Embed presentation
Downloaded 257 times



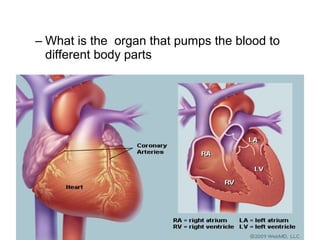
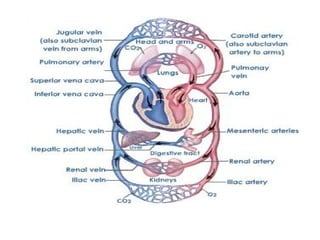
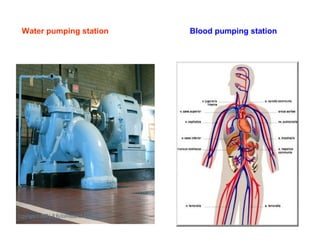
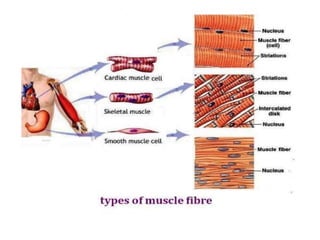

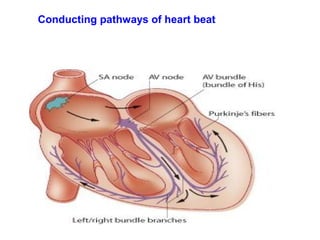
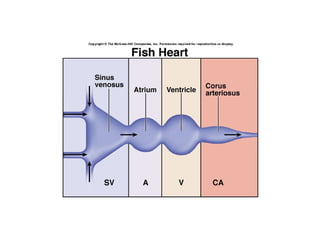
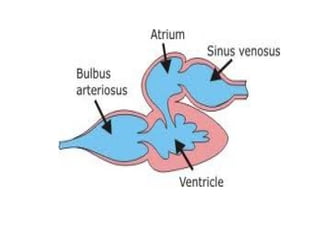
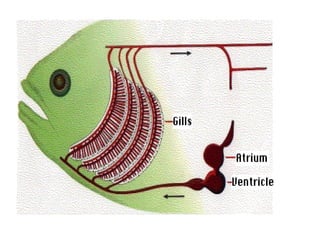
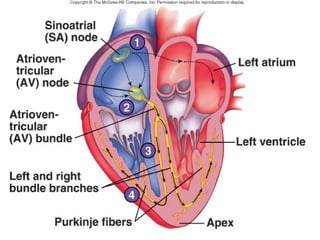
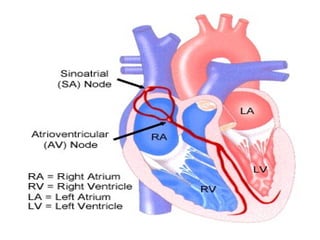
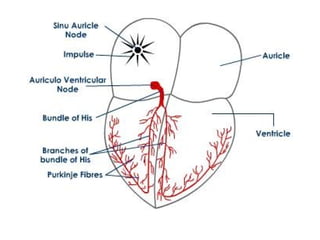
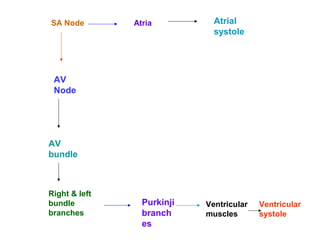
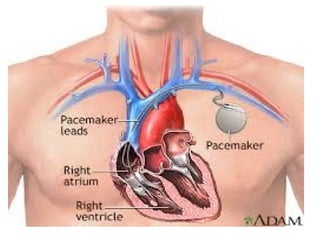
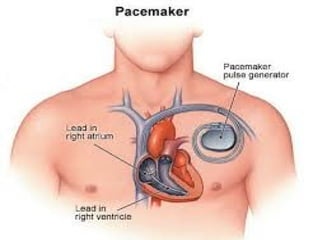
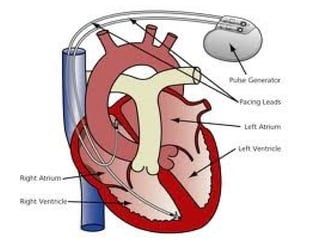
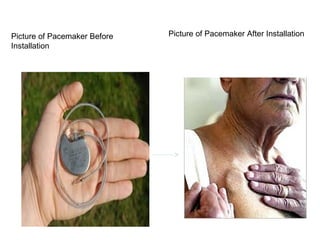
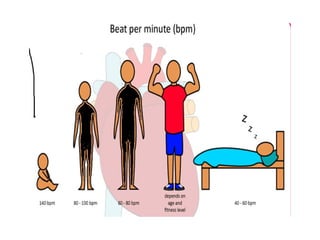

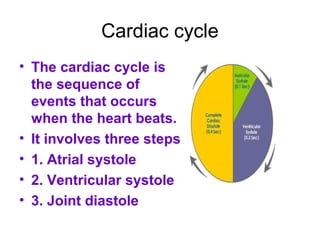
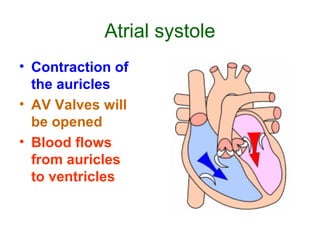
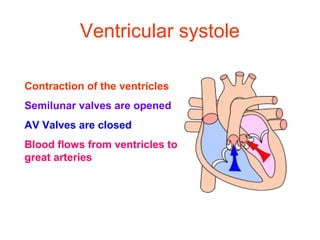
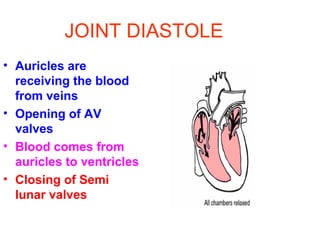
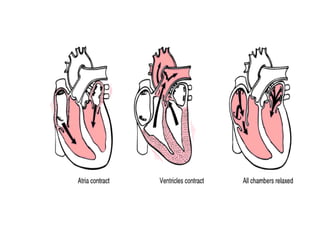

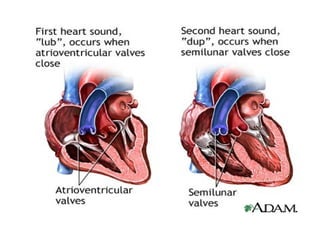
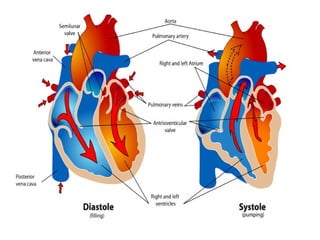


The document summarizes the circulatory system and heart function. It discusses how the circulatory system transports digested food throughout the body using blood pumped by the heart. The heart is the organ that pumps blood through the circulatory system. It describes the cardiac cycle which involves atrial systole, ventricular systole, and joint diastole. It also discusses the pacemaker region that initiates heart contractions, conducting pathways of the heartbeat, and average heart rates at rest for infants, children, and adults.

































