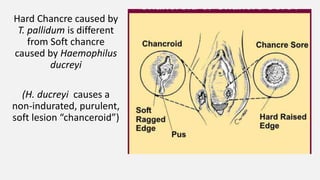
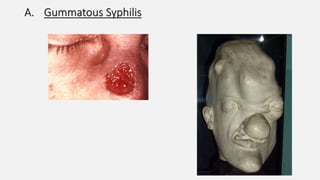
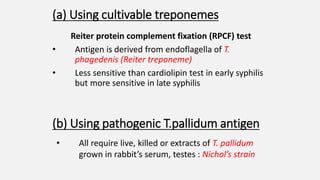
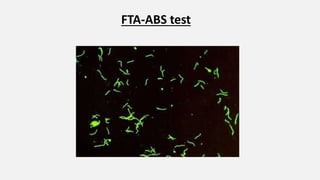
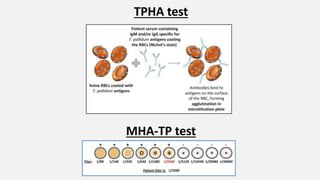
Spirochaetes are elongated, motile bacteria with endoflagella that allow flexing and twisting movements. Treponema pallidum causes syphilis in humans. It has a distinctive morphology and causes primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary stages of infection. Diagnosis involves direct visualization of the spirochete or using serological tests like VDRL, RPR, and treponemal tests that detect antibodies to T. pallidum antigens. Treatment is with penicillin which can cause a Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction.