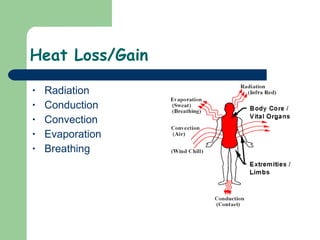
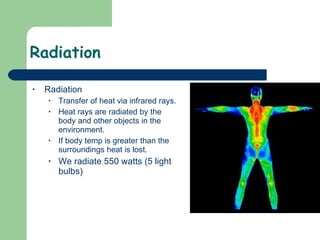
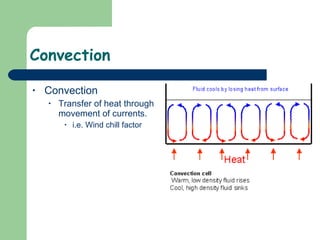
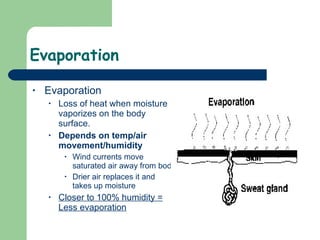
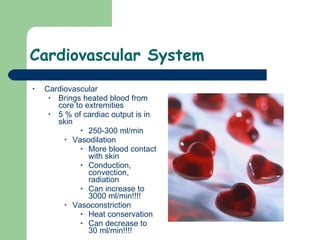
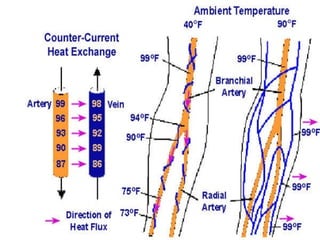
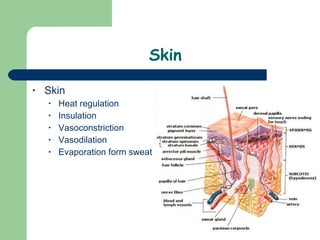
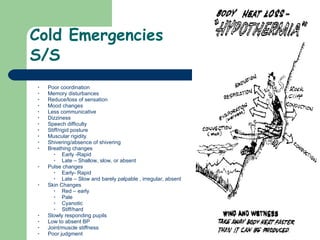
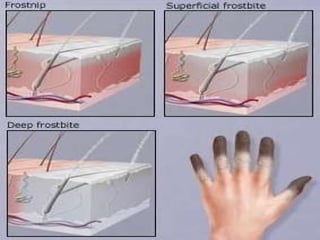
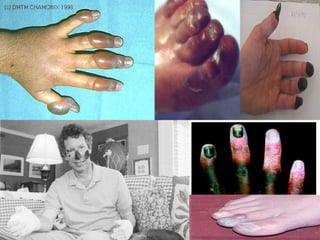
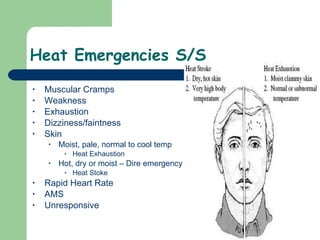
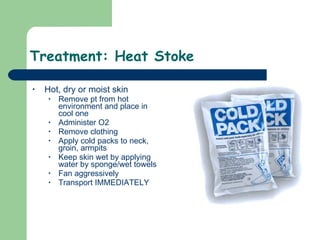
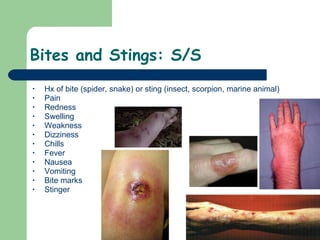
The document discusses various environmental emergencies including heat-related illnesses, hypothermia and cold injuries, bites and stings, and water-related emergencies. It describes the predisposing factors, signs and symptoms, and treatment approaches for these conditions. The key aspects of patient assessment and care are to remove them from the dangerous environment, monitor for changes in mental status and vital signs, provide oxygenation and cooling or warming as indicated, and rapidly transport to definitive care.