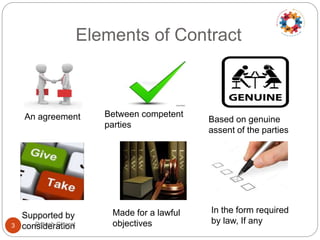
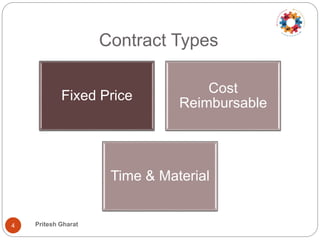
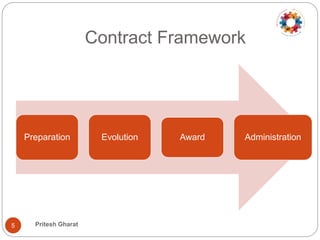
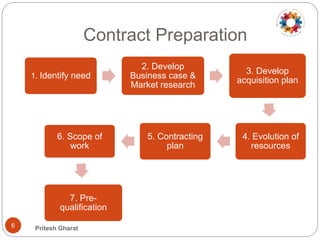
This document discusses contract management principles and practices. It defines a contract as a voluntary and legally binding agreement between two or more parties. Contract management involves creating, executing, and analyzing contracts to maximize performance while reducing risk. It also includes negotiating terms, ensuring compliance, and documenting changes. The document outlines the key elements of a contract as well as common contract types like fixed price, cost reimbursable, and time and material. It also describes the major phases of contract preparation, award, and administration. Tips provided for effective contract management include reading contracts thoroughly, establishing monitoring protocols, managing issues and variations, and documenting lessons learned.