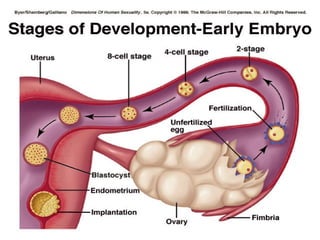
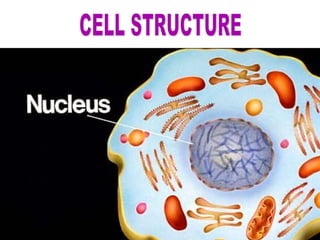
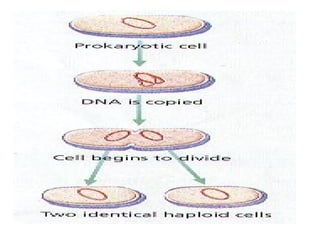
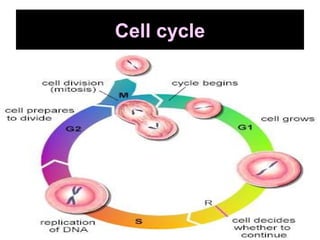
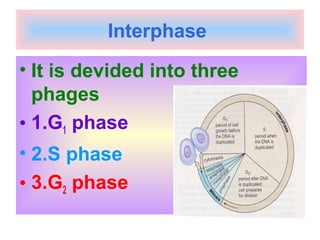
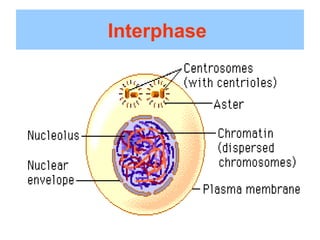
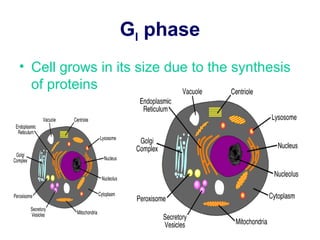
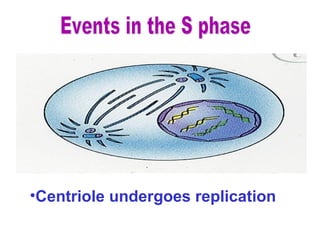
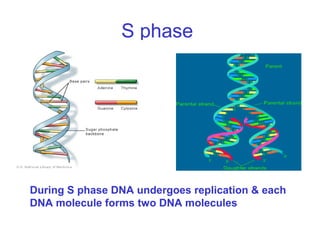
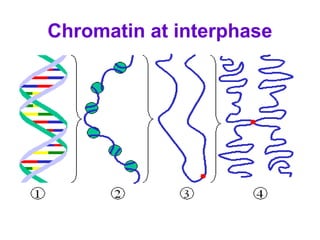
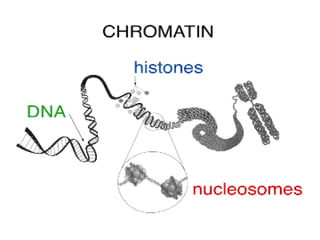
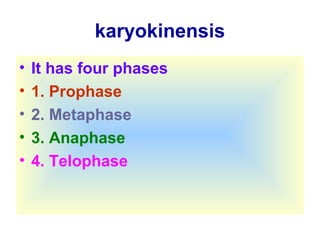
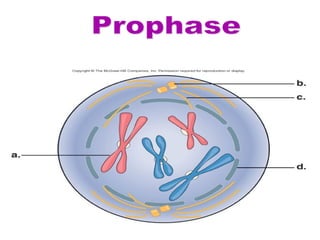
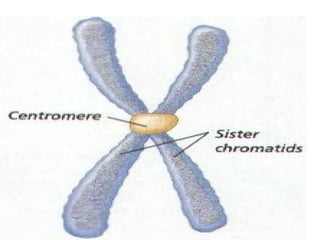
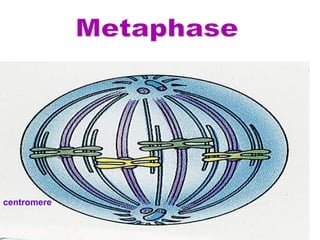
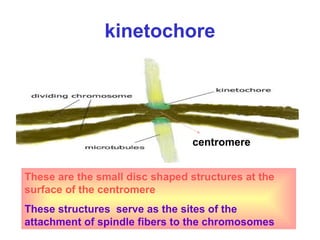
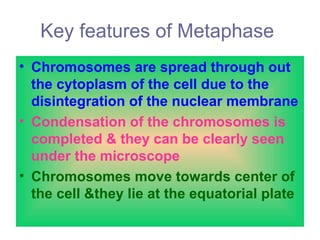
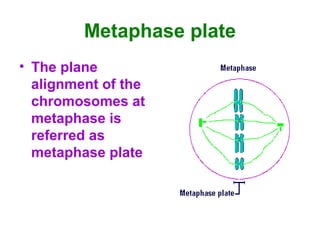
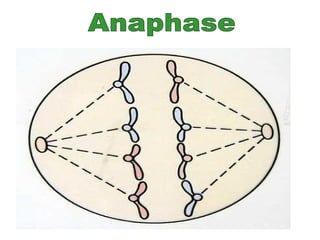
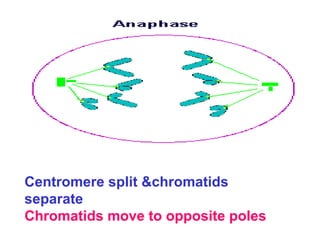
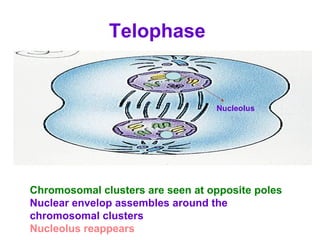
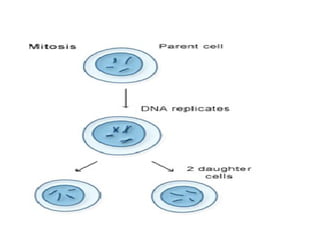
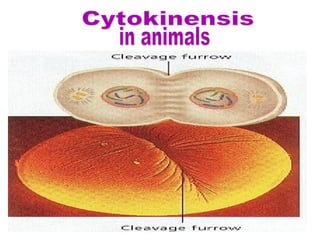
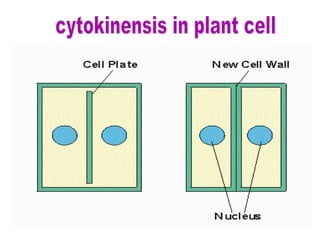
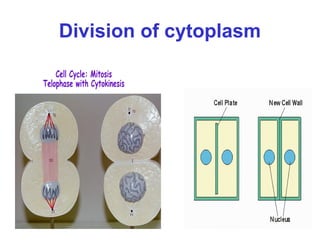
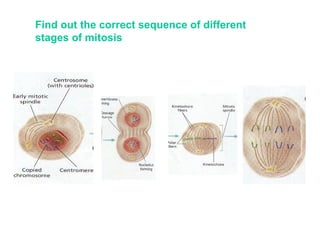
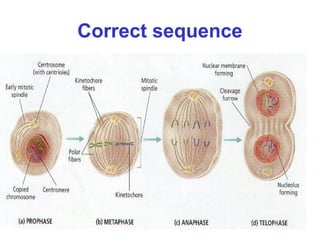
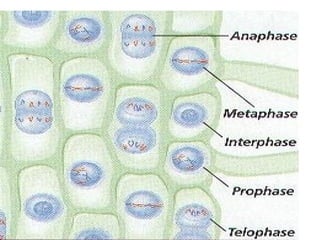
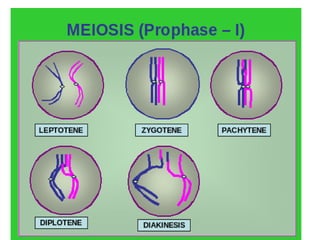
The document discusses the cell cycle and cell division. It begins by listing the chromosome numbers of various organisms. It then describes the two main phases of the cell cycle as interphase and mitosis. Interphase is further divided into G1, S, and G2 phases. The S phase involves DNA replication where each DNA molecule forms two DNA molecules. Mitosis is divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase where the chromosomes align and separate. The document also discusses the key events that occur during each phase of mitosis.