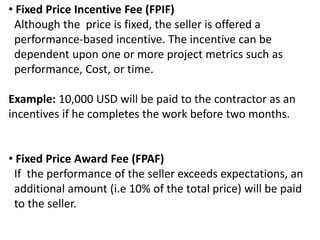
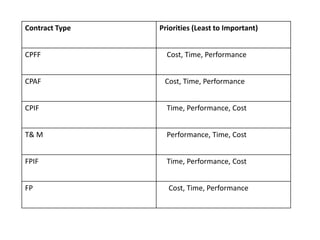
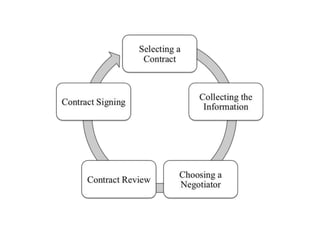
The document provides an overview of contracts, emphasizing their role as enforceable promises between parties in projects involving goods or services. It categorizes contracts into three main types: fixed price, cost reimbursable, and time and materials, detailing their characteristics and advantages. Additionally, it outlines the contracting process and stresses the importance of selecting the appropriate contract type to minimize risks in business agreements.