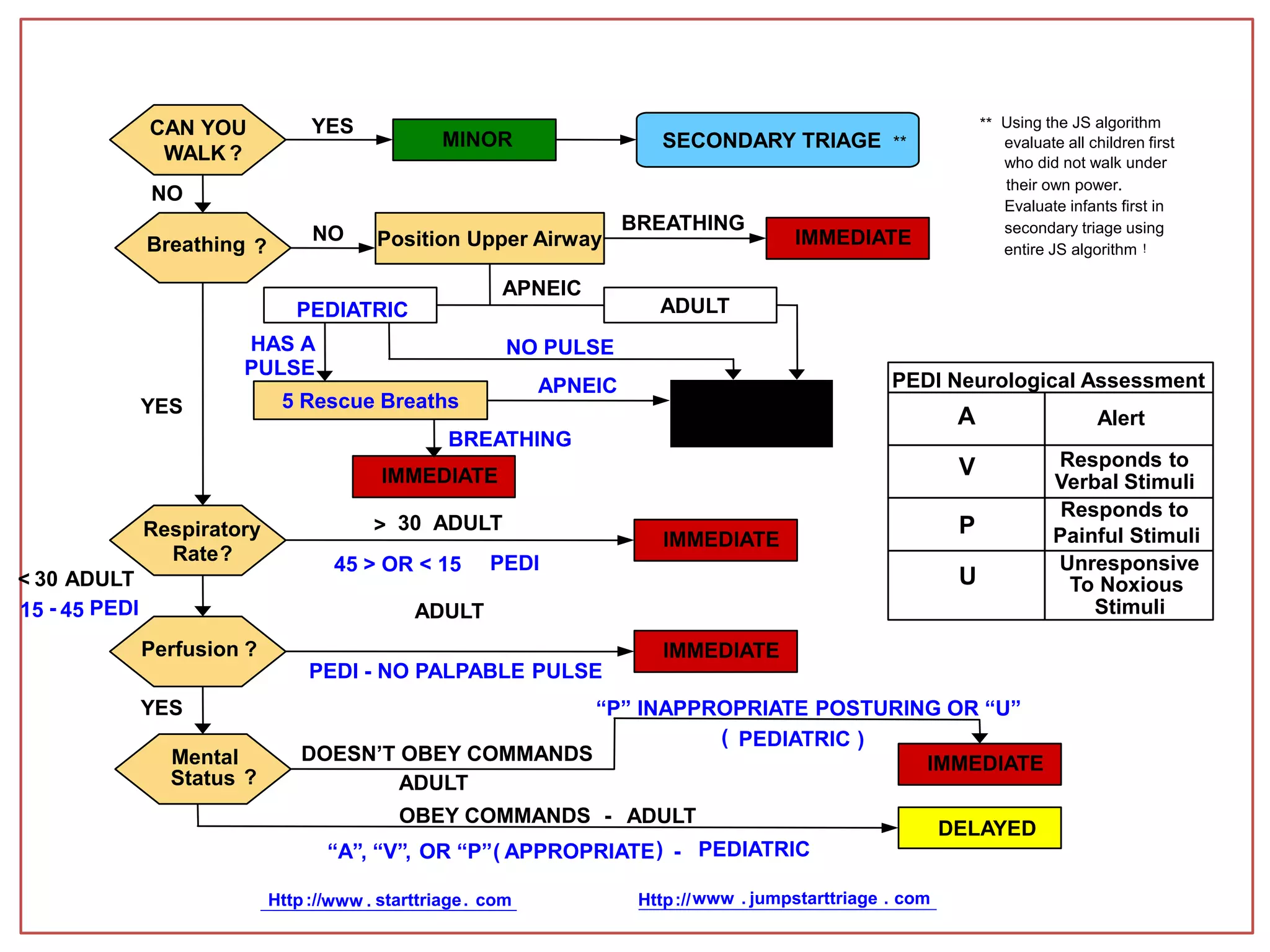
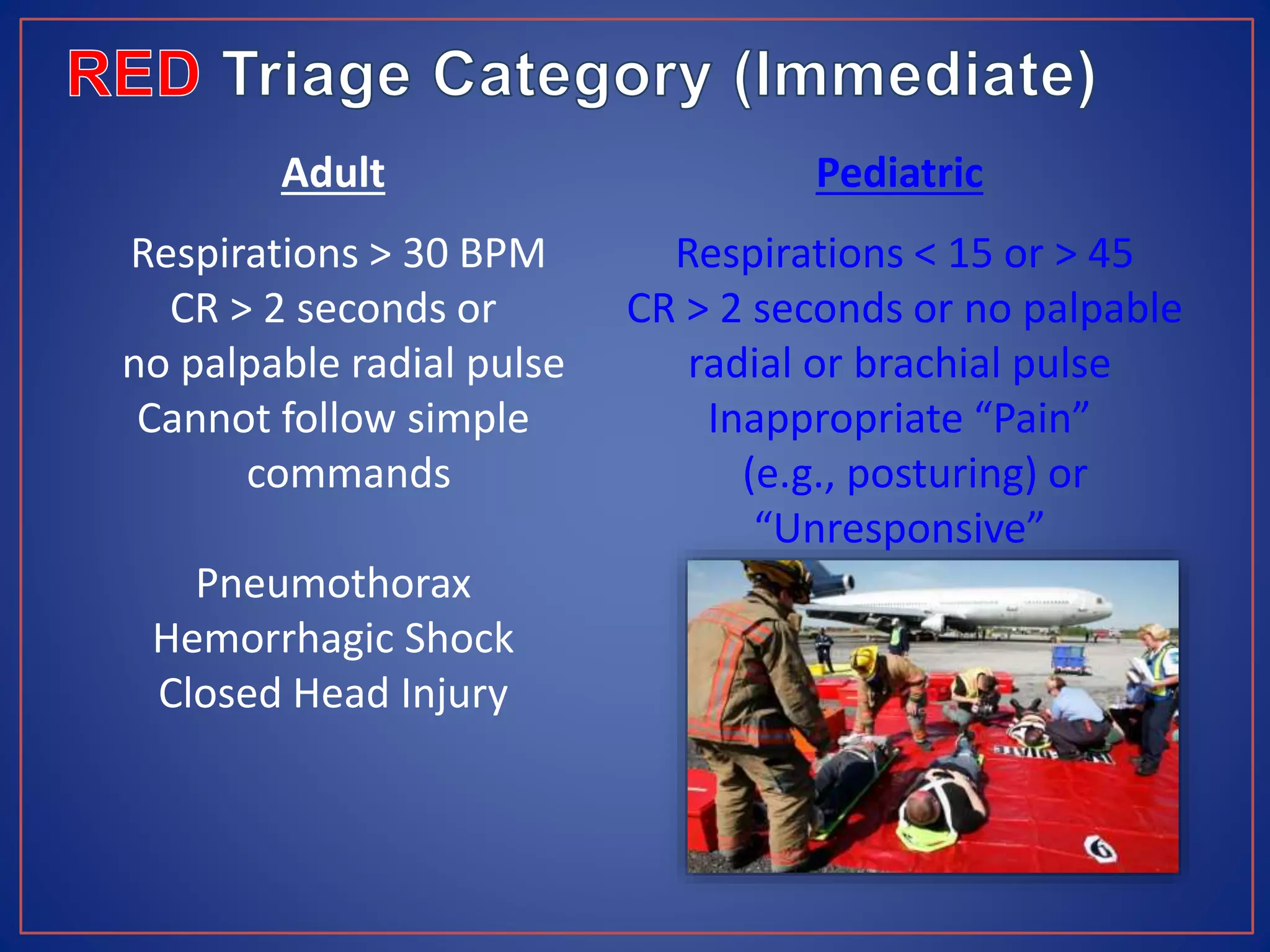
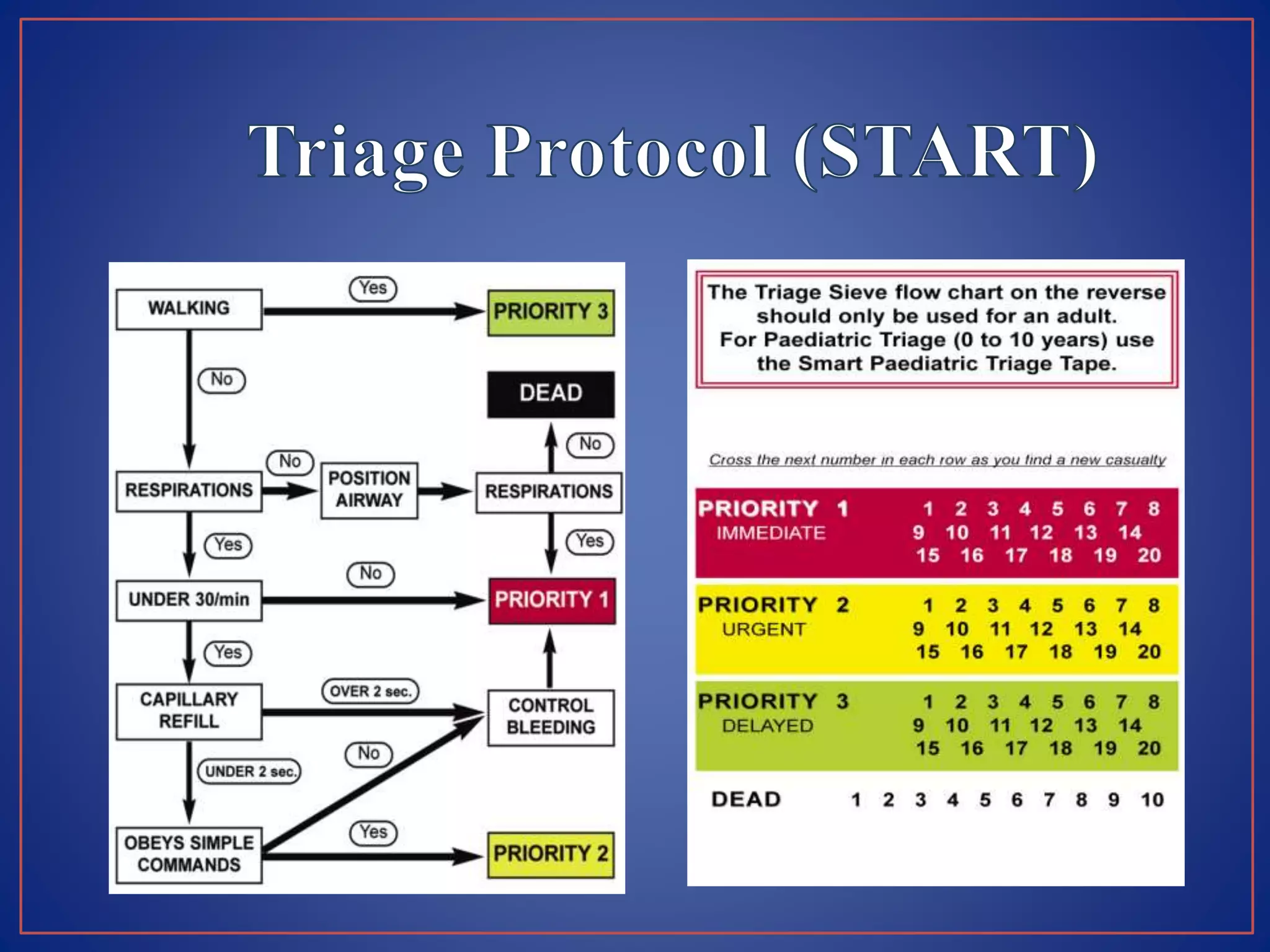
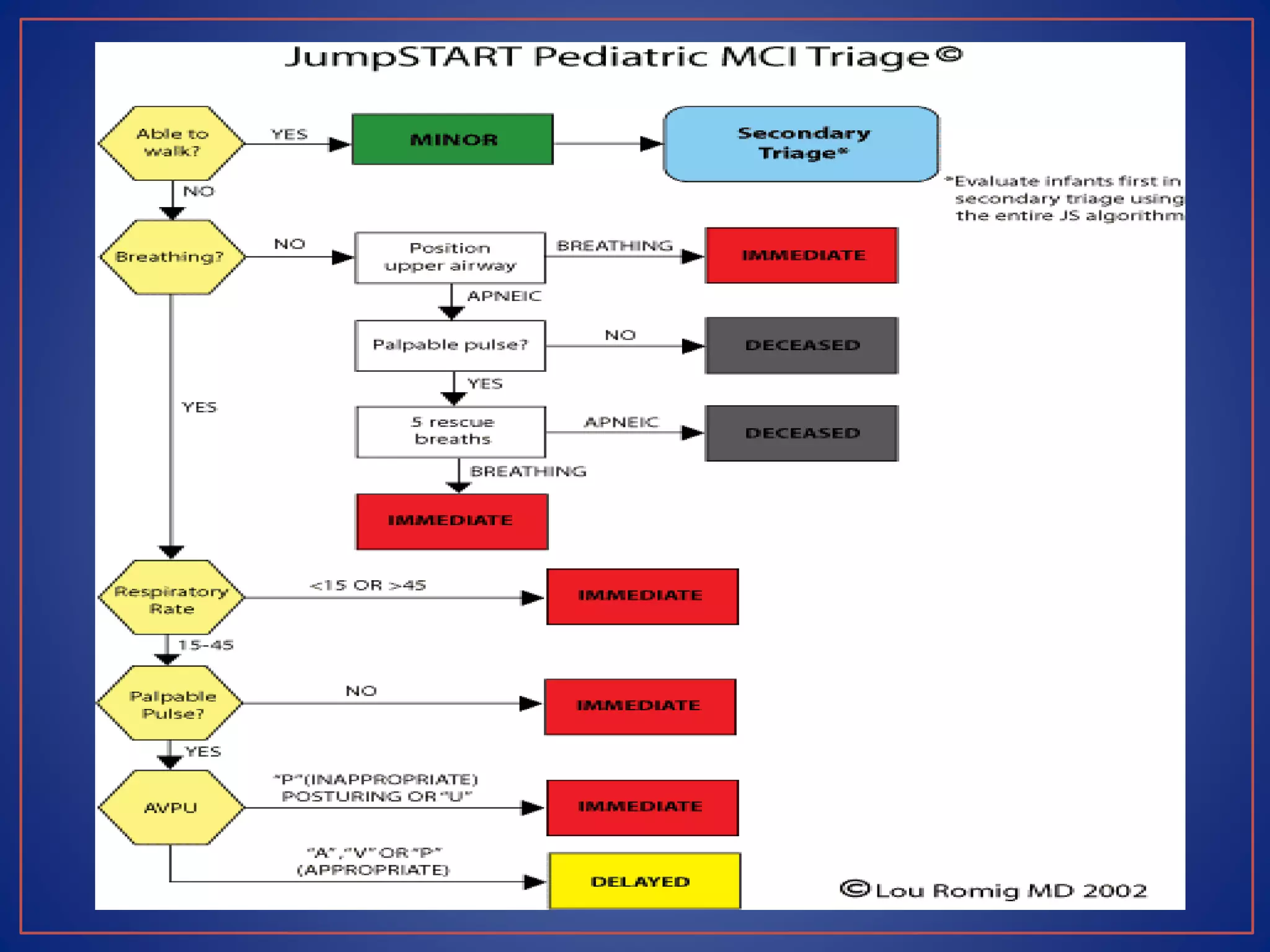
This document provides information on triage systems and procedures. It defines triage as sorting patients based on treatment priority. The START and JumpSTART triage systems categorize patients as red/immediate, yellow/delayed, green/minor, or black/deceased based on their respiration, pulse, and mental status. It outlines how to rapidly assess and tag patients in a mass casualty event using these criteria in 3 sentences or less per patient to maximize survivability. The document recommends clearing walking patients first and prioritizing life-saving interventions for immediate patients before movement or additional treatment.