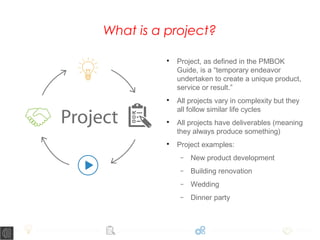
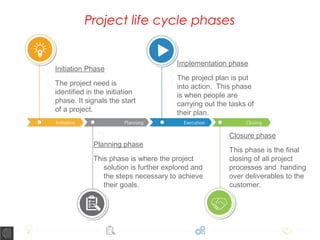
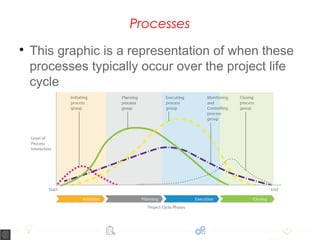
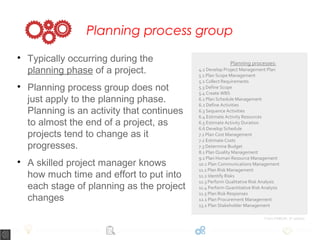
A project is defined as a temporary endeavor to create a unique product, service, or result, consisting of various phases: initiation, planning, implementation, and closure. Each phase has specific tasks such as defining the project scope, coordinating resources, and handing over deliverables. The document emphasizes the importance of processes within these phases to ensure project success and highlights that no two projects are the same.