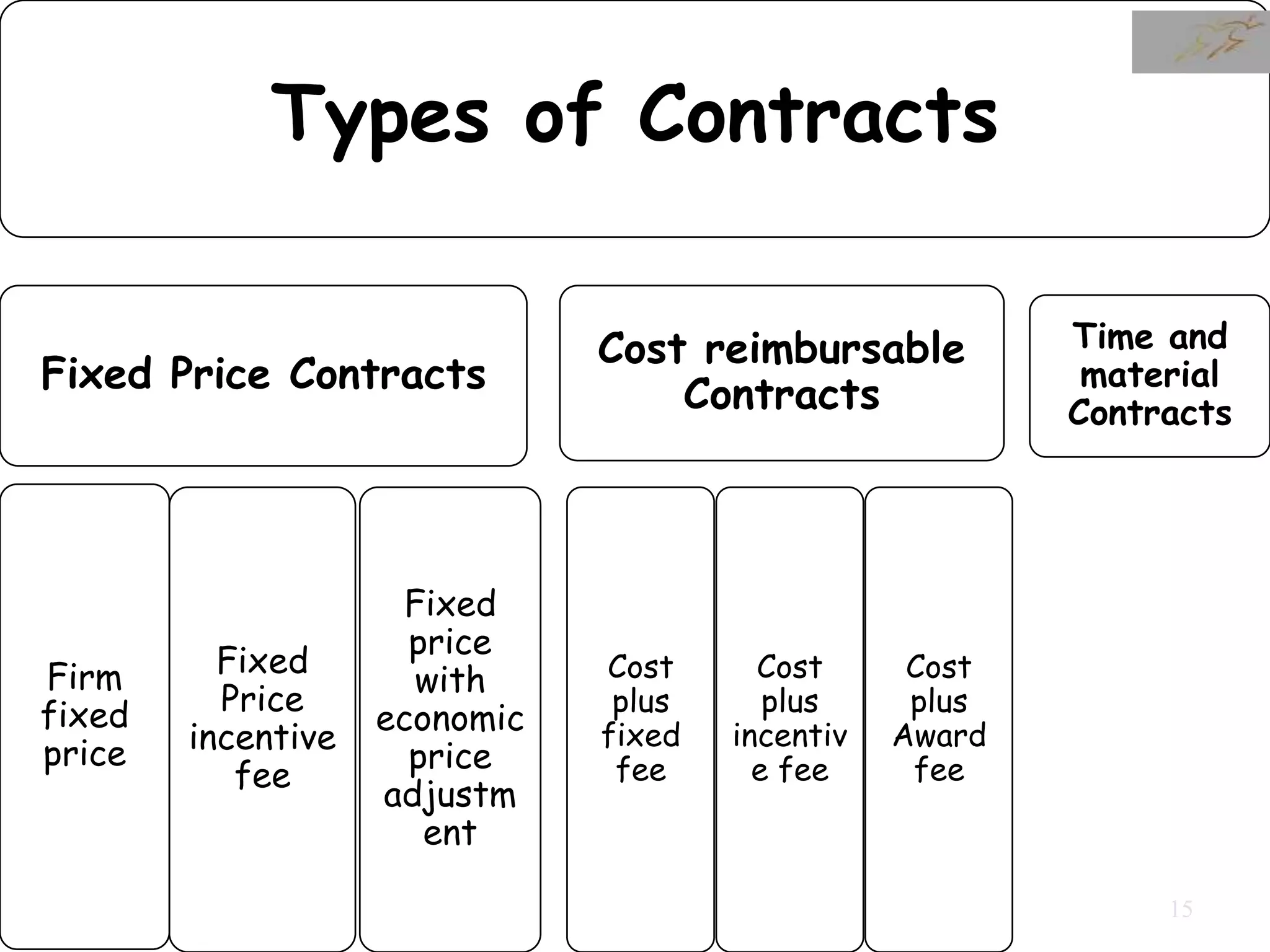
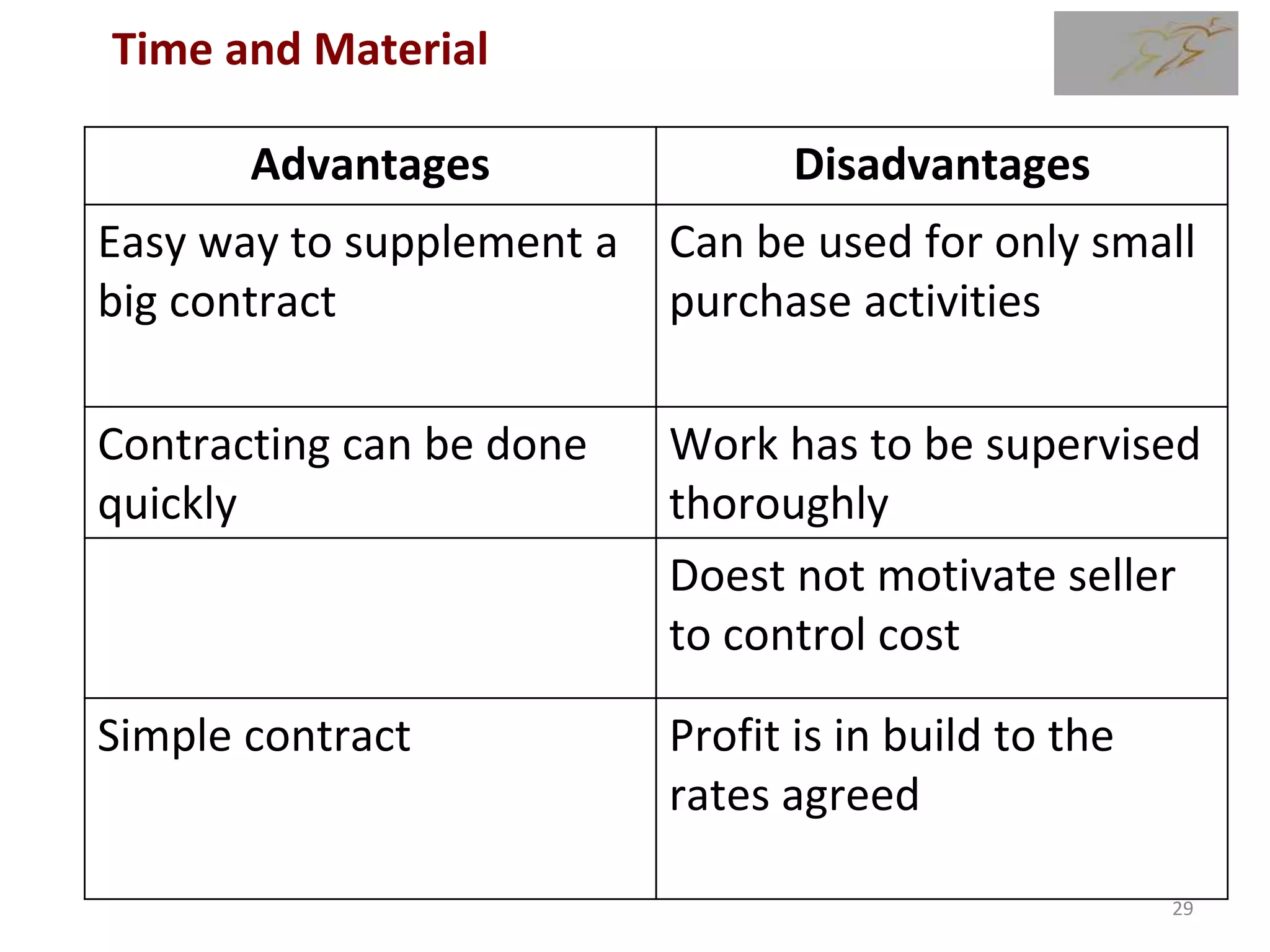
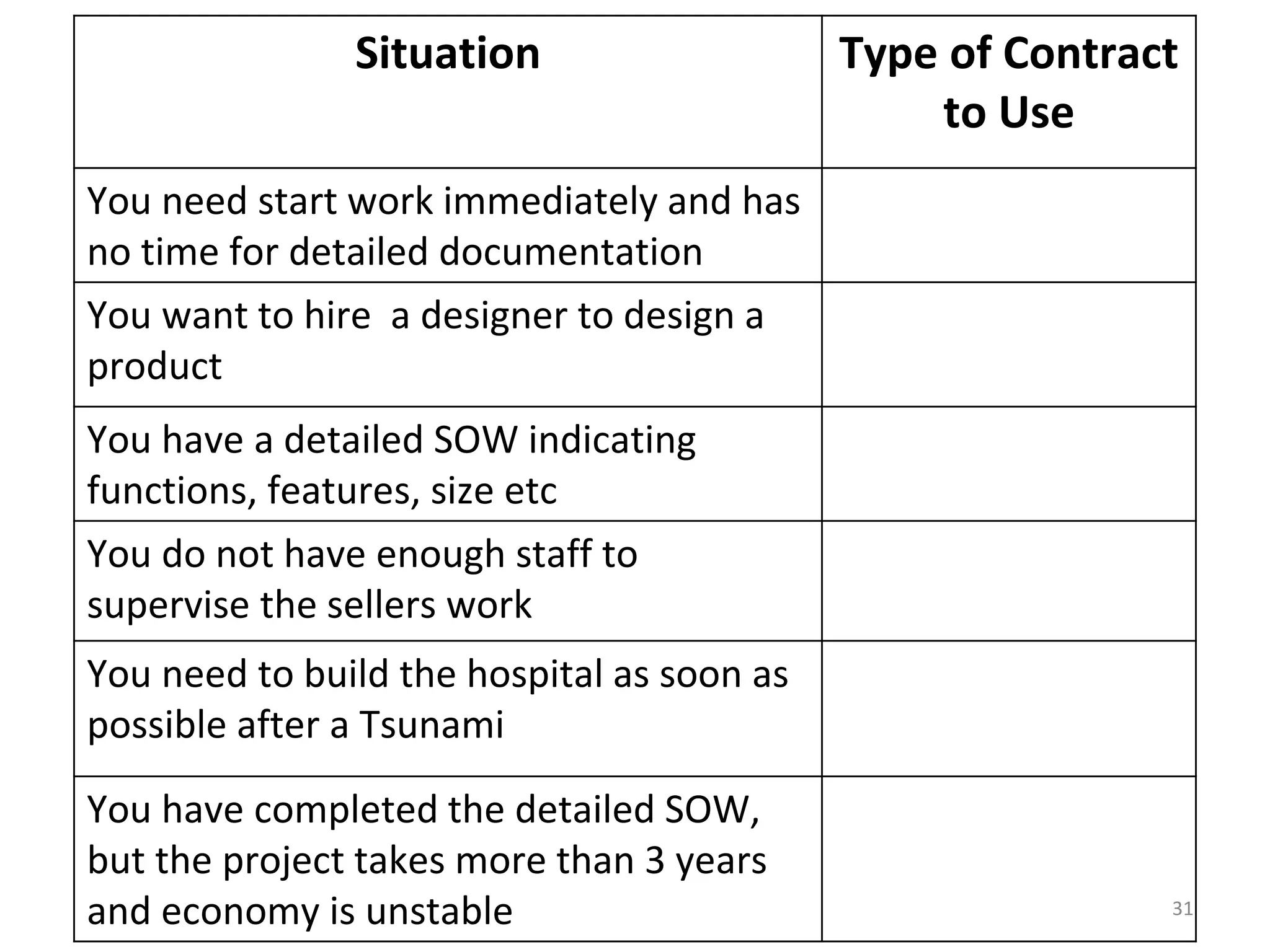
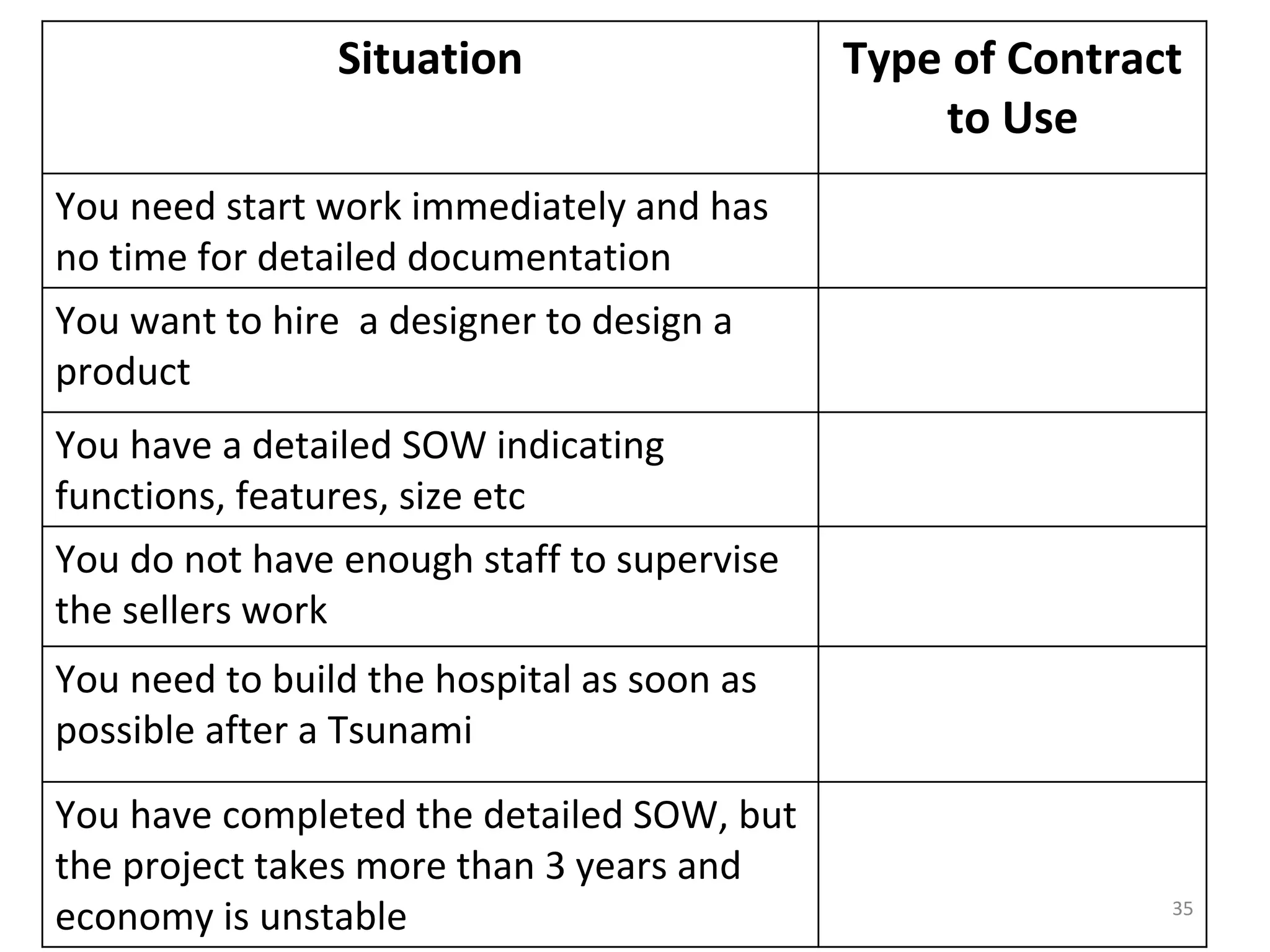
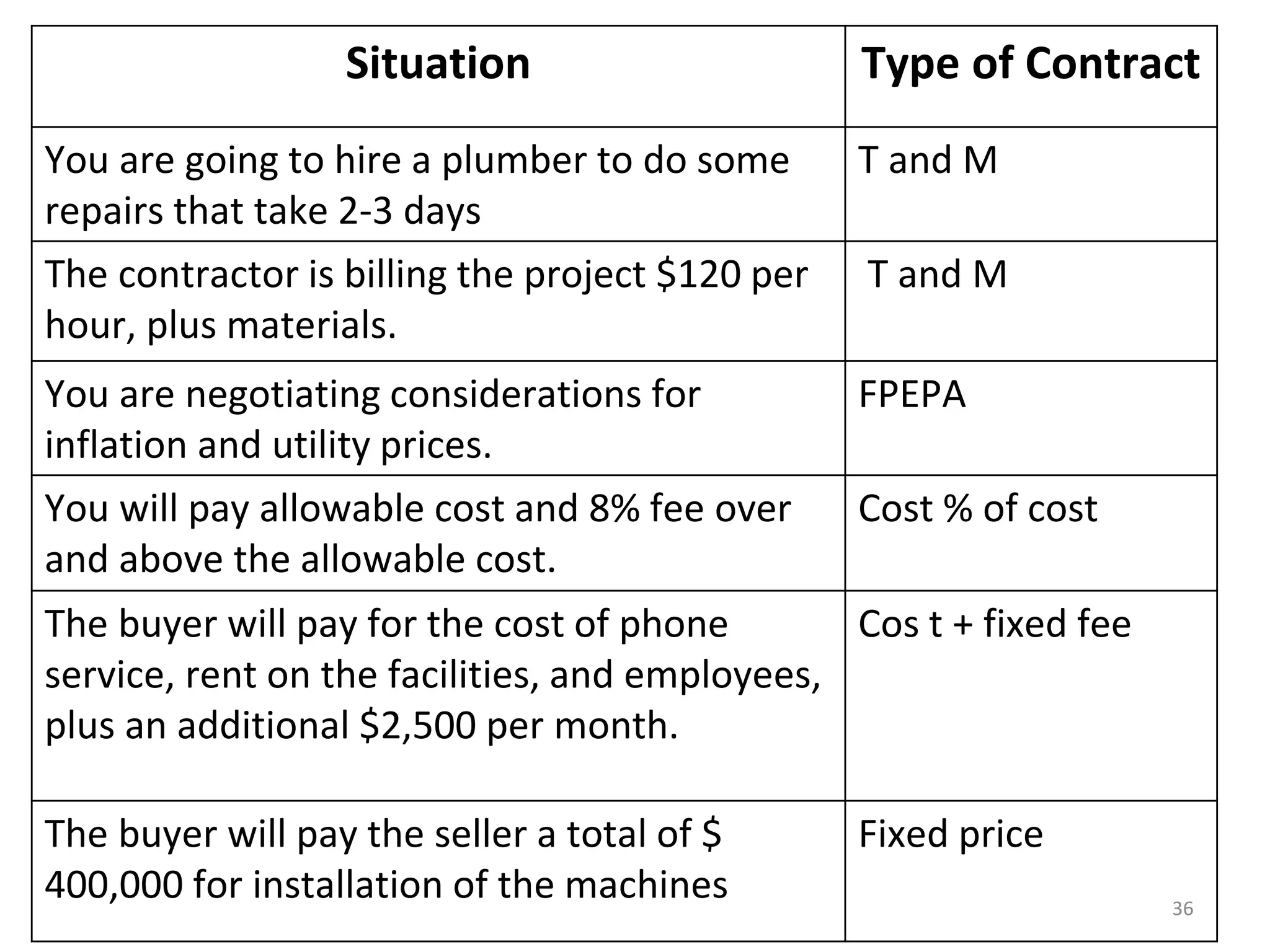
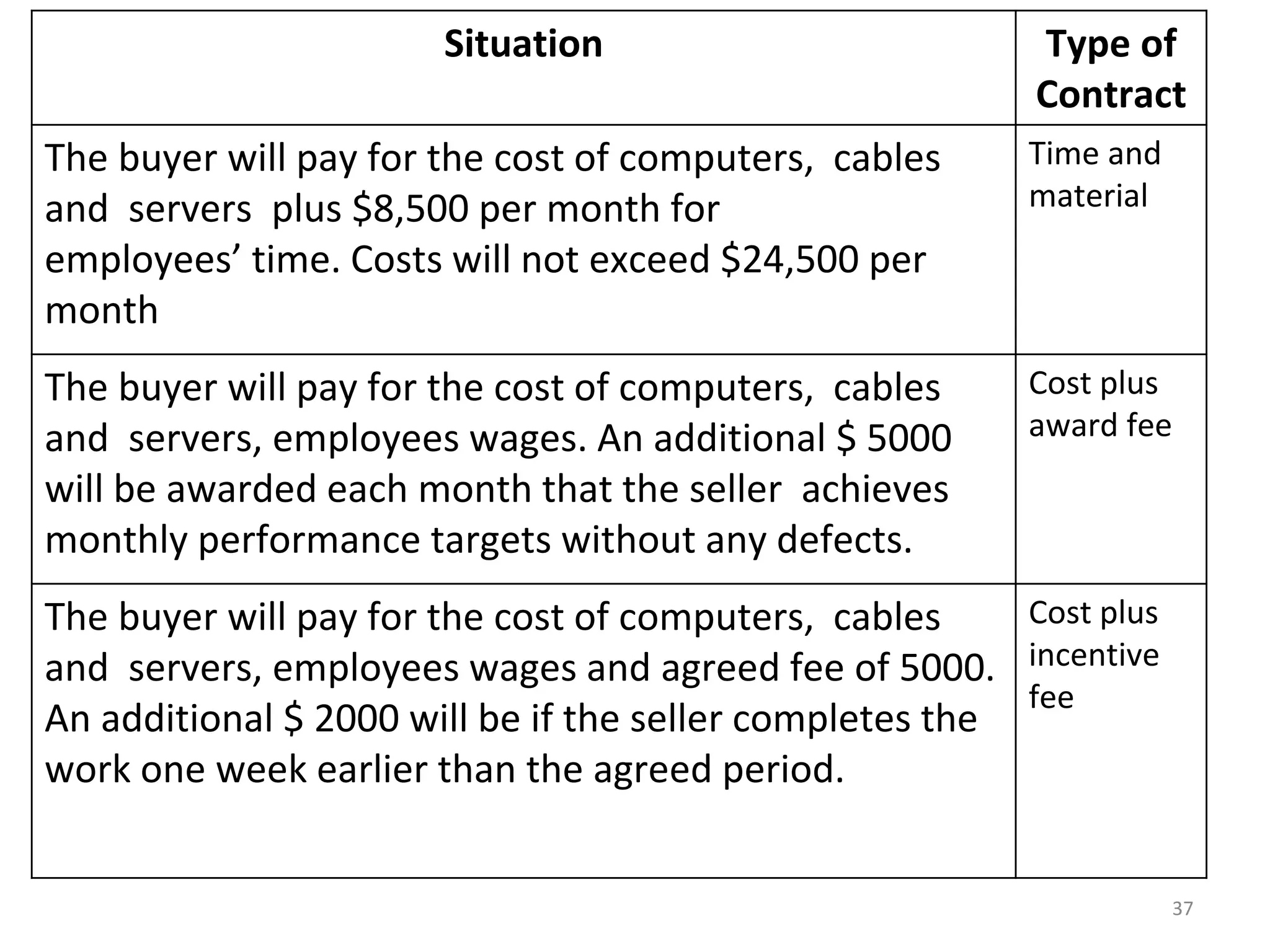
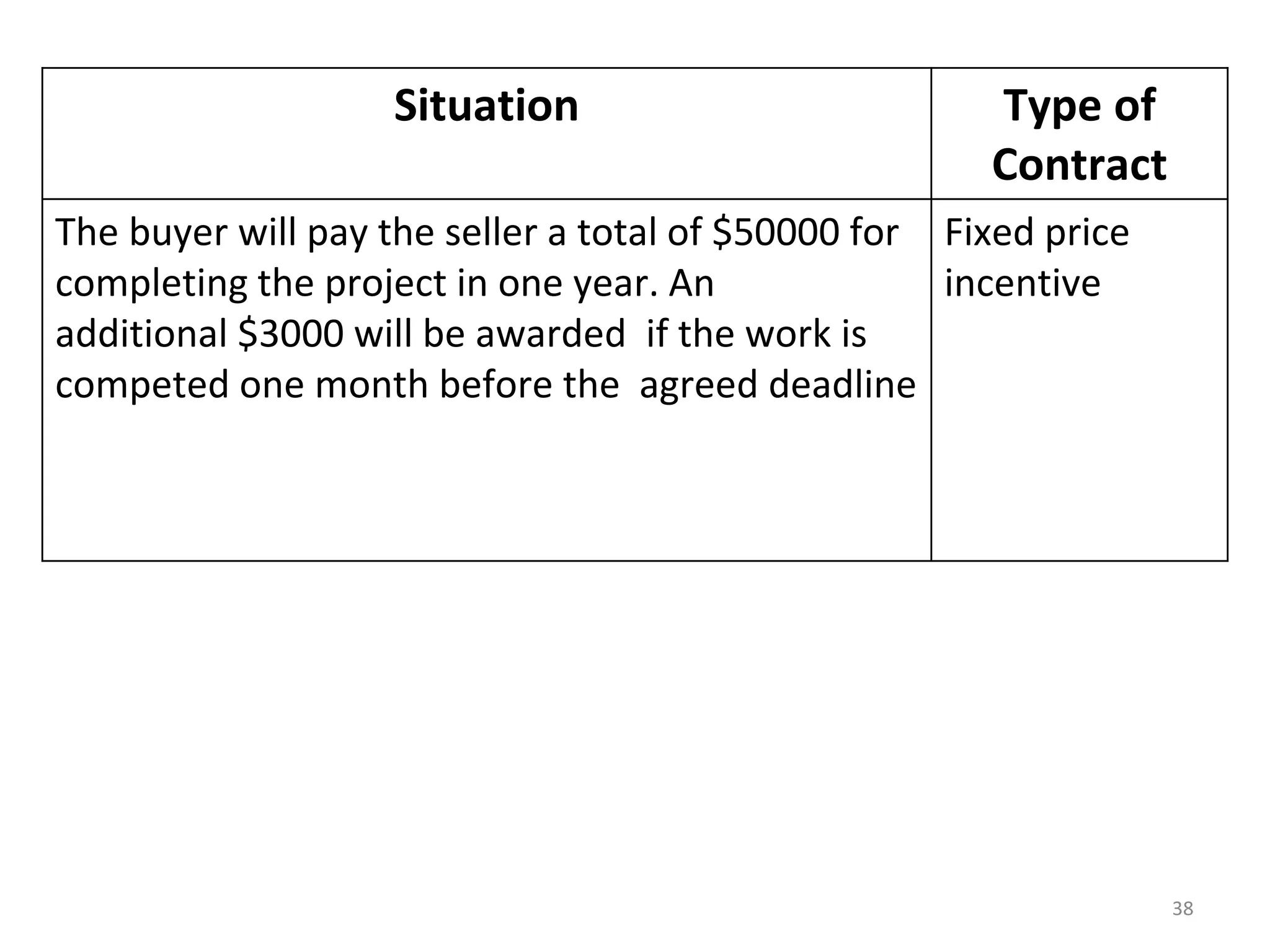
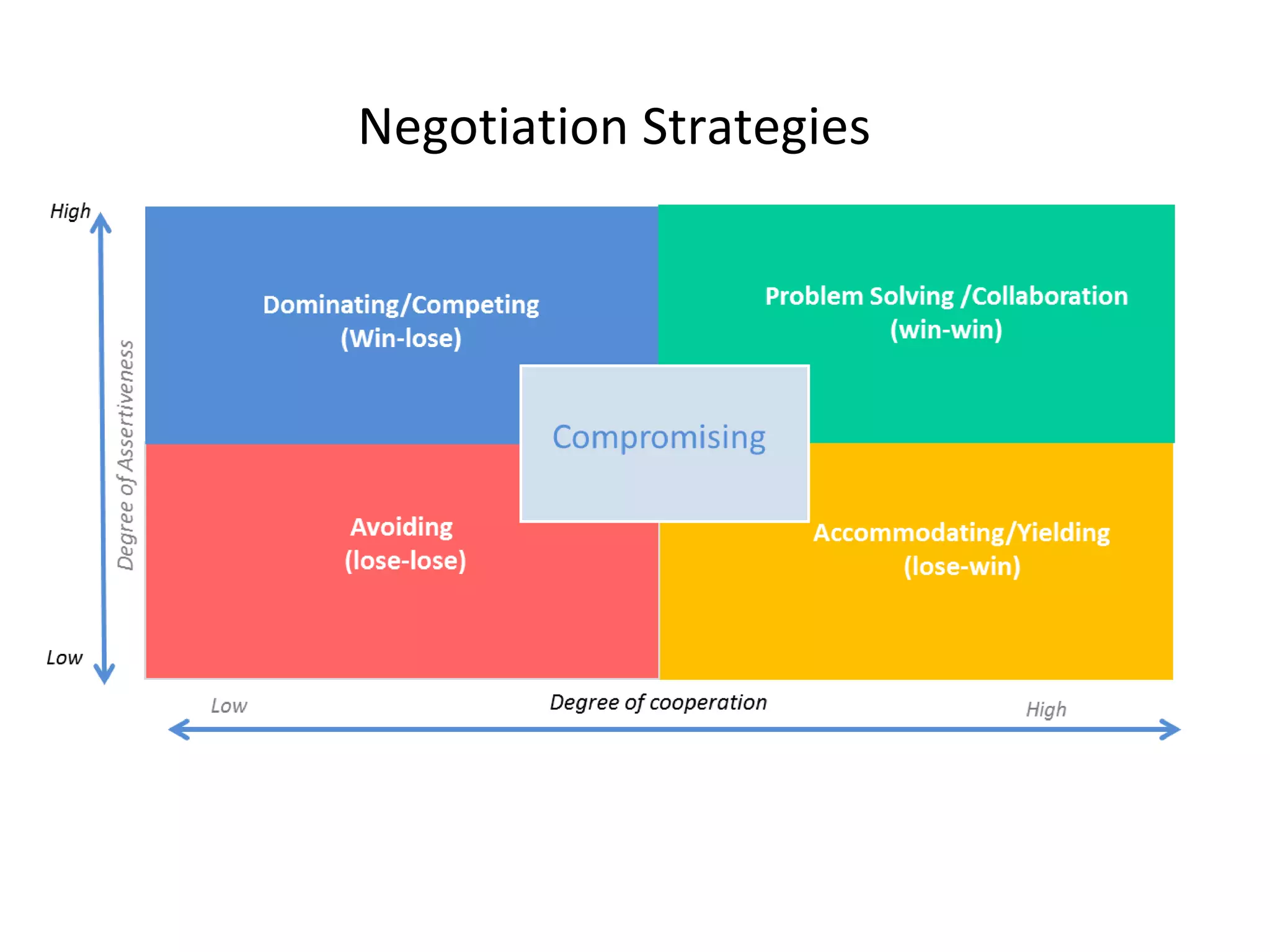
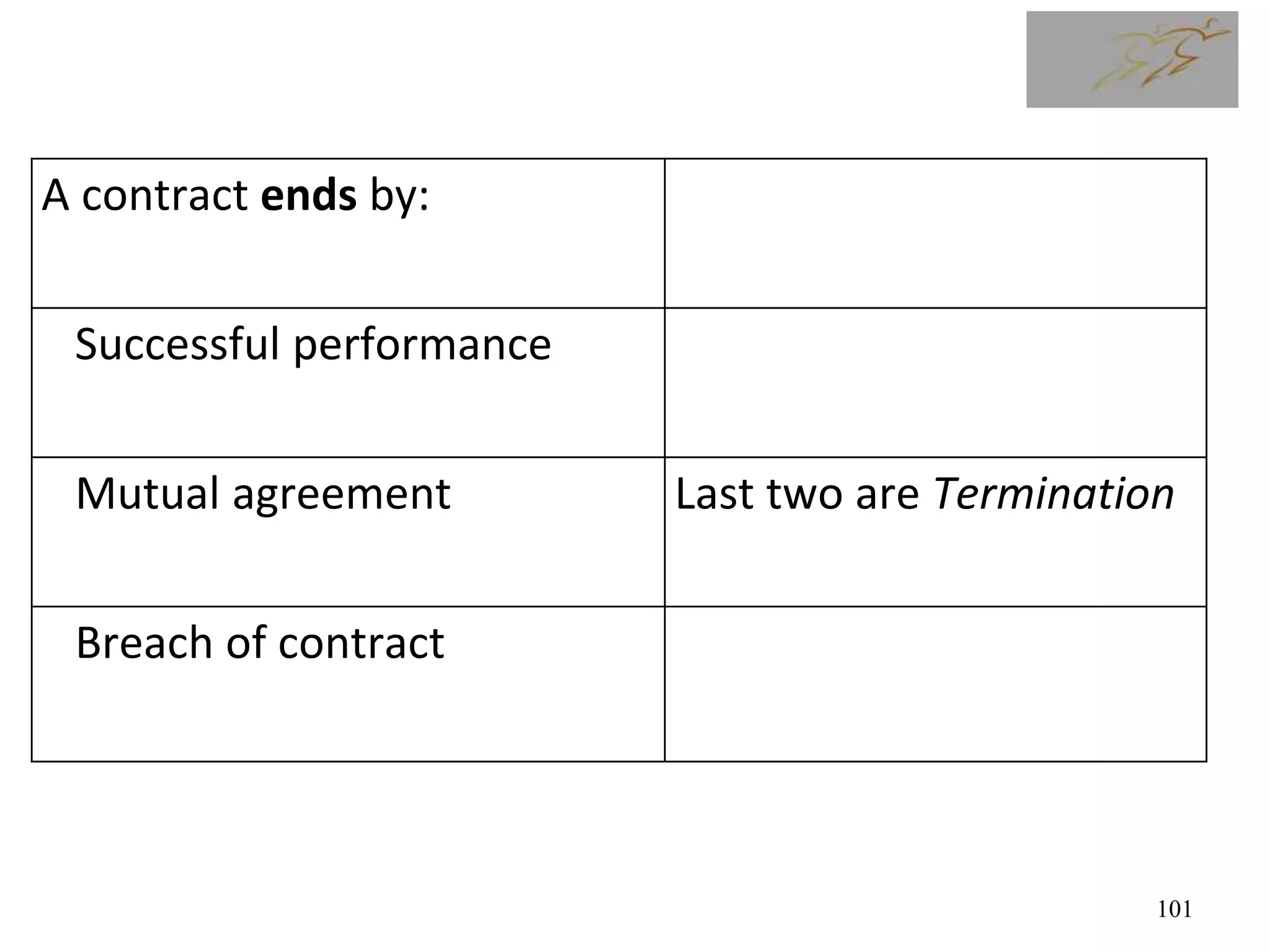
Time and Material
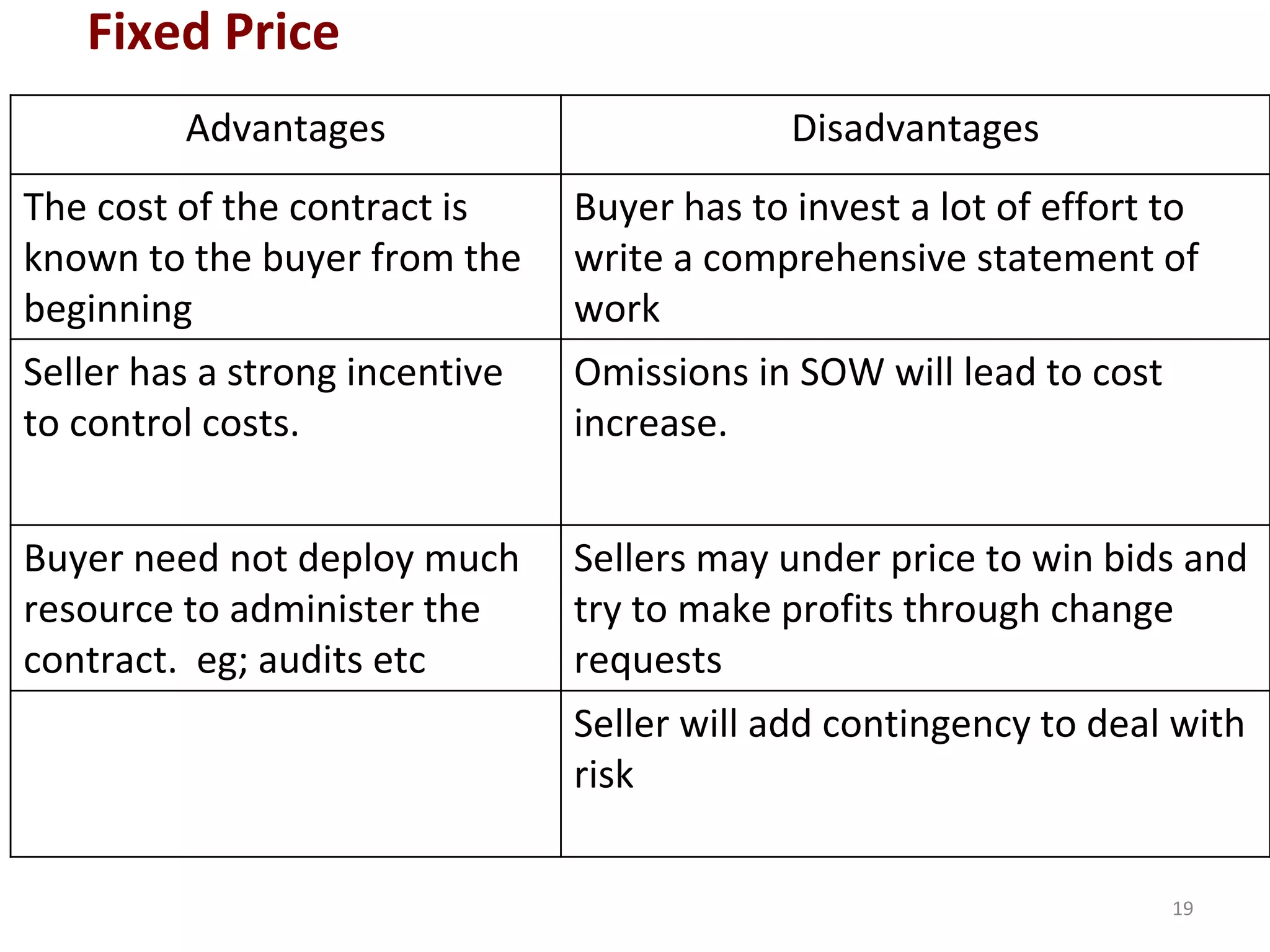
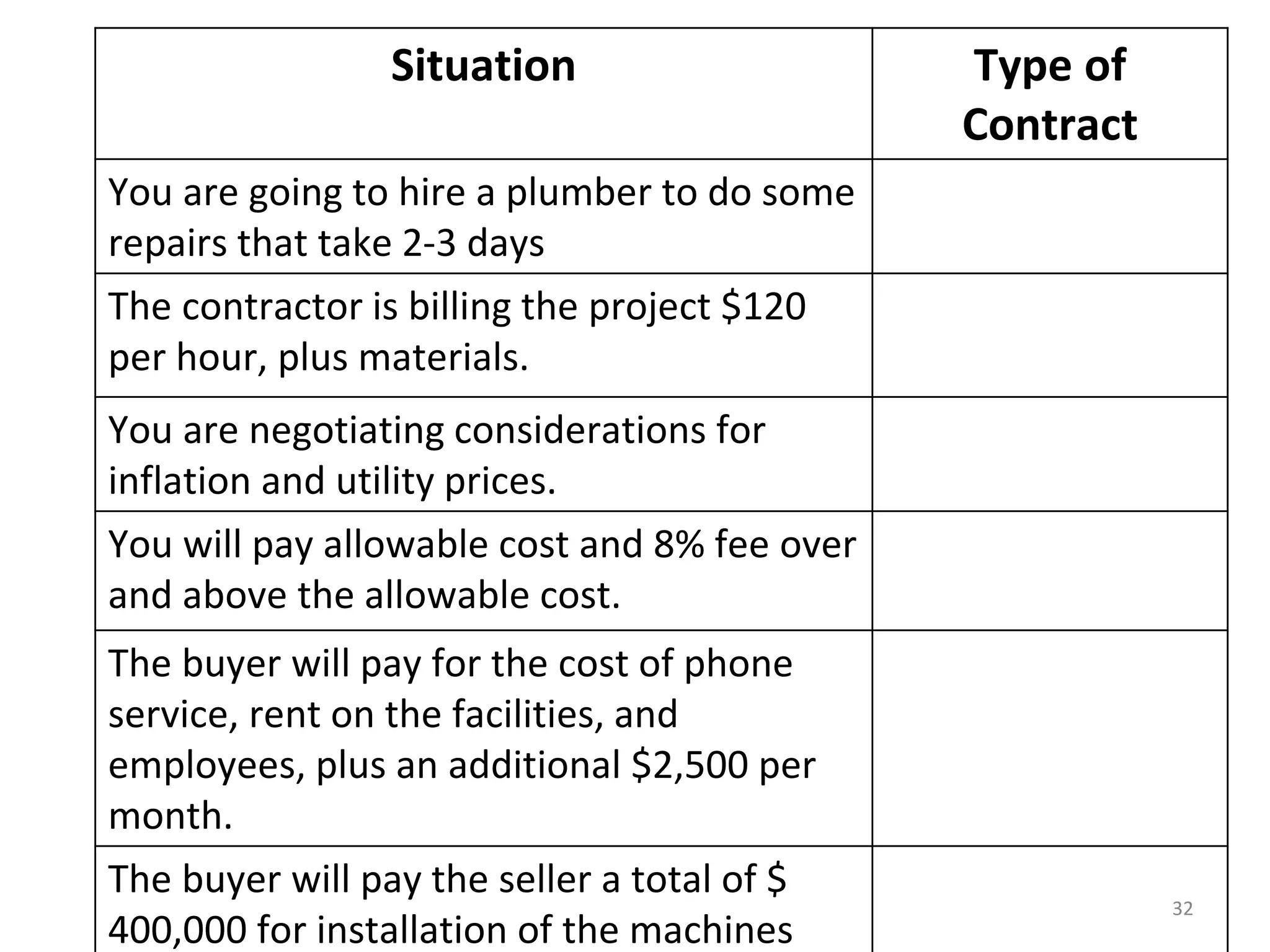
Fixed Price
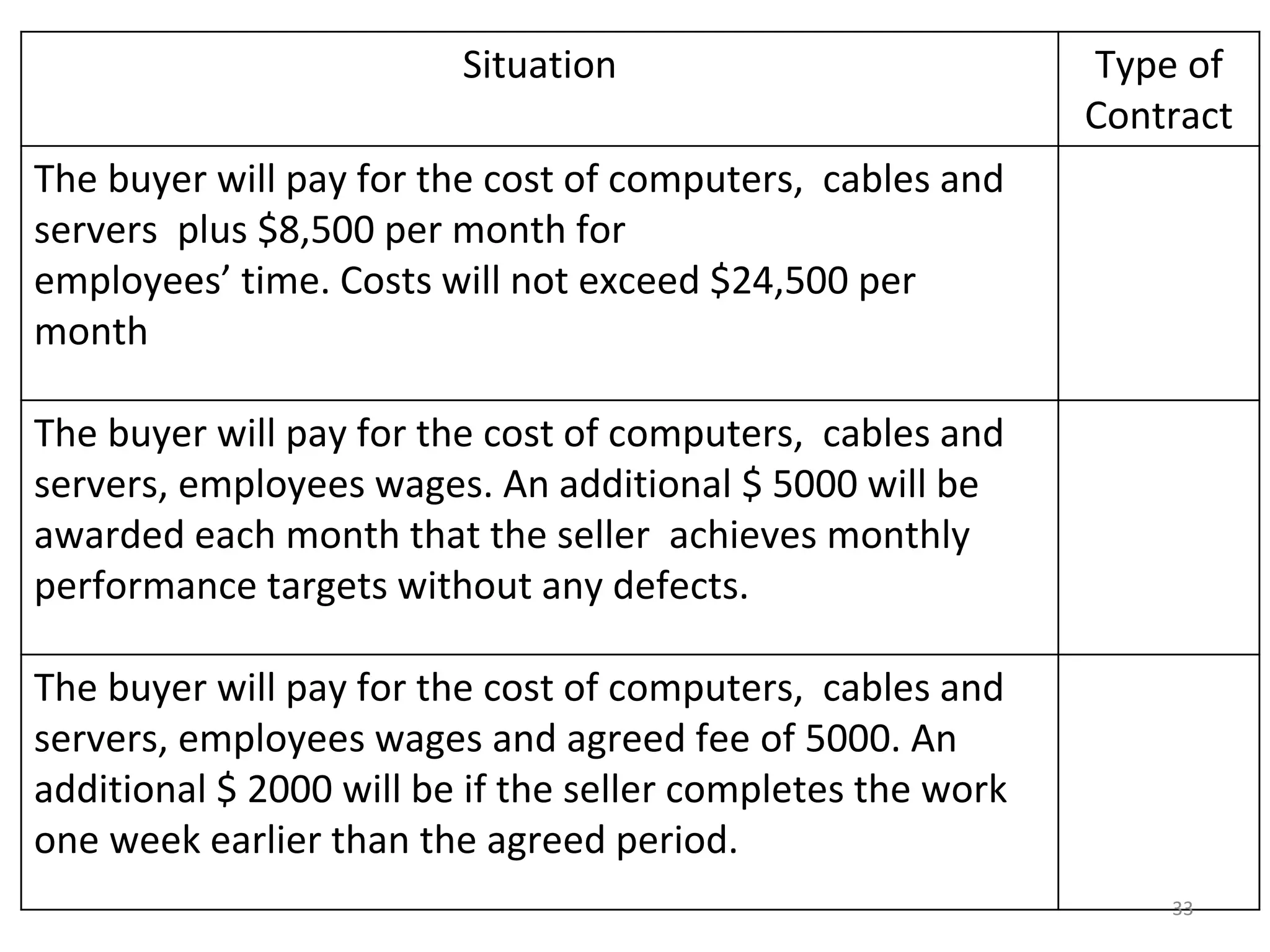
Fixed Price
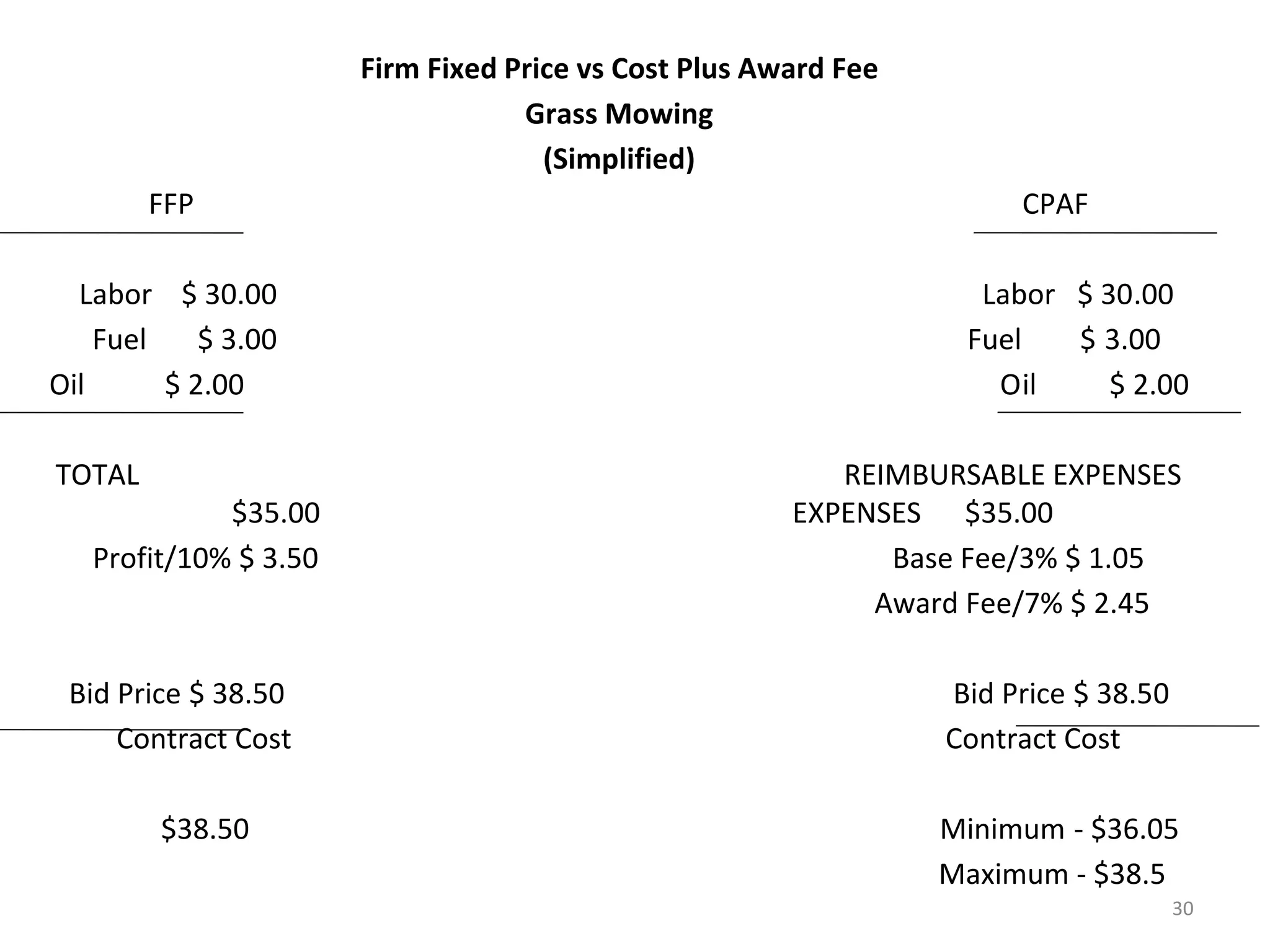
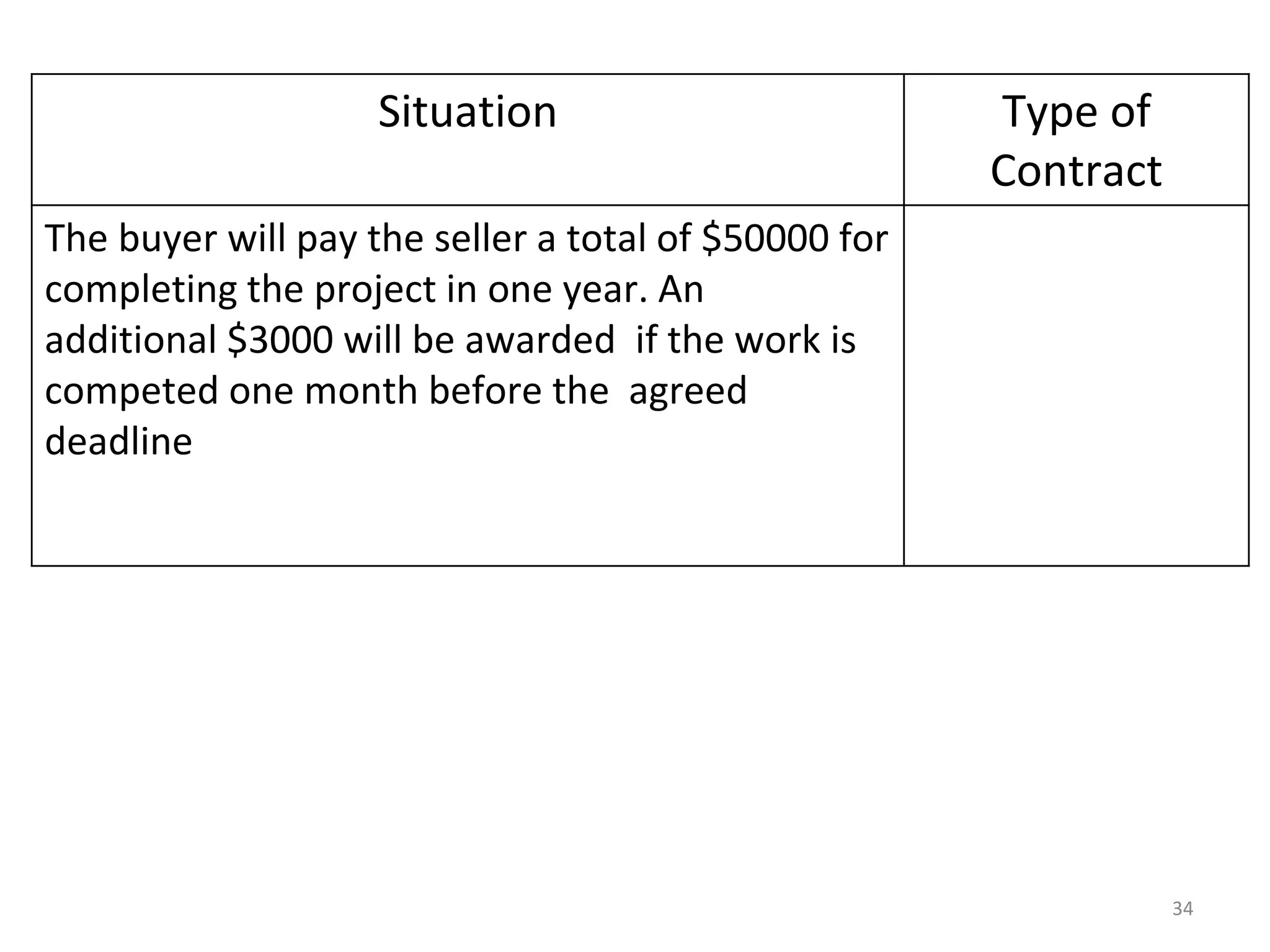
Cost Plus Award Fee
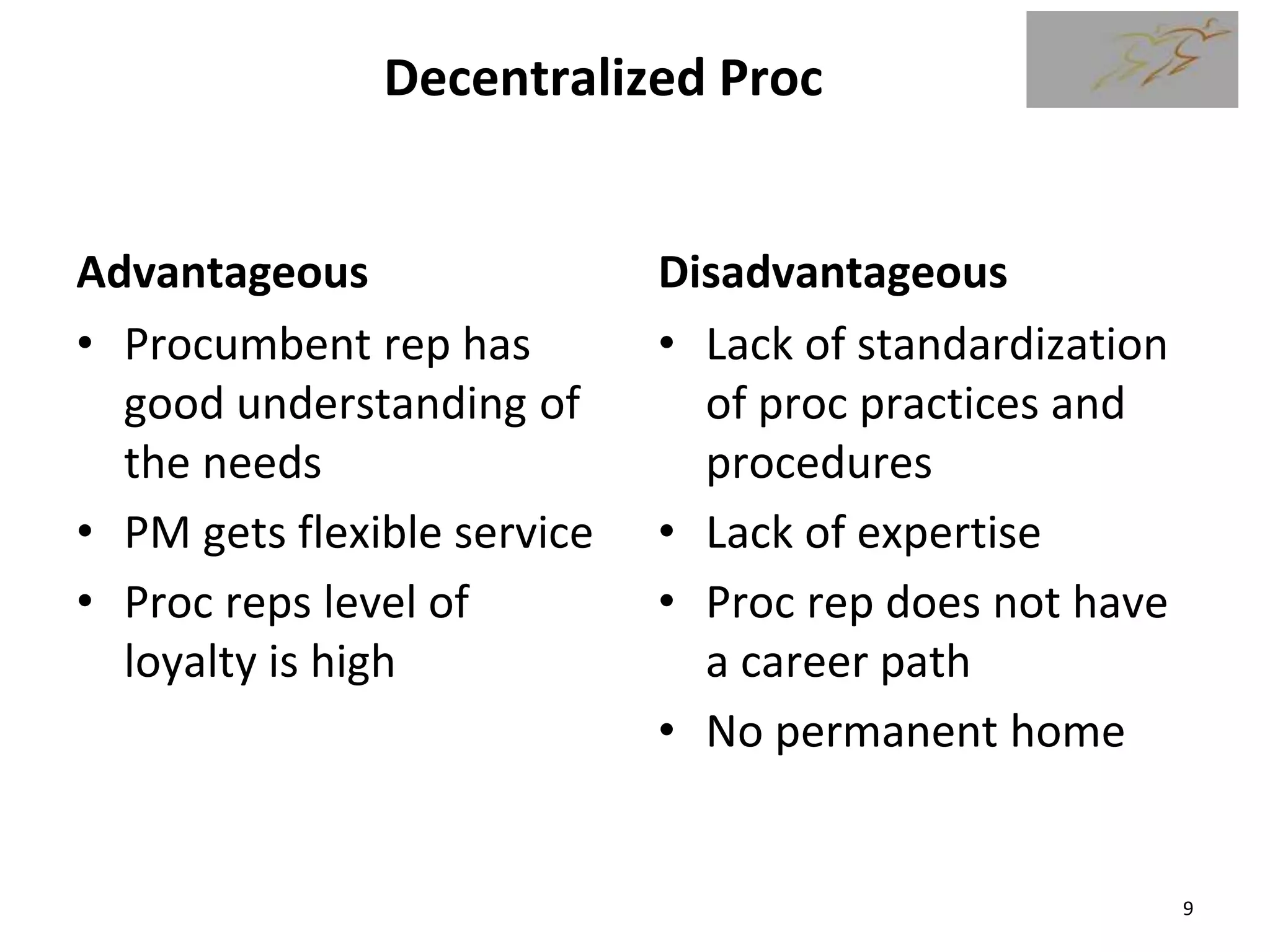
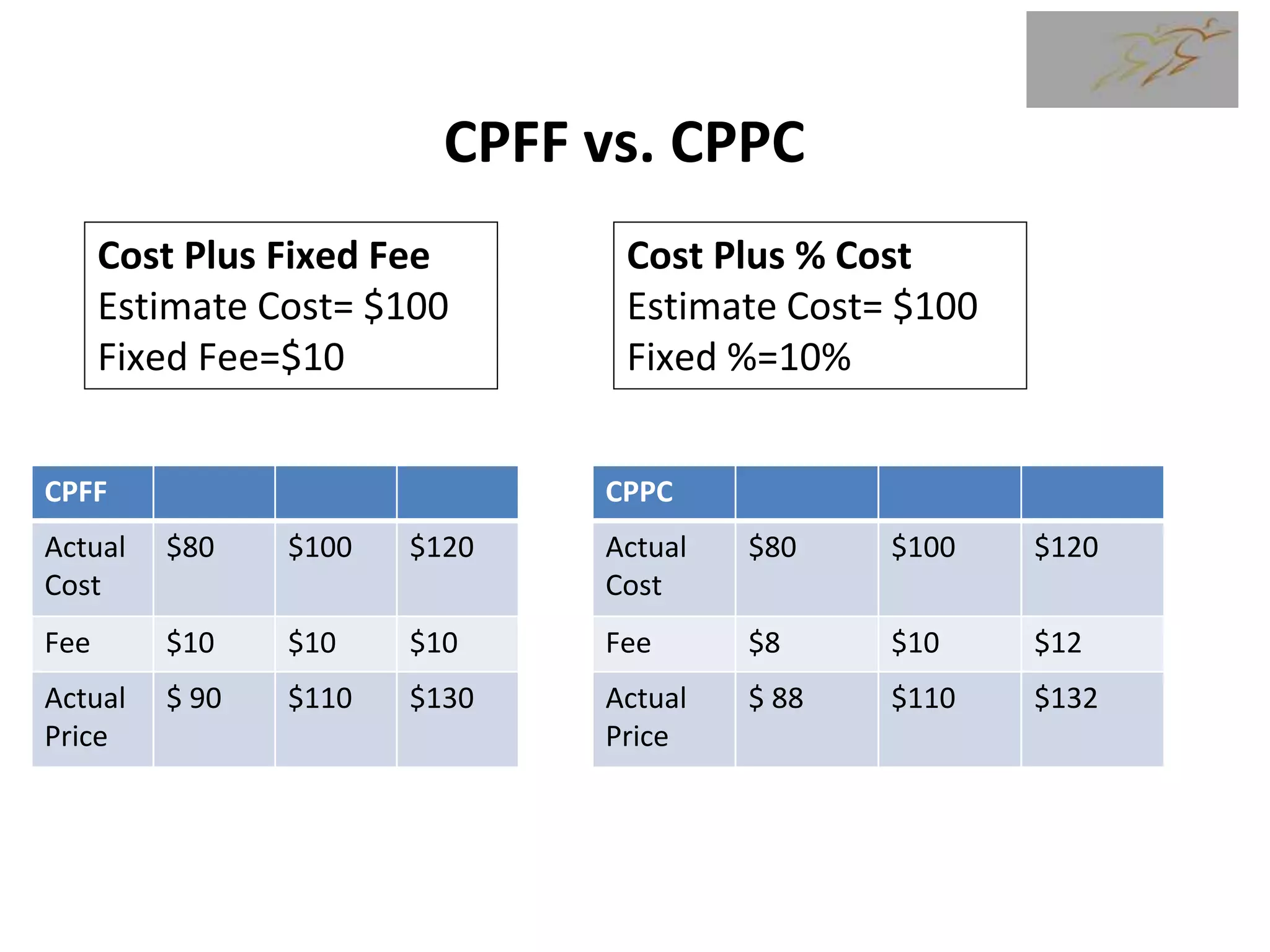
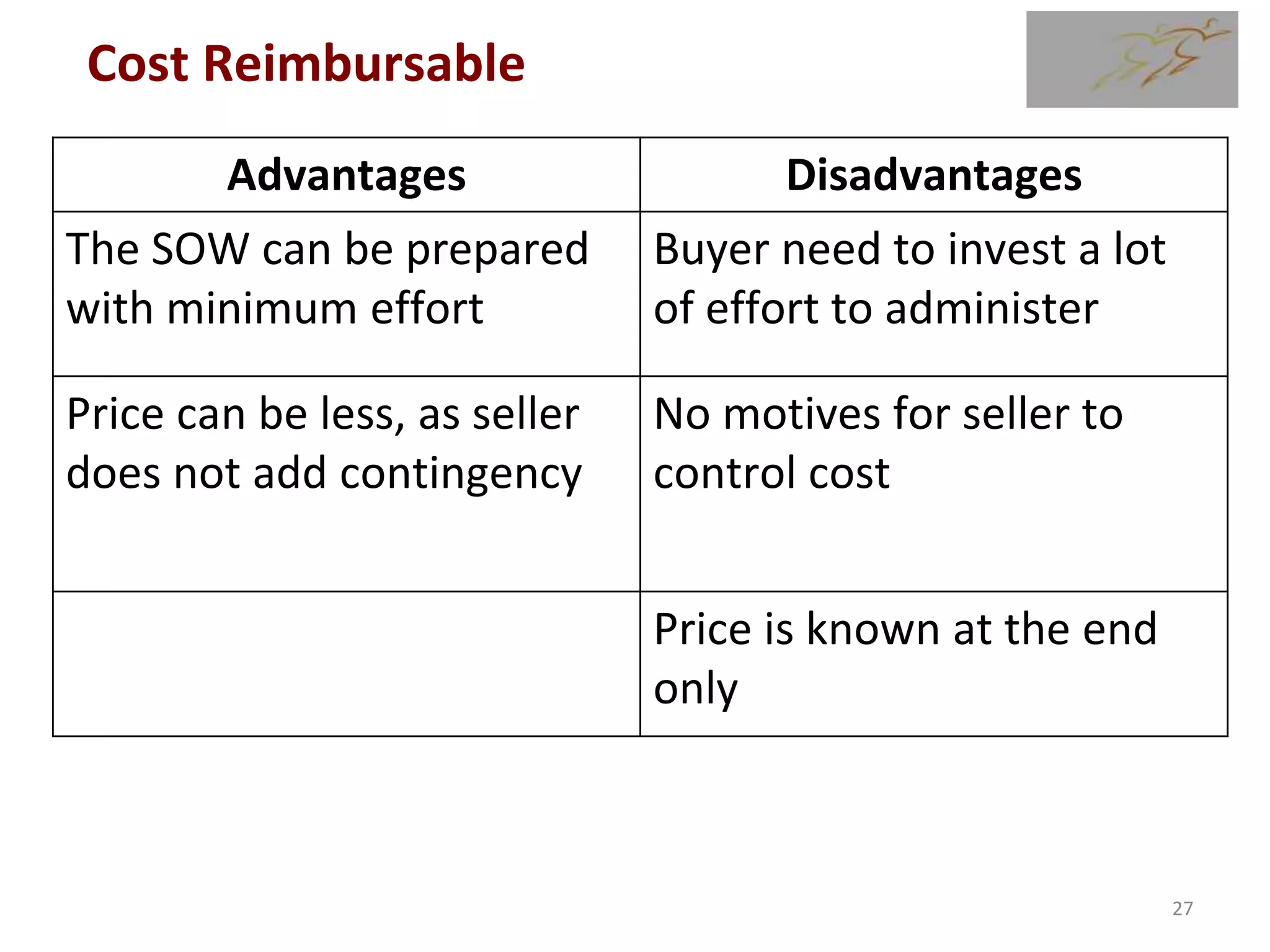
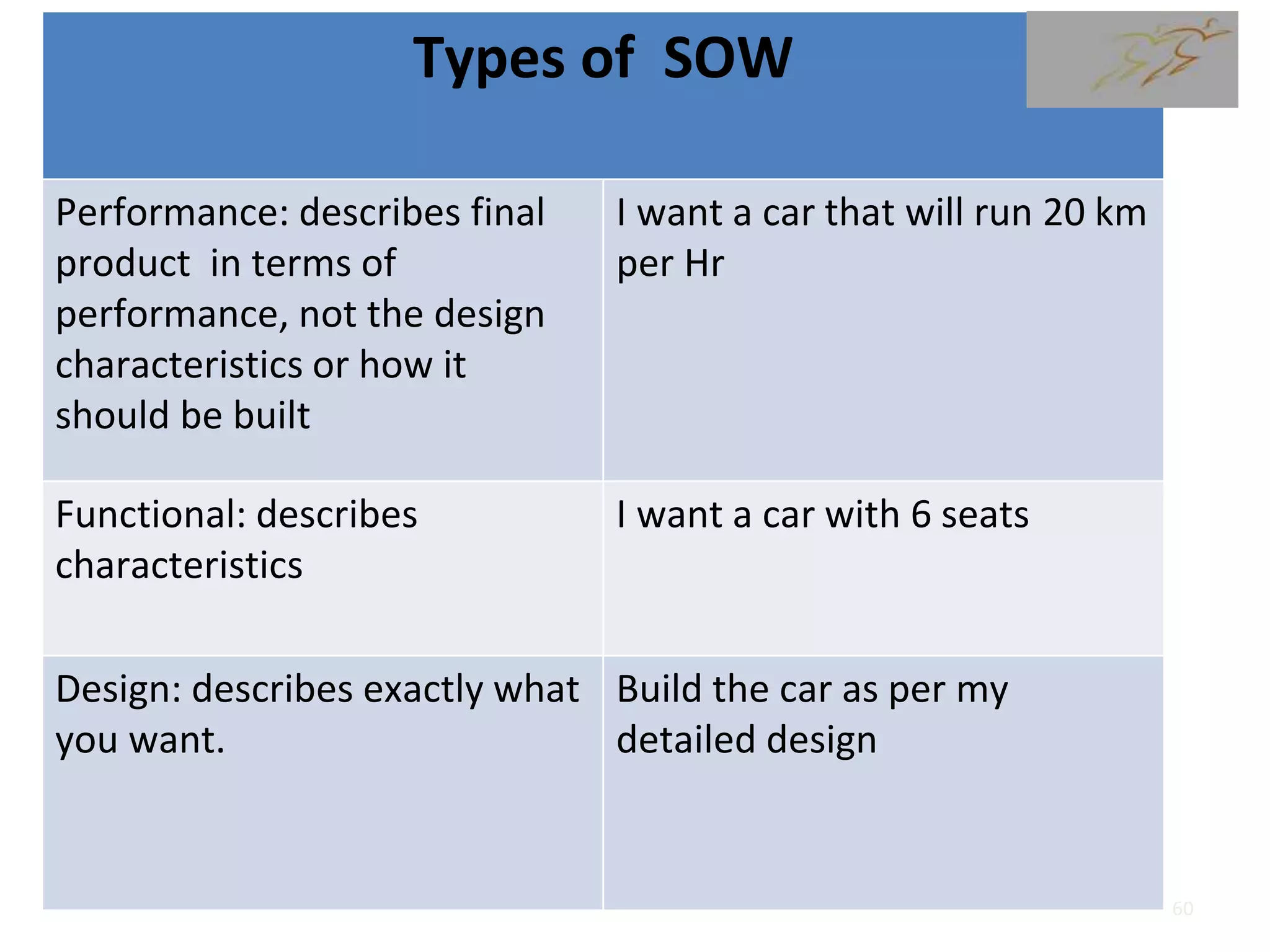
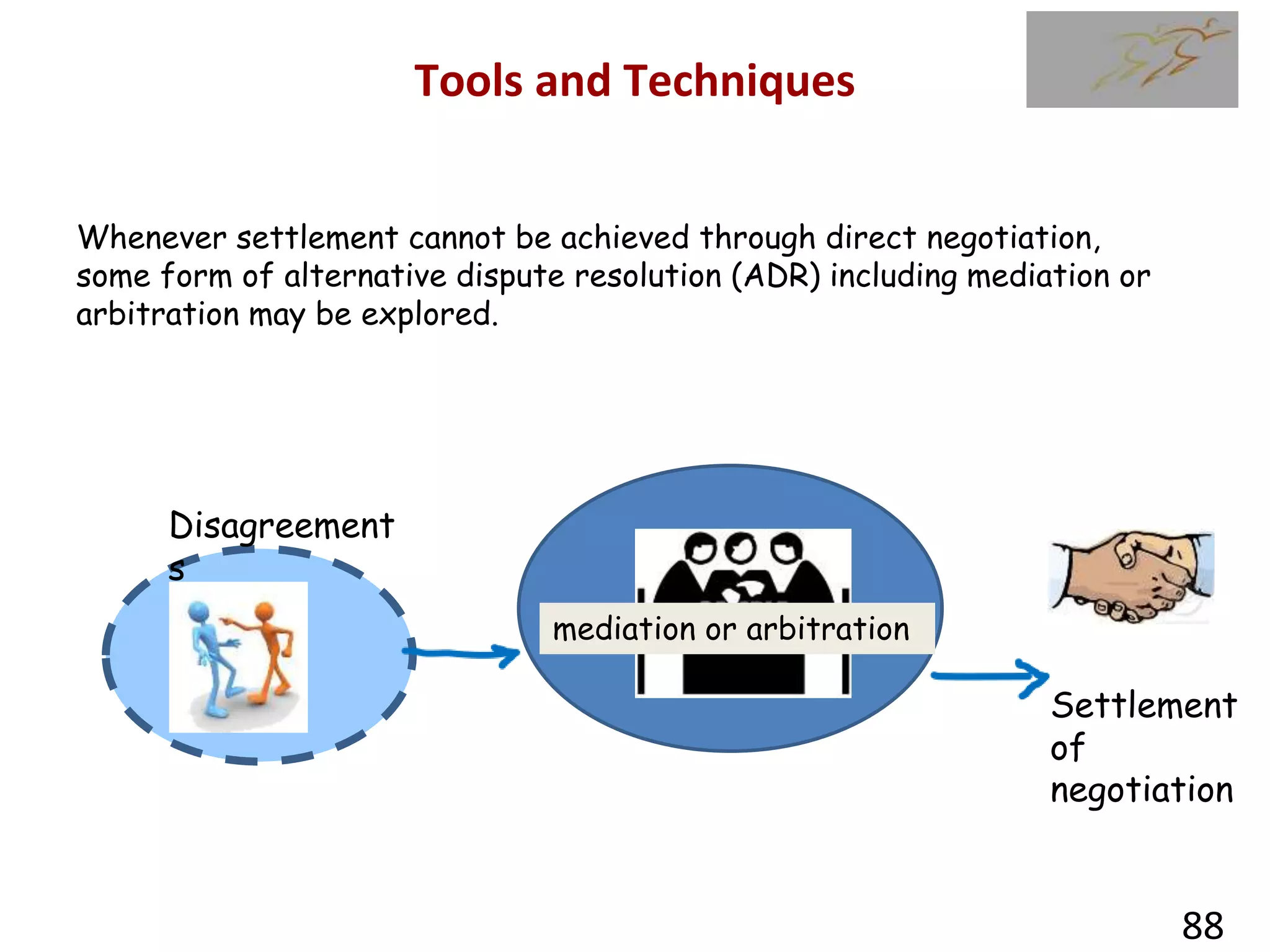
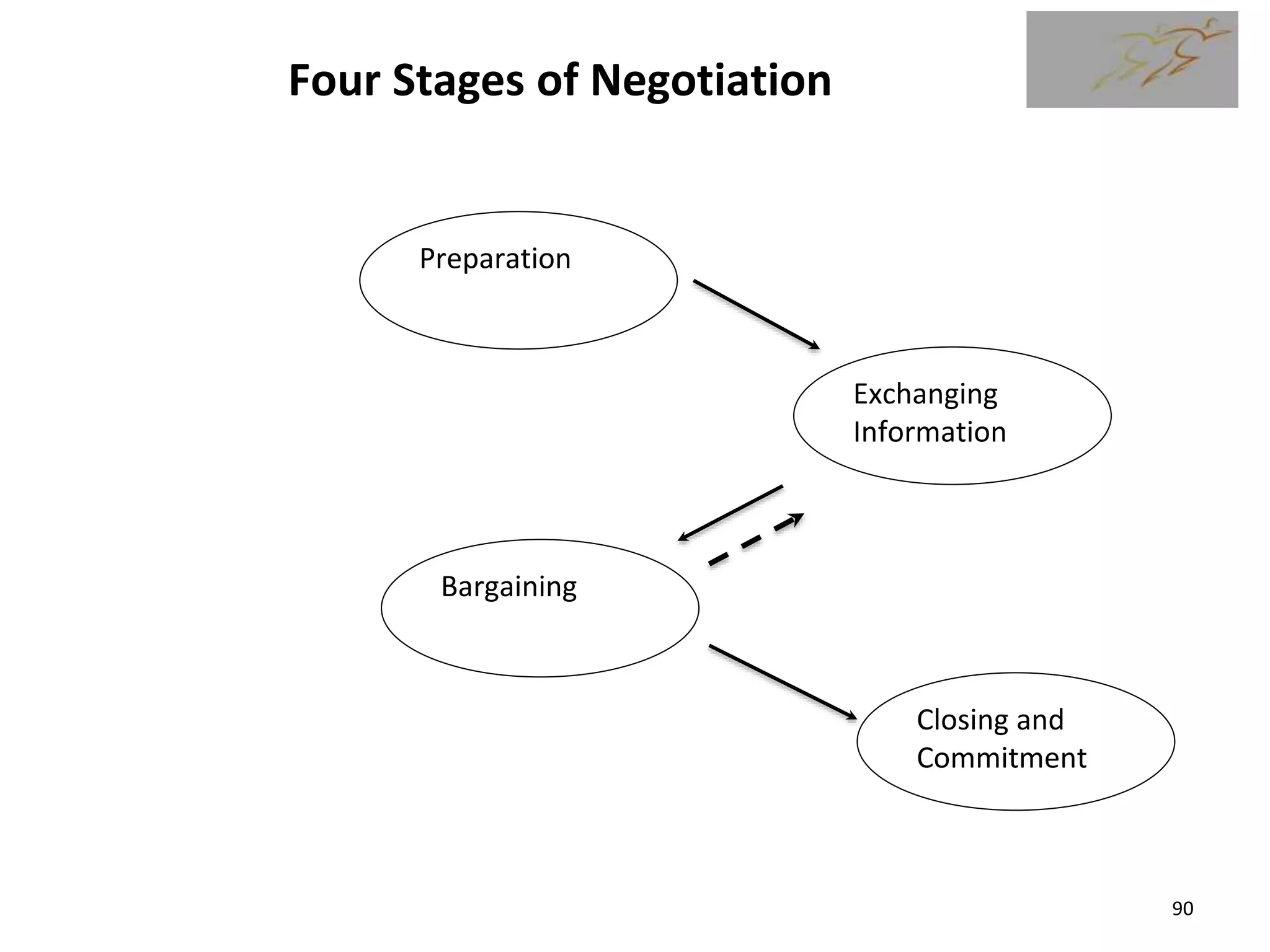
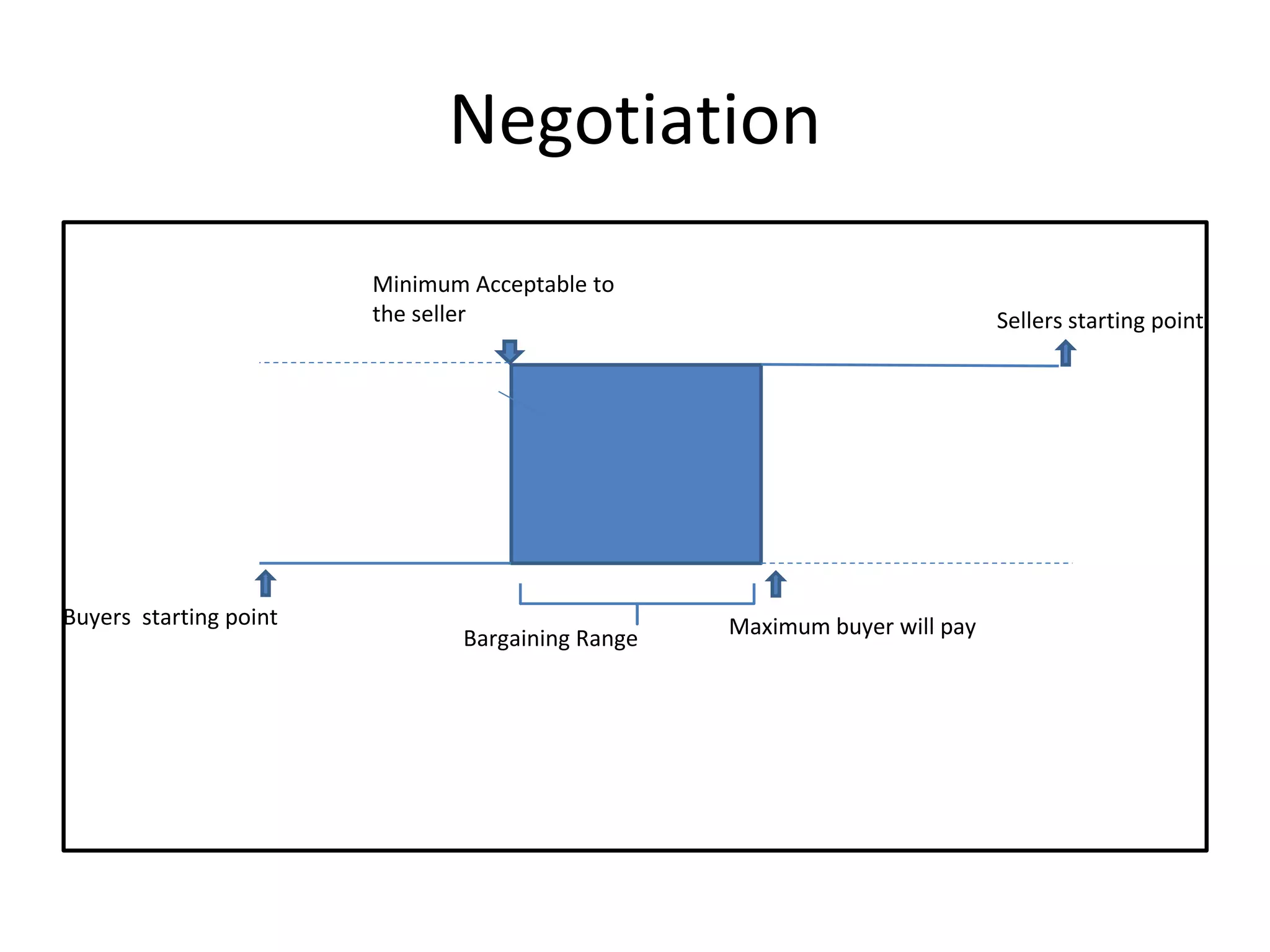
1) The document discusses various types of contracts including fixed price, cost reimbursable, and time and material contracts. It provides examples of each type and their advantages and disadvantages.
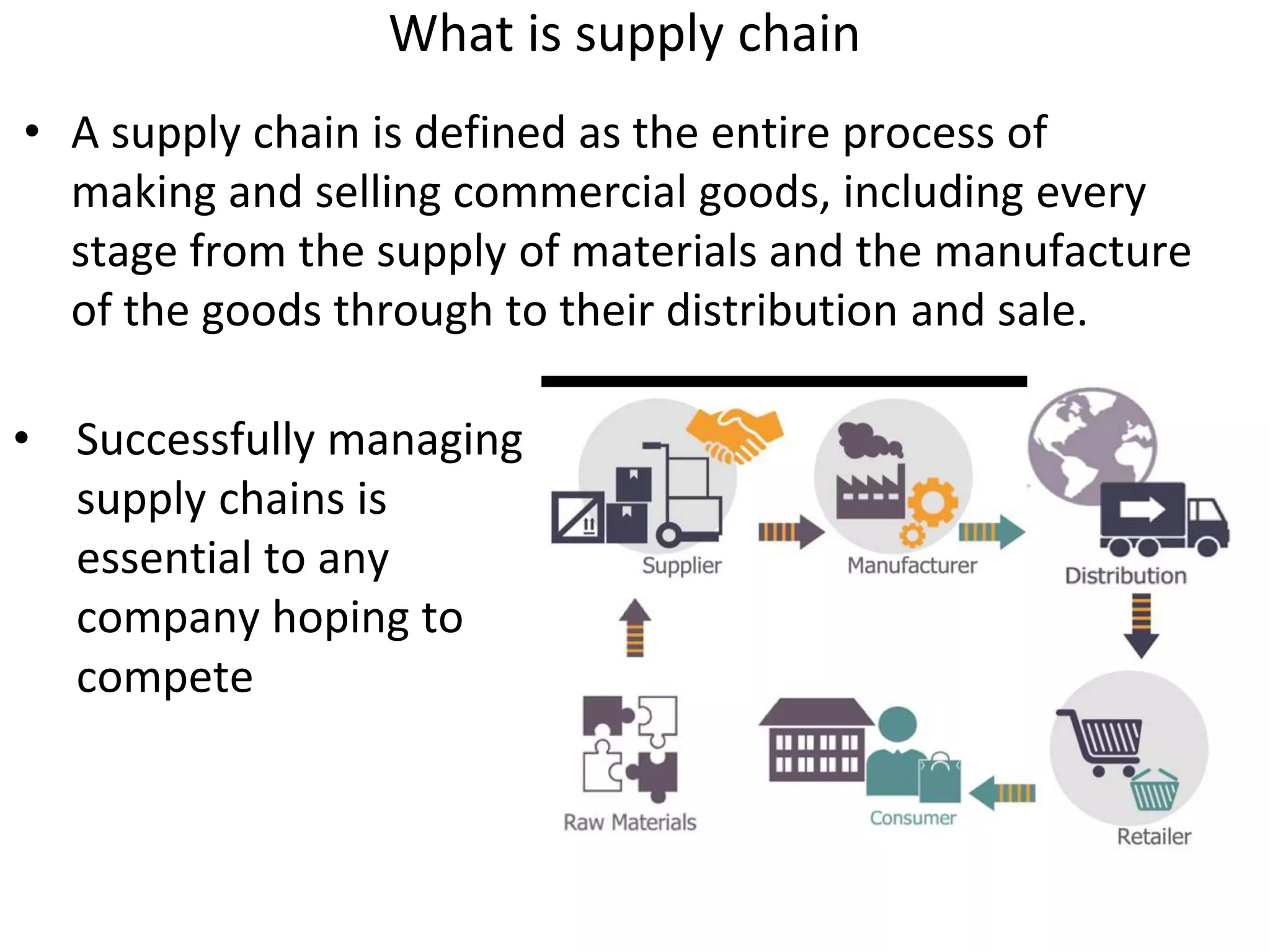
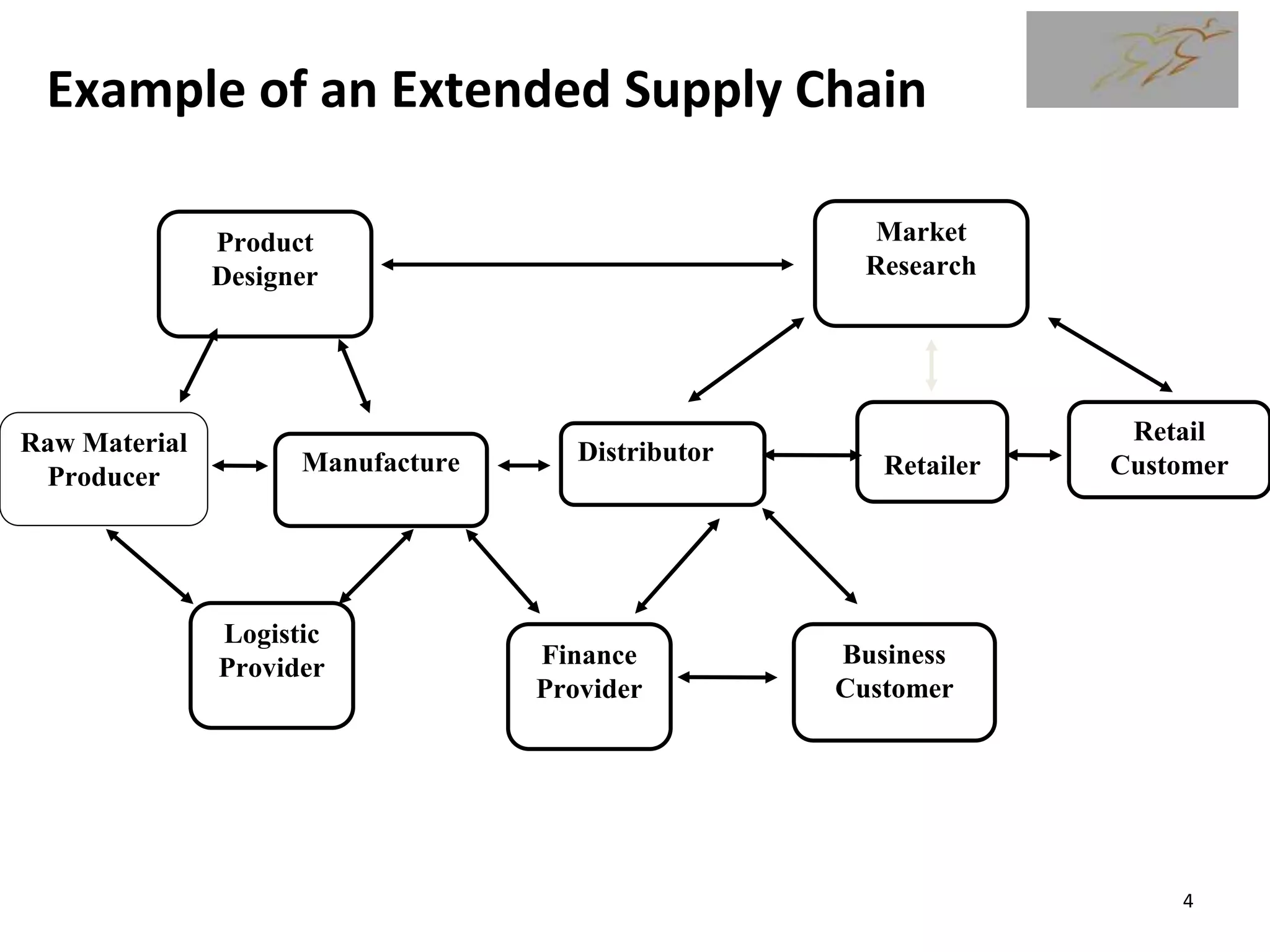
2) A supply chain is defined as the entire process of making and selling goods from raw materials to the final customer. Managing supply chains is important for business competition.
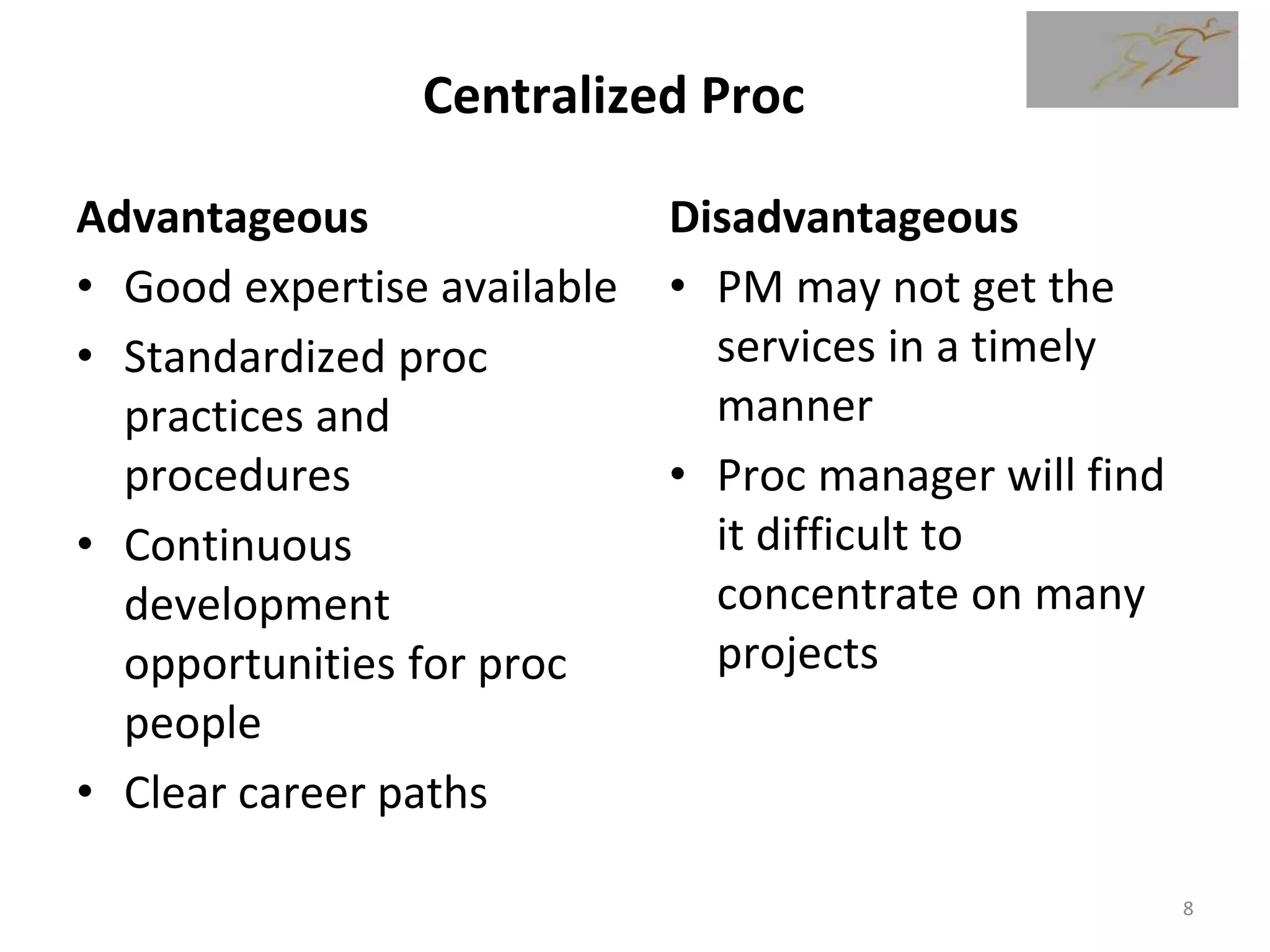
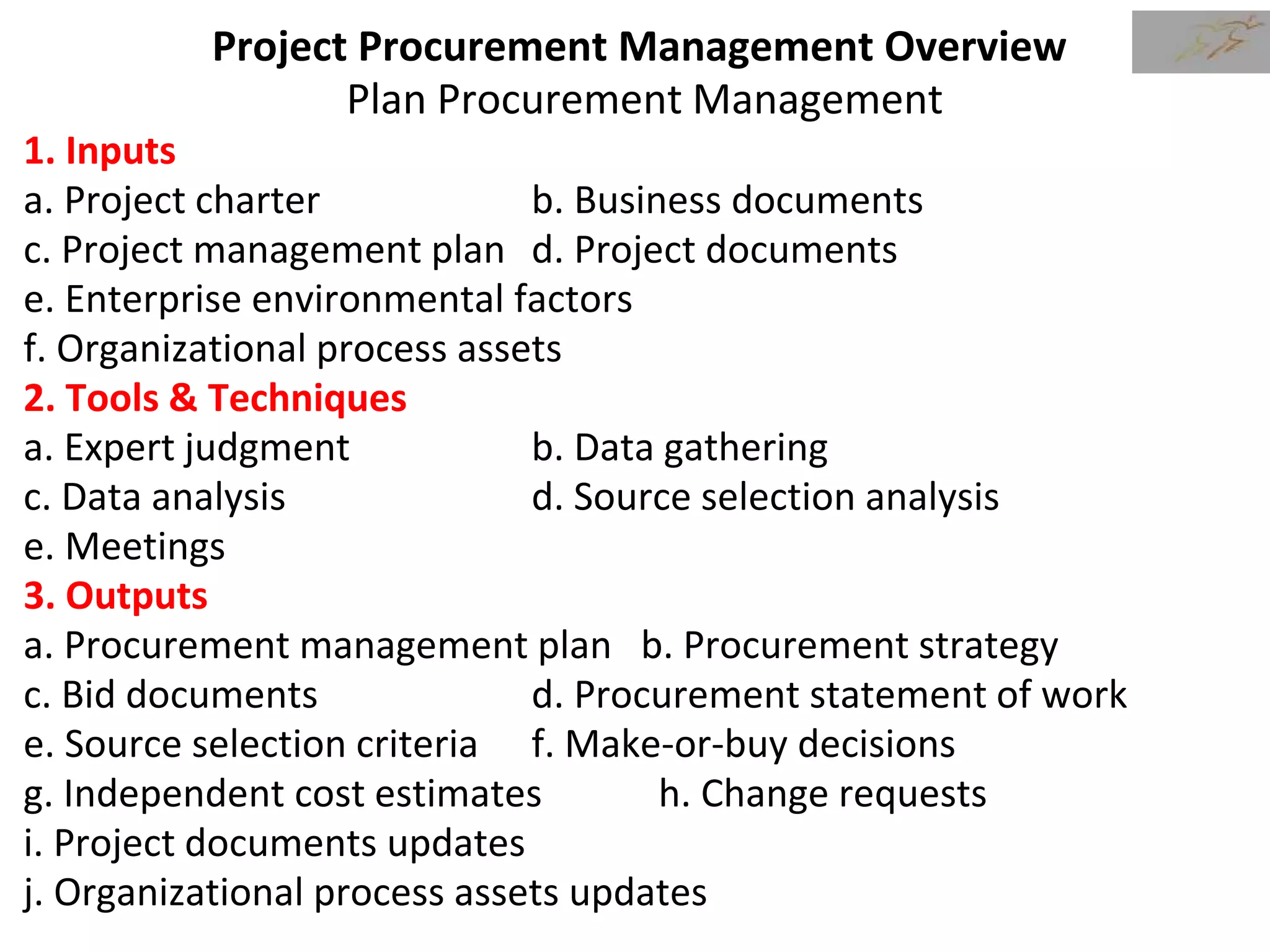
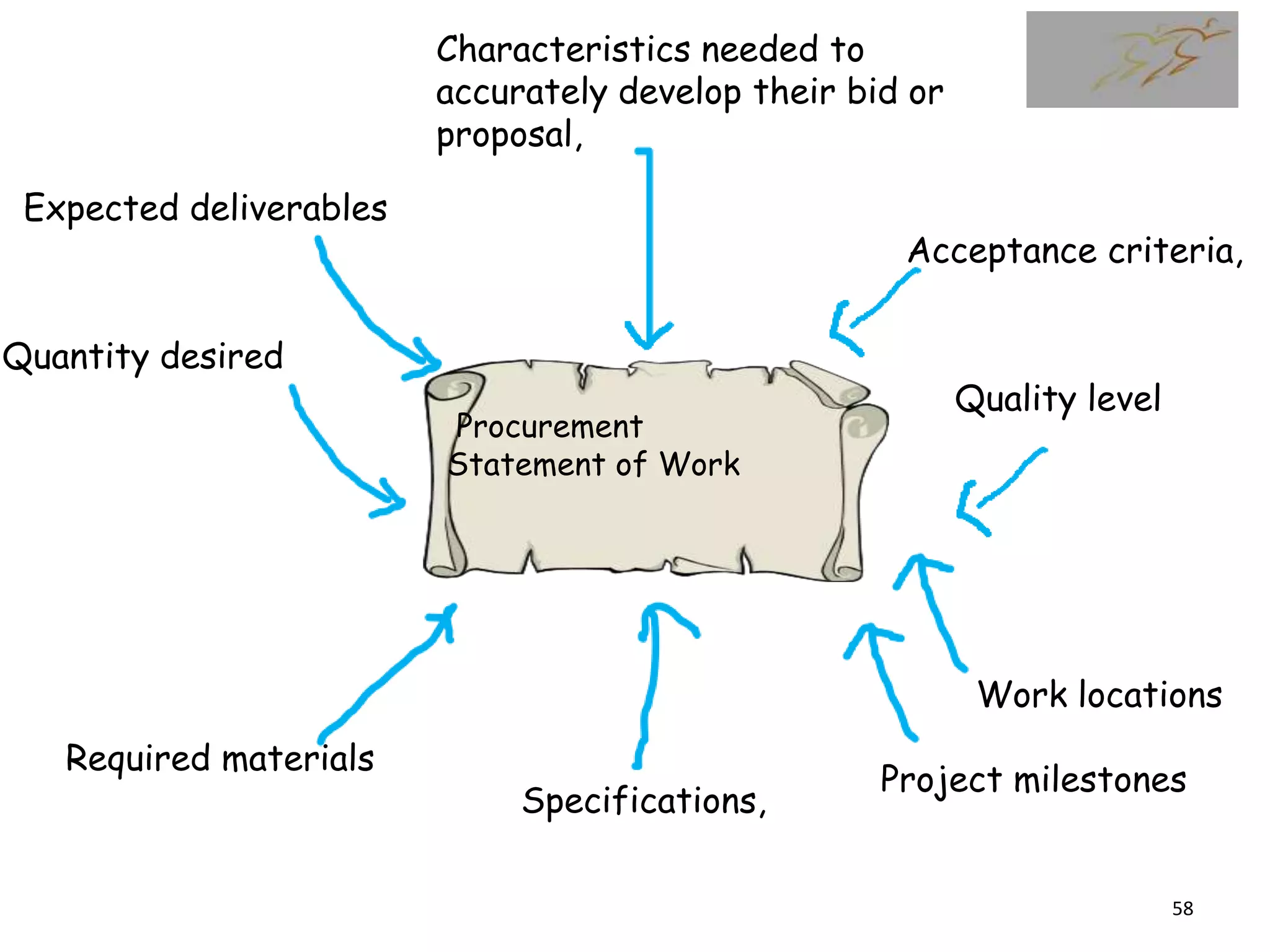
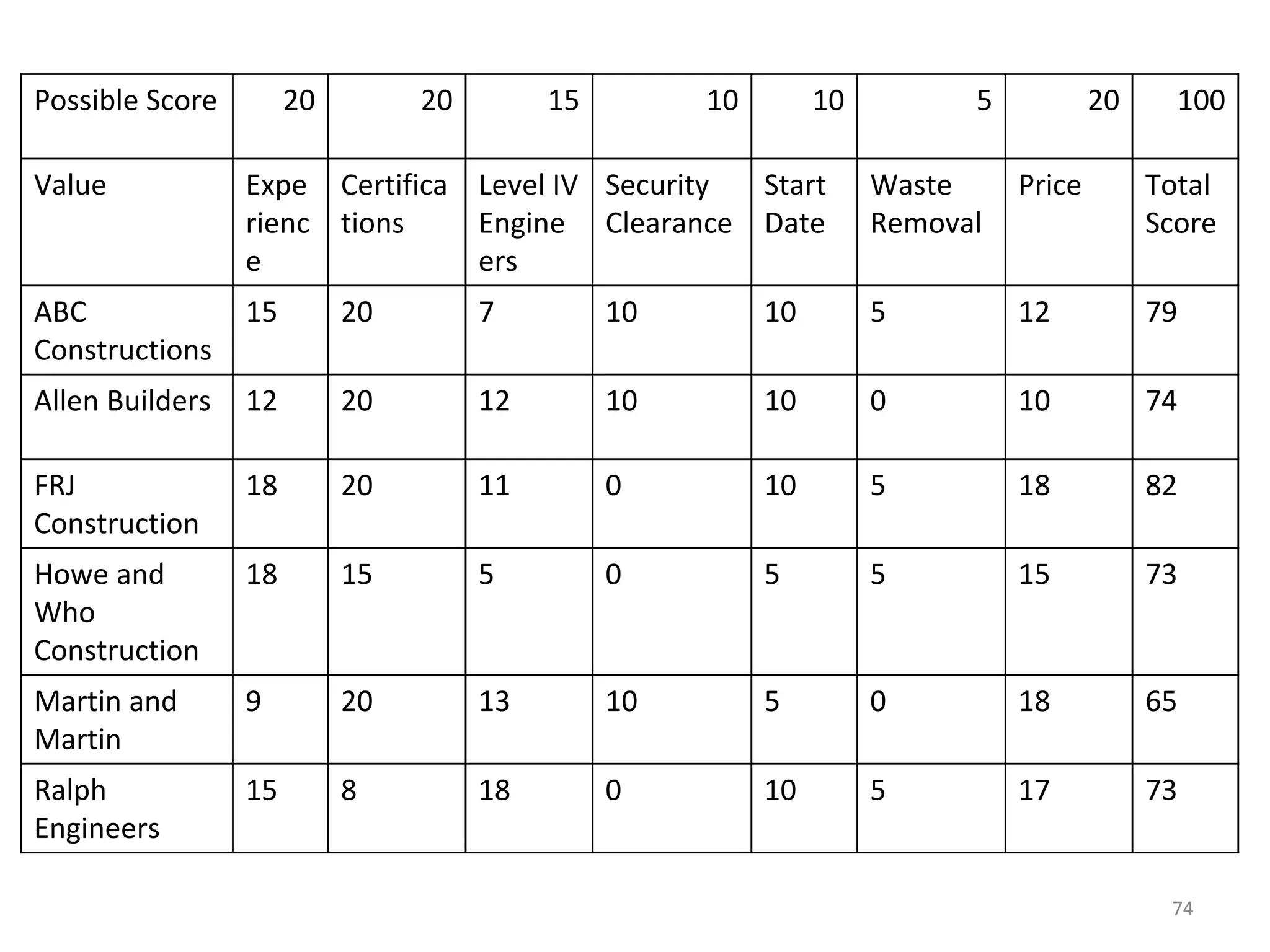
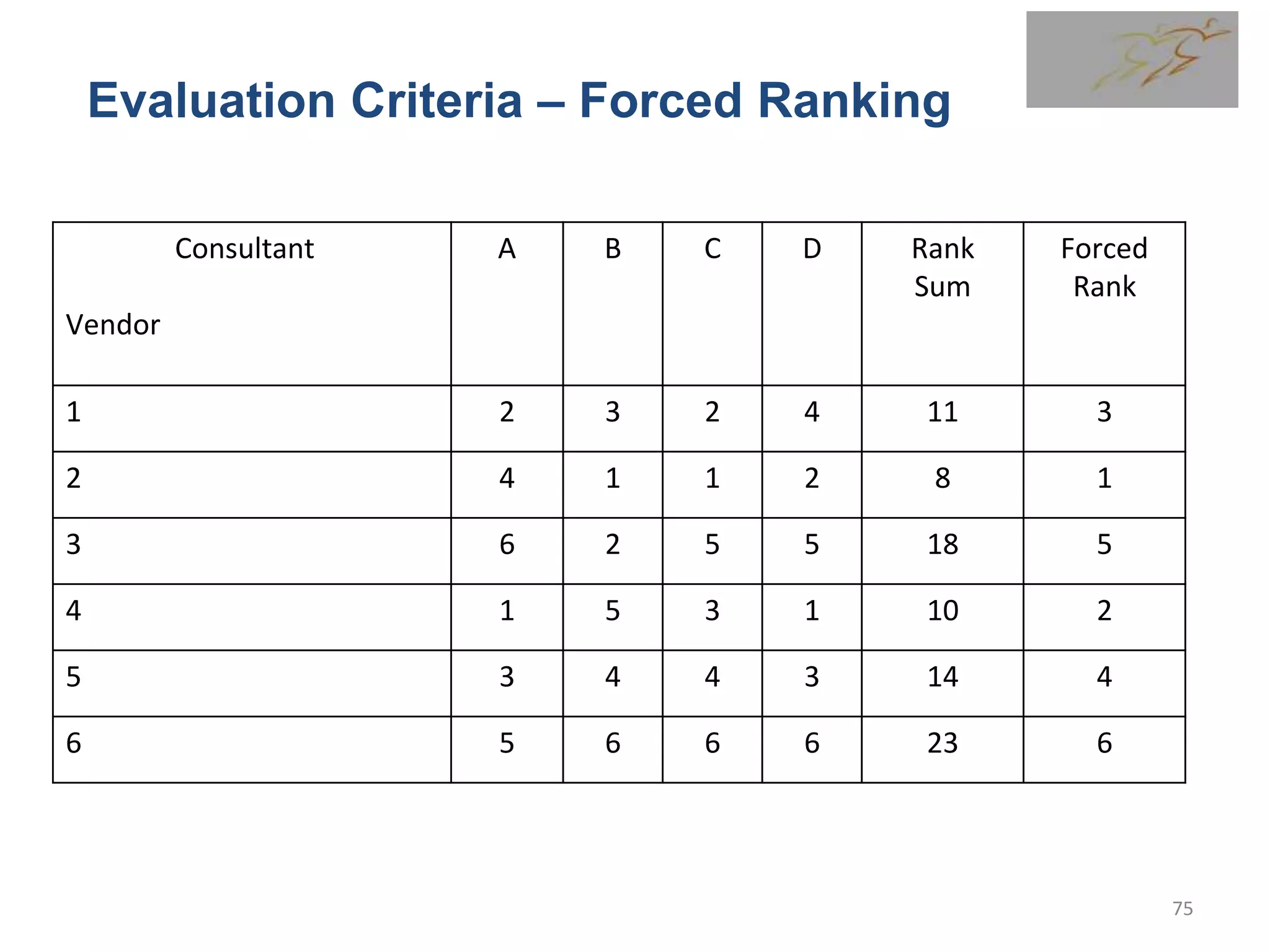
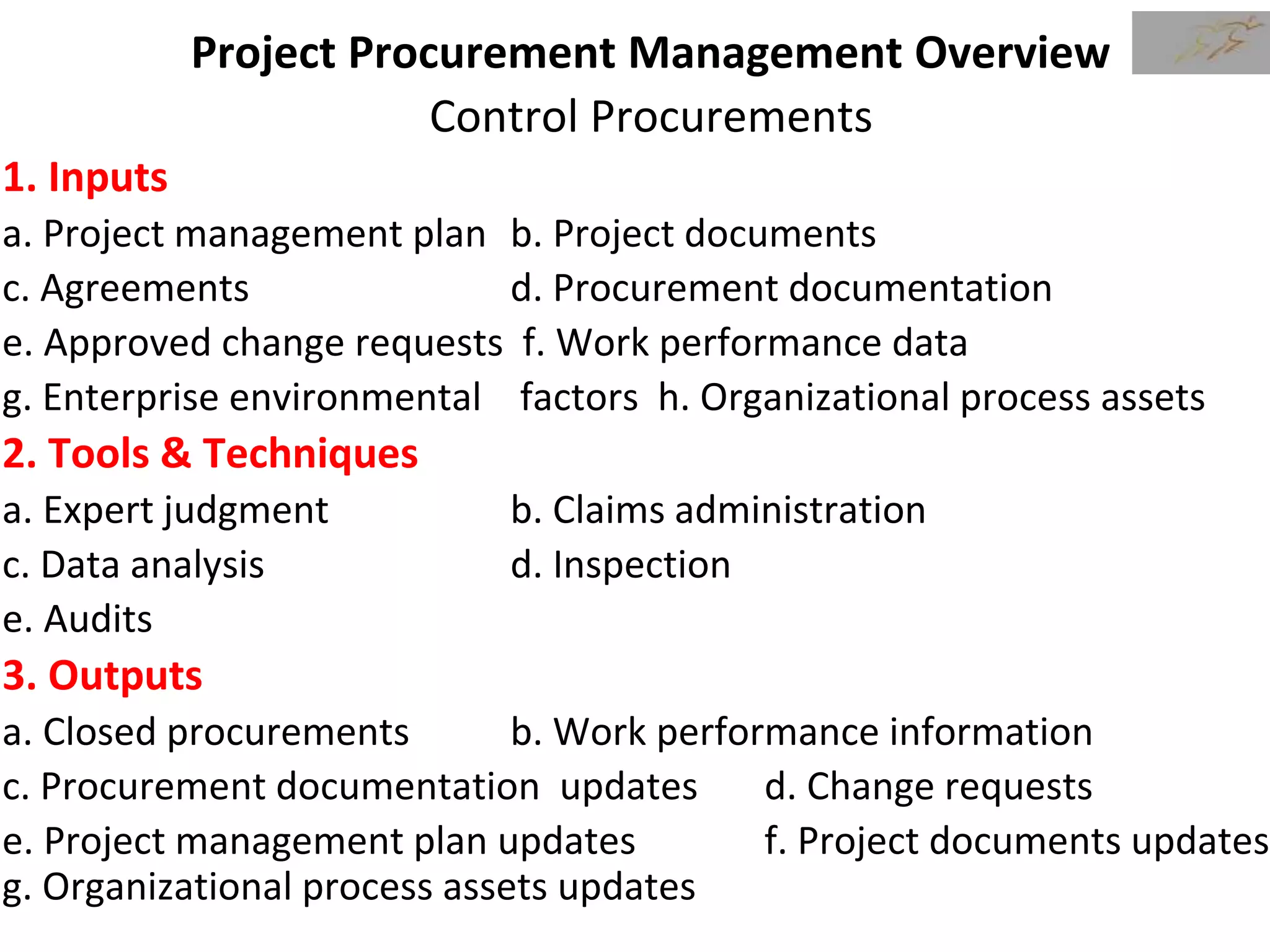
3) The document then discusses how to plan procurement management including defining inputs, tools and techniques, and outputs for the process.