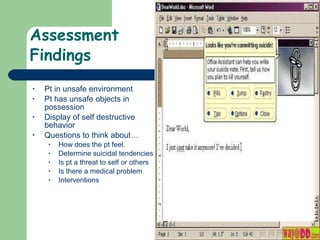
Behavioral emergencies involve abnormal behavior that is unacceptable or dangerous to the patient or others. Common causes include medical issues, drugs/alcohol, psychiatric problems, and situational stress. EMTs must assess for risk of harm, determine if the patient is suicidal or violent, and intervene appropriately which may include restraint if necessary for safety. Any use of force should be reasonable and well-documented to protect EMTs from potential legal issues.