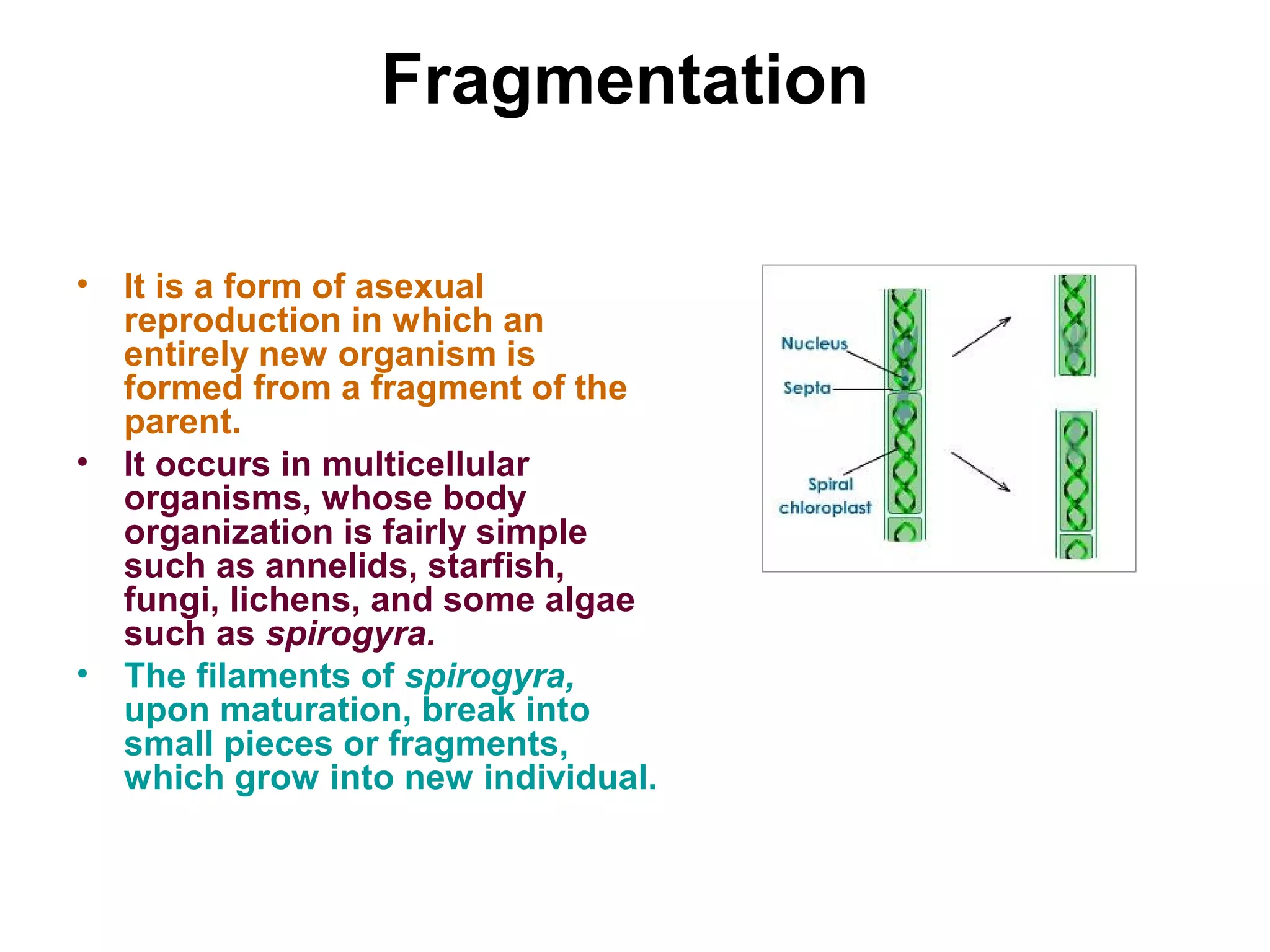
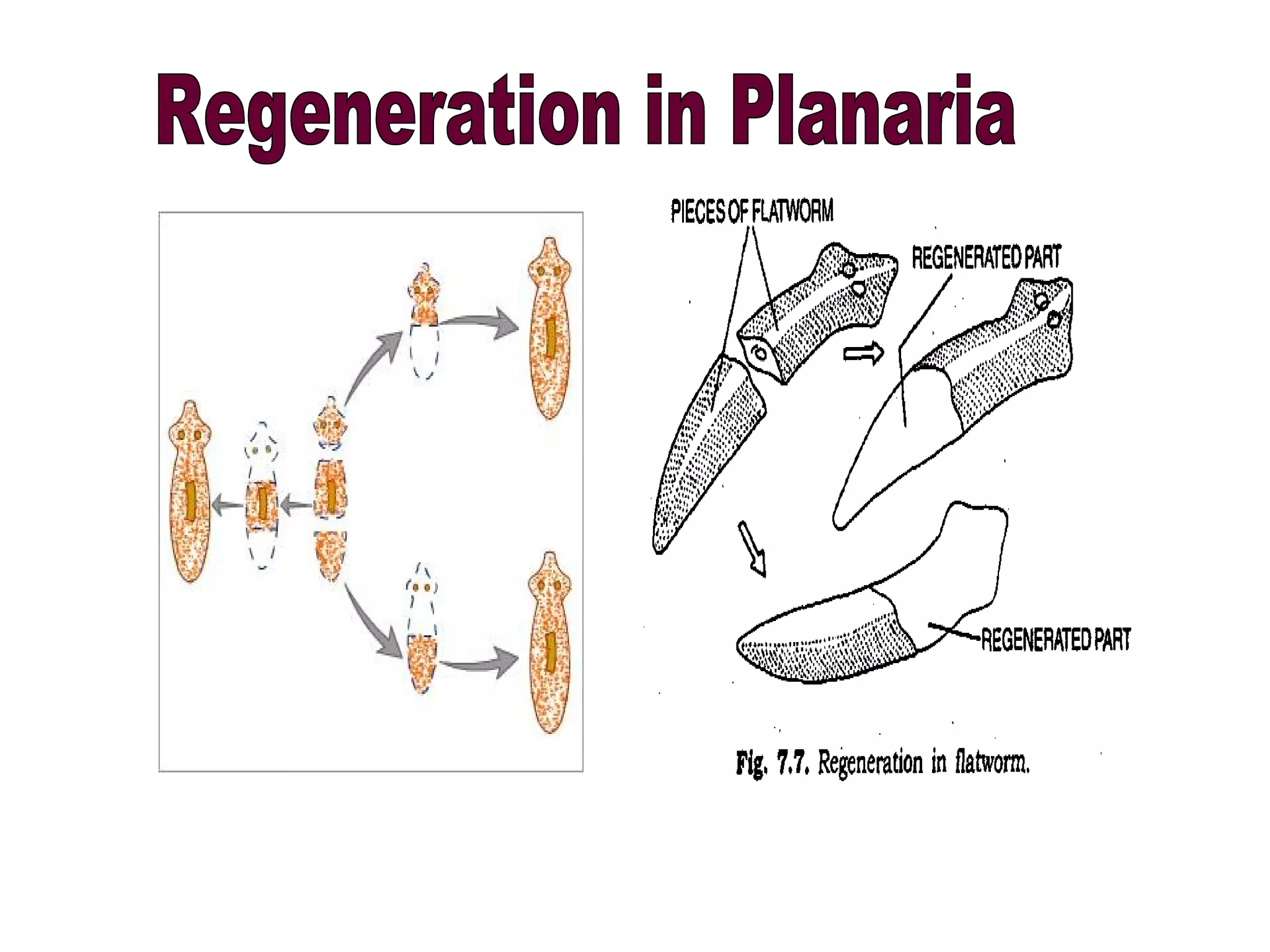
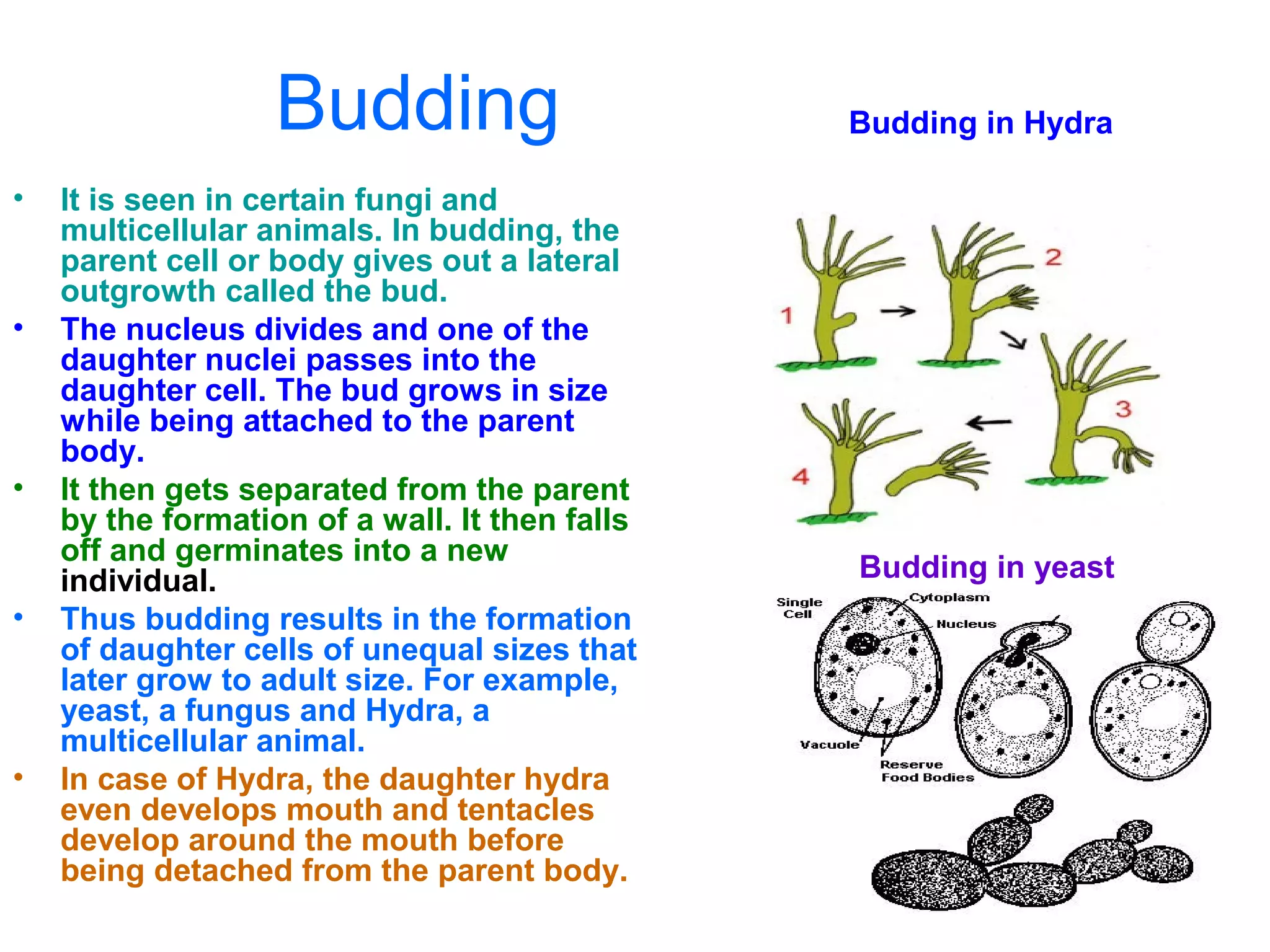
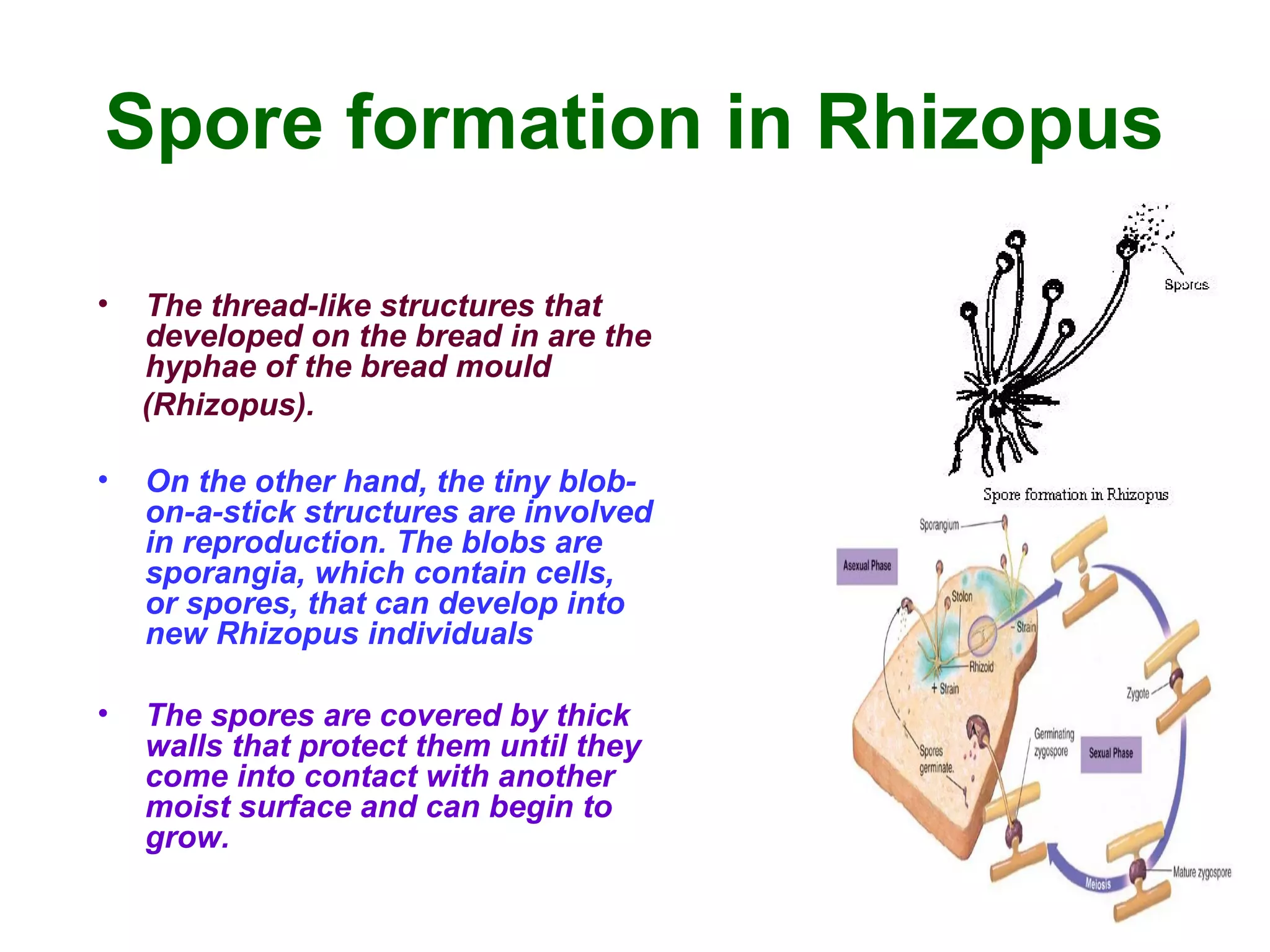
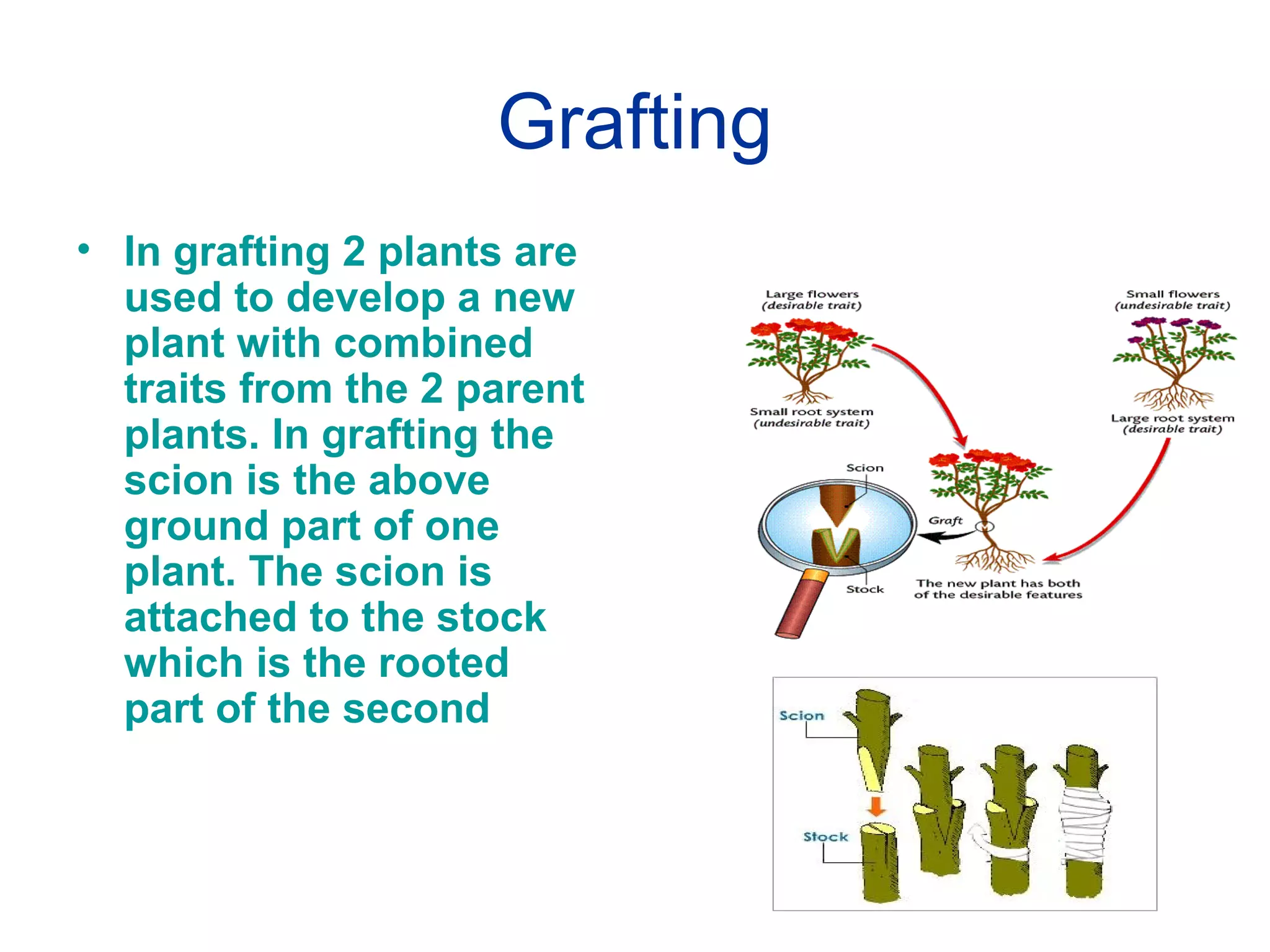
Reproduction enables the continuity of species through generations. Sexual reproduction involves two individuals while asexual reproduction involves a single individual. Unicellular organisms reproduce through cell division while multicellular organisms use specialized reproductive organs. Asexual reproduction methods include fission, fragmentation, budding, regeneration, vegetative propagation, and spore formation. Vegetative propagation uses plant parts like stems, leaves, and roots to generate new plants.