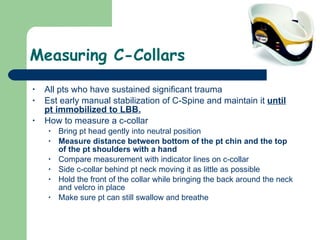
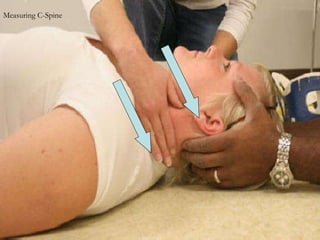
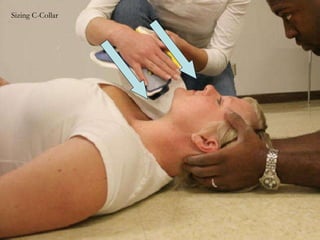
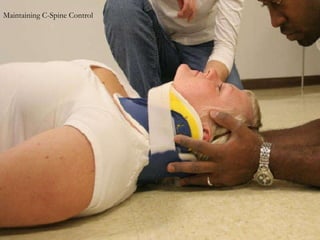
1) The document provides guidance on performing an initial assessment of a patient which includes rapidly evaluating the respiratory, circulatory and nervous systems to identify and treat any life-threatening conditions.
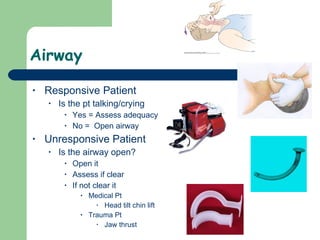
2) The assessment involves checking the patient's mental status, airway, breathing, circulation, and skin to evaluate condition and determine priority of care as either "stay and play" or "load and go".
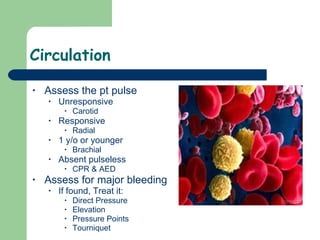
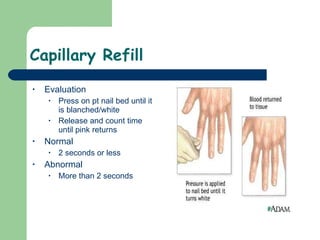
3) Key assessments include checking alertness, breathing rate and effort, pulse, bleeding, temperature, skin color, and capillary refill to evaluate perfusion and oxygenation. Life-threatening issues are treated immediately and transportation priority is determined.